TEMAT:
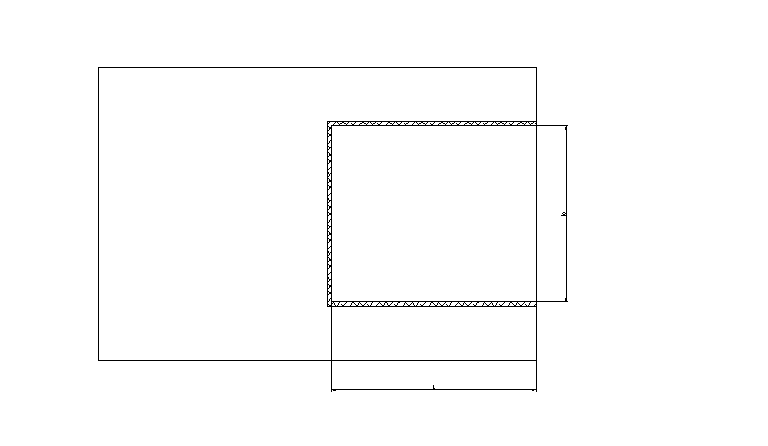
Zaprojektować połączenie typu: styk spawany, oraz połączenie na śruby wg schematu:
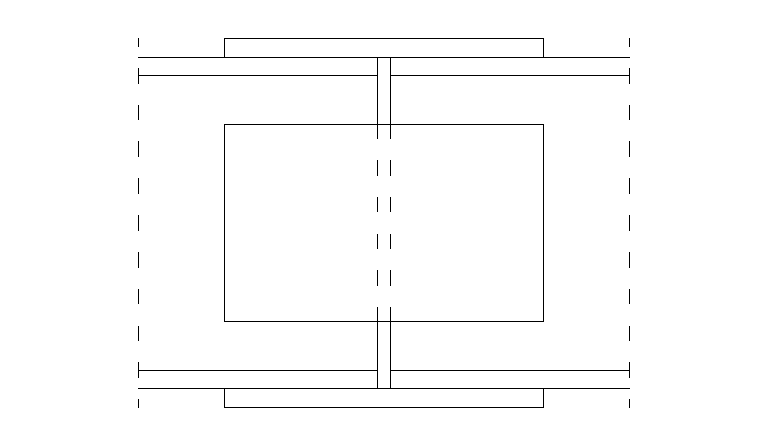
Dane:
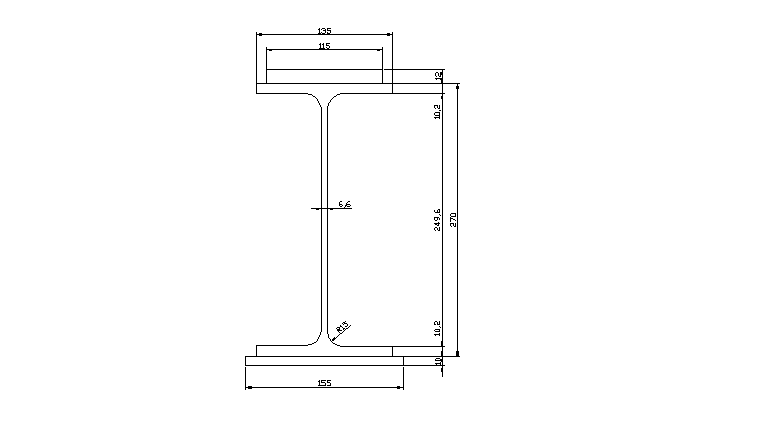
przekrój elementu Ι 270PE
gatunek stali St3S
klasa śrub 5.8.
obciążenie (procent nośności przekroju)
M = 0,65 MR
V = 0,35 VR
Charakterystyka geometryczna przekroju:
Ix = 5790 cm4 h = 270 mm
Iy = 420 cm4 s = 135 mm
Wx = 429 cm3 g = 6,6 mm
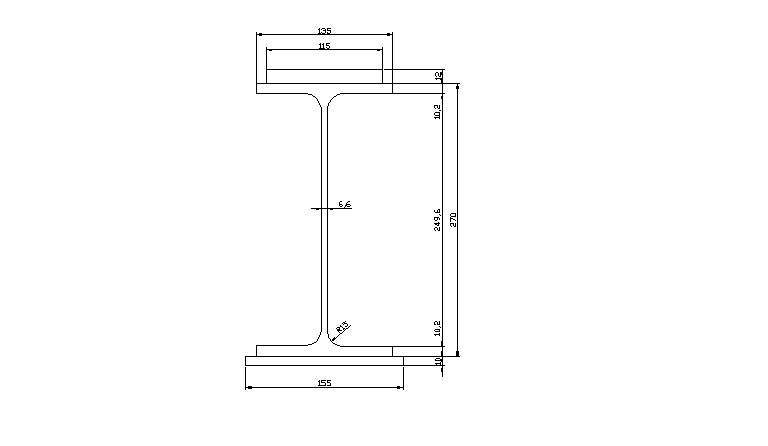
Wy = 62,2 cm3 t = 10,2 mm
r = 15 mm
POŁĄCZENIE SPAWANE
1. Obliczenie wysokości użytecznej środnika.
hśr = h - (2t + 2r) = 27 - (2 • 1,02 + 2 • 1,5) = 21,96 cm
stal St3S t = 10,2 < 16 mm fd = 215 MPa = 21,5 kN/m2
2. Wyznaczenie sił występujących w przekroju.
MR = αpWxfd = 1 • 429 • 21,5 = 9223,5 kNm
VR = 0,58Arfd Ar = hśrt = 21,96 • 1,02 = 22,4 cm4
VR = 0,58 • 22,4 •21,5 = 279,33 kN
Ostatecznie:
M = 0,65MR = 0,65 • 9223,5 = 5995,28 kNcm
V = 0,35VR = 0,35 • 279,33 = 97,77 kN
3. Nakładki.
a) górna
b1 = s - 2,0 = 13,5 - 2,0 = 11,5 cm
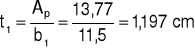
Ap = ts = 1,02 • 13,5 = 13,77 cm2
Przyjmuję: b1 = 11,5 cm
t1 = 1,2 cm
An1 = b1t1 = 11,5 • 1,2 = 13,8 cm2
b) dolna
b2 = s + 2,0 = 13,5 + 2,0 = 15,5 cm
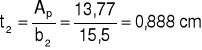
Przyjmuję: b2 = 15,5 cm
t2 = 1,0 cm (=gd)
An2 = b2t2 = 15,5 • 1,0 = 15,5 cm2
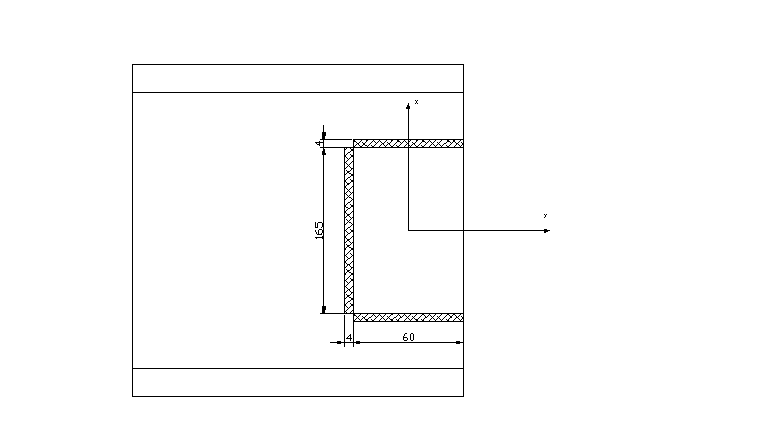
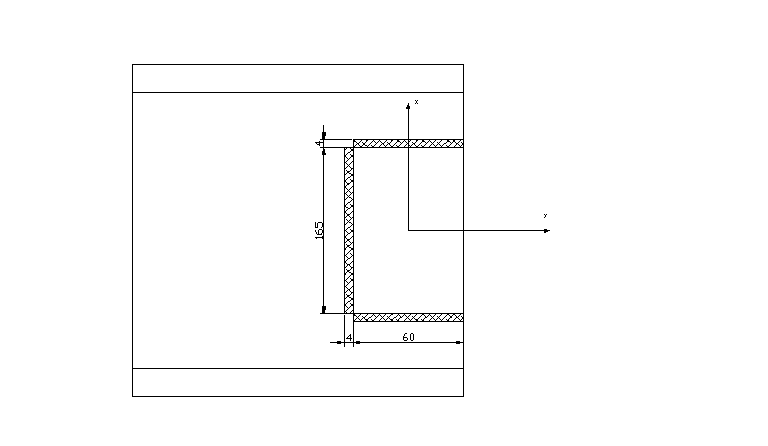
4. Przykładki.
![]()
![]()
hgmax = h - 2t - 2xmin = 270 - 2 • 10,2 - 37,07 • 2 = 175,46 mm
2gp > gśr gp > 6,6 / 2 = 3,3 mm
Przyjmuję: hp = 16,5 cm
gp = 0,6 cm
Ap = 16,5 • 0,6 = 9,9 cm2
5. Sprawdzenie przykładek.
Wp > Wśr
![]()
![]()
54,45 > 53,05 [cm3]
6. Sprawdzenie przykładek i nakładek.
Wp + Wn > WΙ
![]()
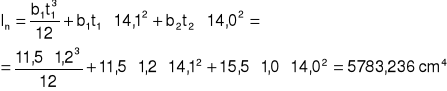
Ip+n = 6232,446 cm4
Wp =54,45 cm3
![]()
Wp + Wn = 447,87 cm3
7. Rozdział momentów.
MR = 9223,5 kNcm
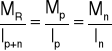
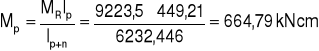
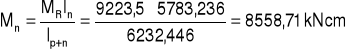
8. Siły działające na nakładki.
![]()
αII = 0,8 Re = 255 MPa
0,2 t2 ≤ a1 ≤ 0,7 t1 t2 > t1
t1 = 1,0 cm
t2 = 1,2 cm
2,4 ≤ a1 ≤ 7,0
Przyjmuję: a1 = 5,0 mm
10 a ≤ l ≤ 100 a
50 ≤ l ≤ 500
l ≥ b2
![]()
l ≥ 15,5 a
Przyjmuję: l1 = 20,0 cm
9. Wyznaczenie spoin przykładek.
0,2 t2 ≤ a ≤ 0,7 t1 t1 = 6,0 mm
1,32 ≤ a ≤ 4,2 t2 = 6,6 mm
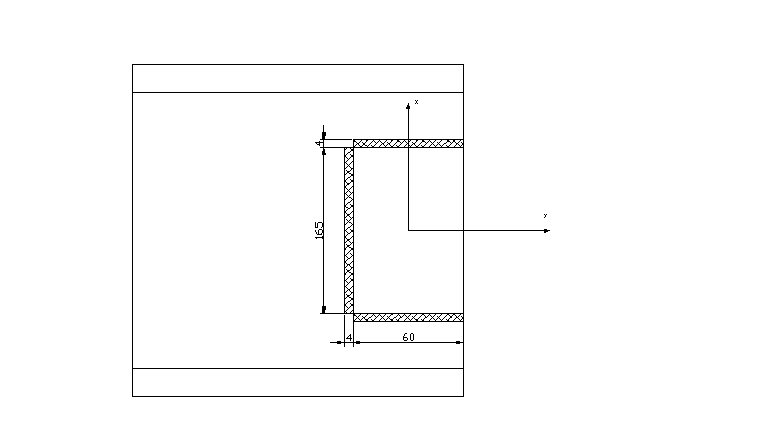
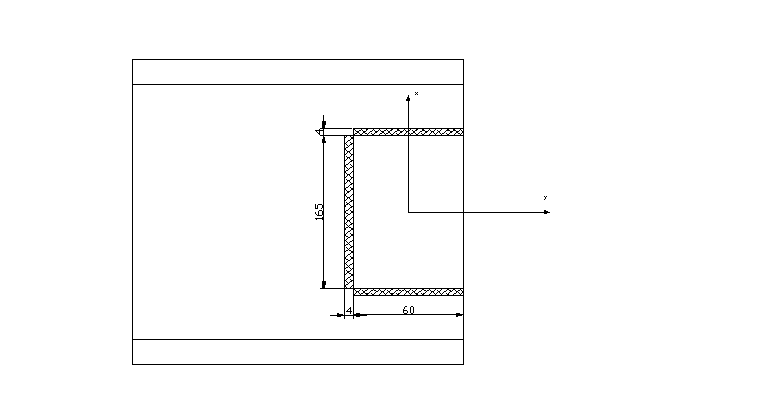
Przyjmuję: a = 4,0 cm
a) środek ciężkości
![]()
x = 1,84 + 3,0 = 4084 cm
y = 8,25 + 0,2 = 8,45 cm
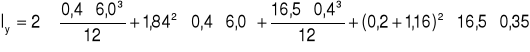
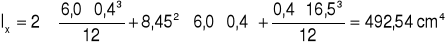
Iy = 42,96 cm4
I0 = Ix + Iy = 492,54 + 42,96 = 535,5 cm4
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
16,776 < 19,35 [kN/cm2]
![]()
POŁĄCZENIE NA ŚRUBY
I Nakładki.
1. Grubość nakładek.
b = 13,5 cm
Ap = 13,77 cm2
![]()
Przyjmuję: b = 13,5 cm
g = 1,2 cm
An = b•g = 13,5 • 1,2 = 16,2 cm2
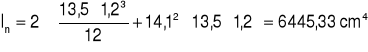
2. Sprawdzenie nakładek.
![]()
Wxp = 54,45 cm3
Wxn + Wxp > Wx
438,46 + 54,45 > 429
492,91 > 429 [cm3]
3. Rozdział momentów.
M = 5995,28 kNm2
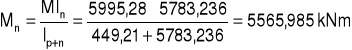
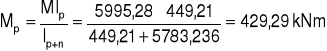
![]()
4. Przyjęcie średnicy śrub.
Przyjmuję: śruby M16 , klasy 5.8 (kat A)
5. Siły działające na nakładki.
![]()
6. Liczba śrub.
![]()
Przyjęto: 6 sztuk
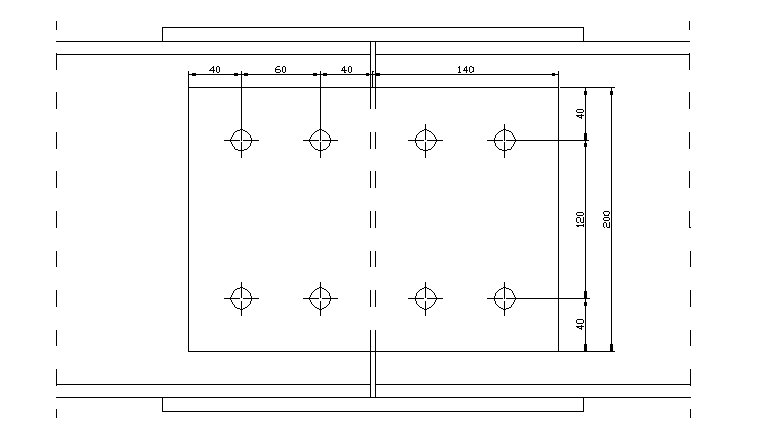
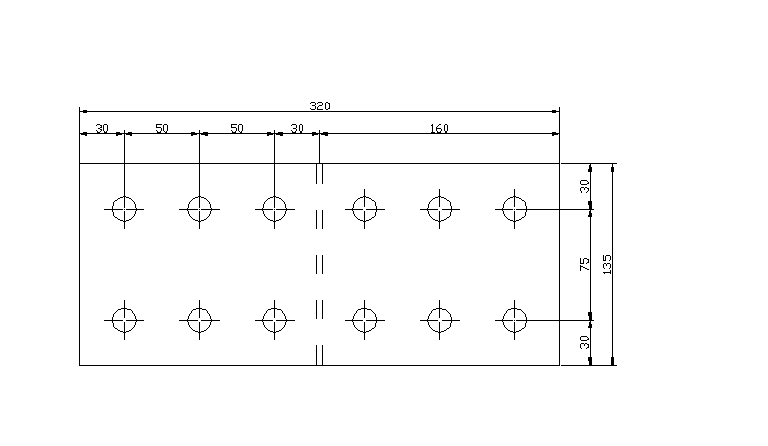
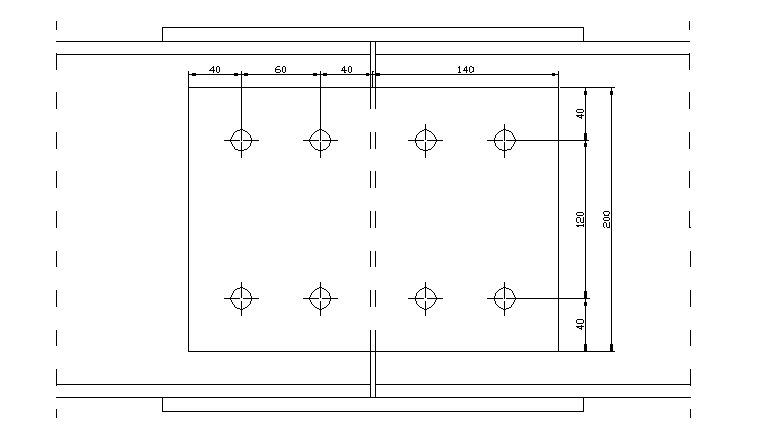
7. Rozstaw śrub.
mina1 = mina2 = 1,5d = 1,5 • 1,6 = 2,4 cm
mina3 = mina = 2,5d = 2,5 • 1,6 = 4,0 cm
Przyjęto: a1 = 3,0 cm
a2 = 3,0 cm
a3 = 7,5 cm
a = 5,0 cm
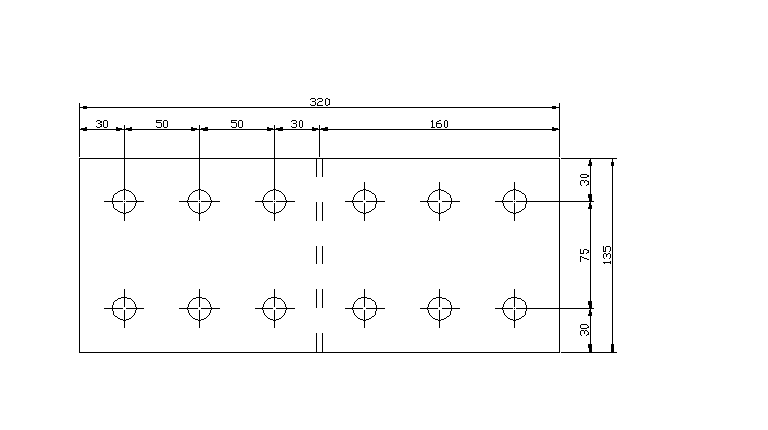
![]()
![]()
8. Stan graniczny.
Uplastycznienie wskutek docisku trzpienia do ścianki otworu.
SRb = αfddΣt = 1,88 • 21,5 • 1,6 • 1,02 = 54,737 kN
9. Obliczenie nośności.
NRj = nηSR
NRjv = nηSRv = 6 • 1,0 • 47 = 282 kN > N
NRjb = nηSRb = 6 • 1,0 • 54,737 = 328,42 kN
NRj = 282 > 206,148 [kN]
II Przykładki.
1. Średnica śrub.
![]()
Przyjęto: śruby M16 , kl. 5.8 (kat A)
2. Rozstaw śrub.
mina1 = mina2 = 1,5d = 1,5 • 1,6 = 2,4 cm
mina3 = mina = 2,5d = 2,5 • 1,6 = 4,0 cm
Przyjmuję: a1 = 4,0 cm
a2 = 4,0 cm
a3 = 12 cm
a = 6 cm
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
3. Sprawdzenie warunków nośności.
SRb = αfddΣt = 2,5 • 21,5 • 1,6 • 0,66 = 56,76 kN
SRv = 47 • 2 = 94 kN
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
34,46 < 49,665 [kN]
4. Sprawdzenie osłabienia przekroju.
Złożony stan naprężeń.
![]()
![]()
Ścinanie![]()
.
Avn = 24,96 • 0,66 - 2 • (0,66 • 1,6) = 14,07 cm2
Av = 24,96 • 0,66 = 16,47 cm2
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
16,86 ≤ 21,5 [kN/cm2]
11
![]()
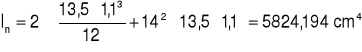
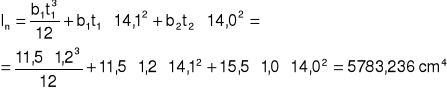
![]()
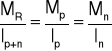
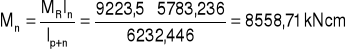
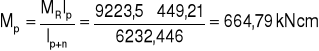
![]()
![]()
![]()
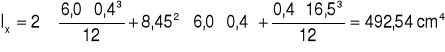
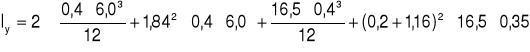
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
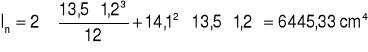
![]()
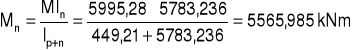
![]()
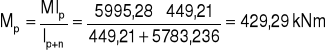
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Wyszukiwarka