I. Zagadnienia do samodzielnego opracowania
Prąd sinusoidalnie zmienny, wielkości charakterystyczne - wartość średnia, skuteczna i szczytowa.
Elementy R, L, C w obwodzie prądu zmiennego. Pojęcie reaktancji.
Wykresy wektorowe (fazowe).
Obwód szeregowy R L C. Pojęcie impedancji.
Pomiary i obliczenia
Schemat pomiarowy dla cewki przy prądzie stałym:
Wyniki pomiarów:
|
|
u(U_)[V ] |
u(I_)[mA] |
R[Ω] |
R±u(R) [Ω] |
|||
3,00 |
100,00 |
0,21 |
2,10 |
30,00 |
30,00±2,02 |
|||
5,00 |
260,00 |
0,21 |
2,10 |
19,20 |
19,20±2,02 |
|||
7,00 |
380,00 |
0,21 |
2,10 |
18,40 |
18,40±2,02 |
|||
8,50 |
480,00 |
0,21 |
2,10 |
17,70 |
17,70±2,02 |
|||
10,0 |
570,00 |
0,21 |
2,10 |
17,50 |
17,50±2,02 |
|||
11,50 |
650,00 |
0,21 |
2,10 |
17,70 |
17,70±2,02 |
|||
∆I= 3,75 mA
∆U= 375 mV
Schemat pomiarowy dla cewki przy prądzie przemiennym:
Wyniki pomiarów:
|
|
u(U~)[V ] |
u(I~)[mA] |
Z[Ω] |
Z±u(Z) [Ω] |
L±u(L) [mH] |
30,00 |
0,60 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
50,00 |
50,00±1,39 |
0,12±0,29 |
40,00 |
0,76 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
52,60 |
52,60±1,39 |
0,15±0.29 |
60,00 |
1,10 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
54,50 |
54,50±1,39 |
0,16±0.29 |
70,00 |
1,28 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
54,70 |
54,70±1,39 |
0,16±0.29 |
80,00 |
1,44 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
55,50 |
55,50±1,39 |
0,17±0.29 |
90,00 |
1,50 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
60,00 |
60,00±1,39 |
0,18±0.29 |
∆I= 3,75 mA
∆U= 1,5 V
Schemat pomiarowy dla kondensatora przy prądzie przemiennym:
Wyniki pomiarów:
|
|
u(U~)[V ] |
u(I~)[mA] |
|
XC±u(XC) [Ω] |
C±u(C) [ F] |
30,00 |
0,36 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
83,30 |
83,30±1,76 |
38,20±0,75 |
40,00 |
0,46 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
87.00 |
87.00±1,76 |
36,60±0,75 |
60,00 |
0,66 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
91.00 |
91.00±1,76 |
34,90±0,75 |
70,00 |
0,76 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
92.00 |
92.00±1,76 |
34,60±0,75 |
90,00 |
0,88 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
91.00 |
91.00±1,76 |
34,90±0,75 |
95,00 |
1,00 |
0,86 |
2,10 |
95.00 |
95.00±1,76 |
33,50±0,75 |
∆I= 3,75 mA
∆U= 1,5 V
Obliczenia:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
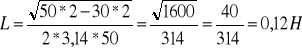
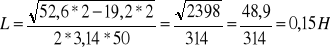
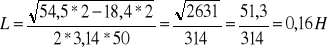
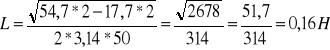
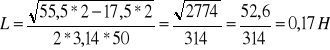
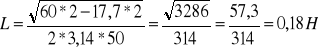
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Obliczanie niepewności
∆x= ![]()
![]()
dla prądu stałego i zmiennego
![]()
dla prądu zmiennego
![]()
dla prądu stałego
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
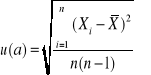
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Wykres zależności U(I) dla obwodu z cewką zasilanego prądem stałym.
Wykres zależności U(I) dla obwodu z cewką zasilanego prądem przemiennym.
Wykres zależności U(I) dla obwodu z kondensatorem zasilanego prądem przemiennym.
Wyszukiwarka