MASS TRANSFER
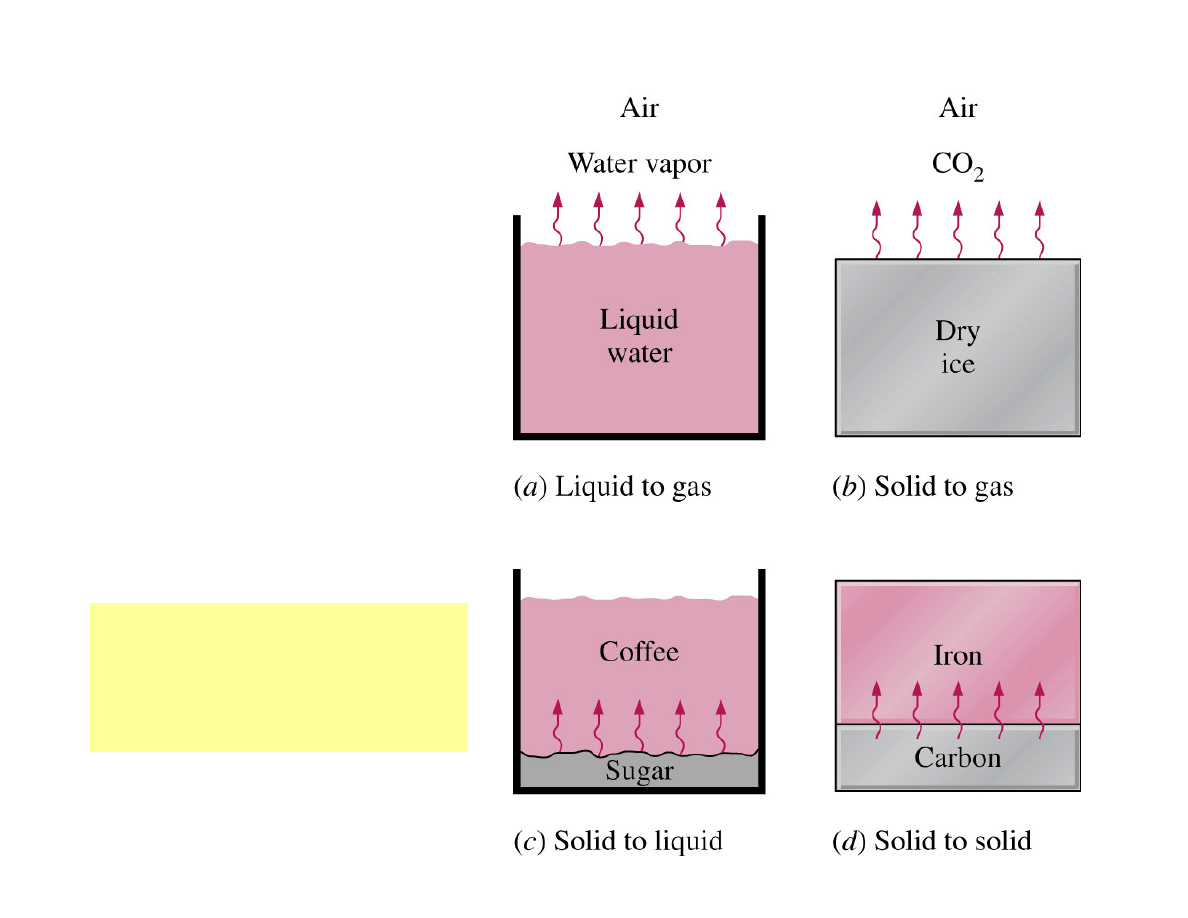
Examples of mass transfer
Mass transfer requires
the presence of two
regions
at different
chemical compositions
→
→
→
→
movement of
chemical species from a
high concentration
region toward a lower
concentration (non-
homogeneous medium).
•
Note:
Fluid flow due to the
pressure difference.

dx
dC
DA
m
−
=
•
Mass diffusion
Concentration difference
is the driving force for mass transfer.
where
D
is the
diffusion coefficient
of the medium
• Note:
The diffusion rates are higher in gases than in liquids and in
solids.
Mass flow rate ∝
∝
∝
∝
Normal area
A
×
×
×
×
Concentration gradient
dC/dx
(kg/s)
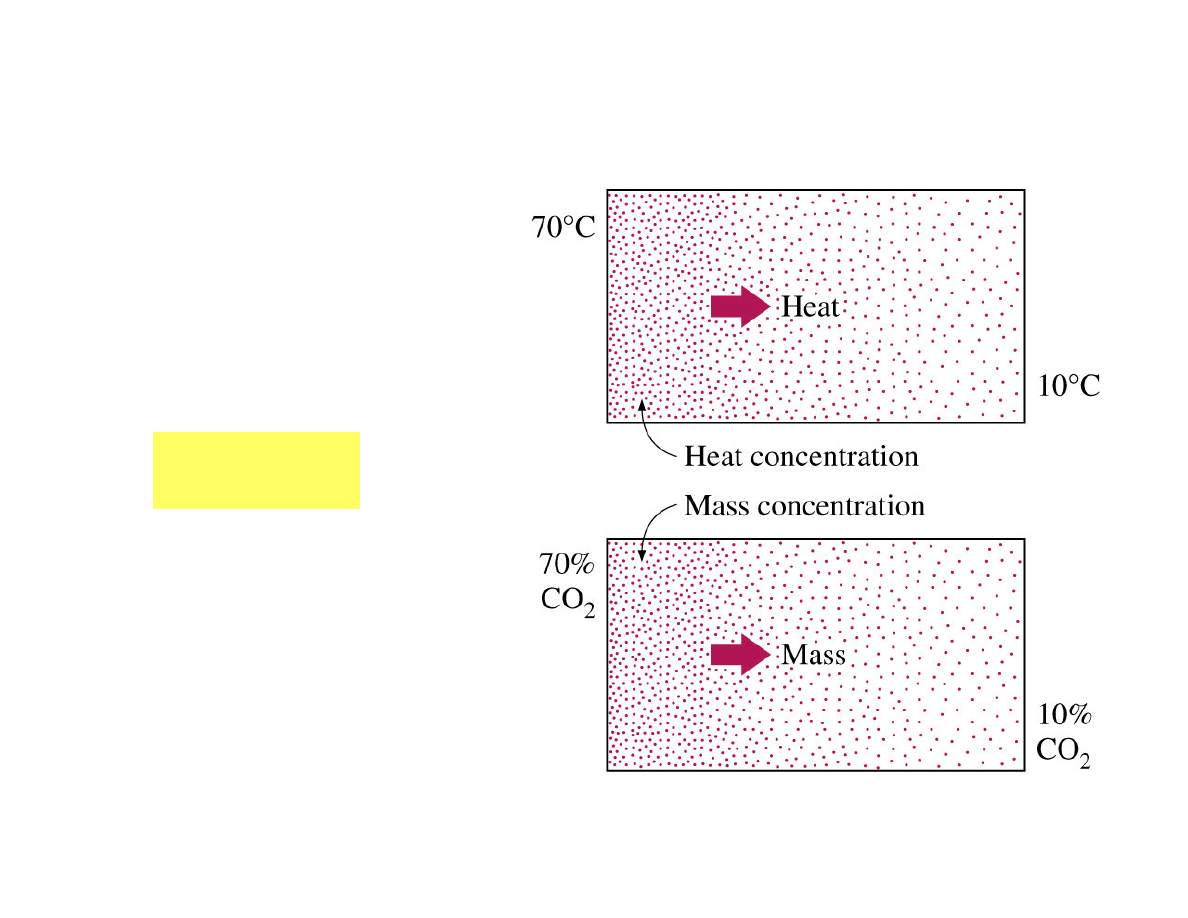
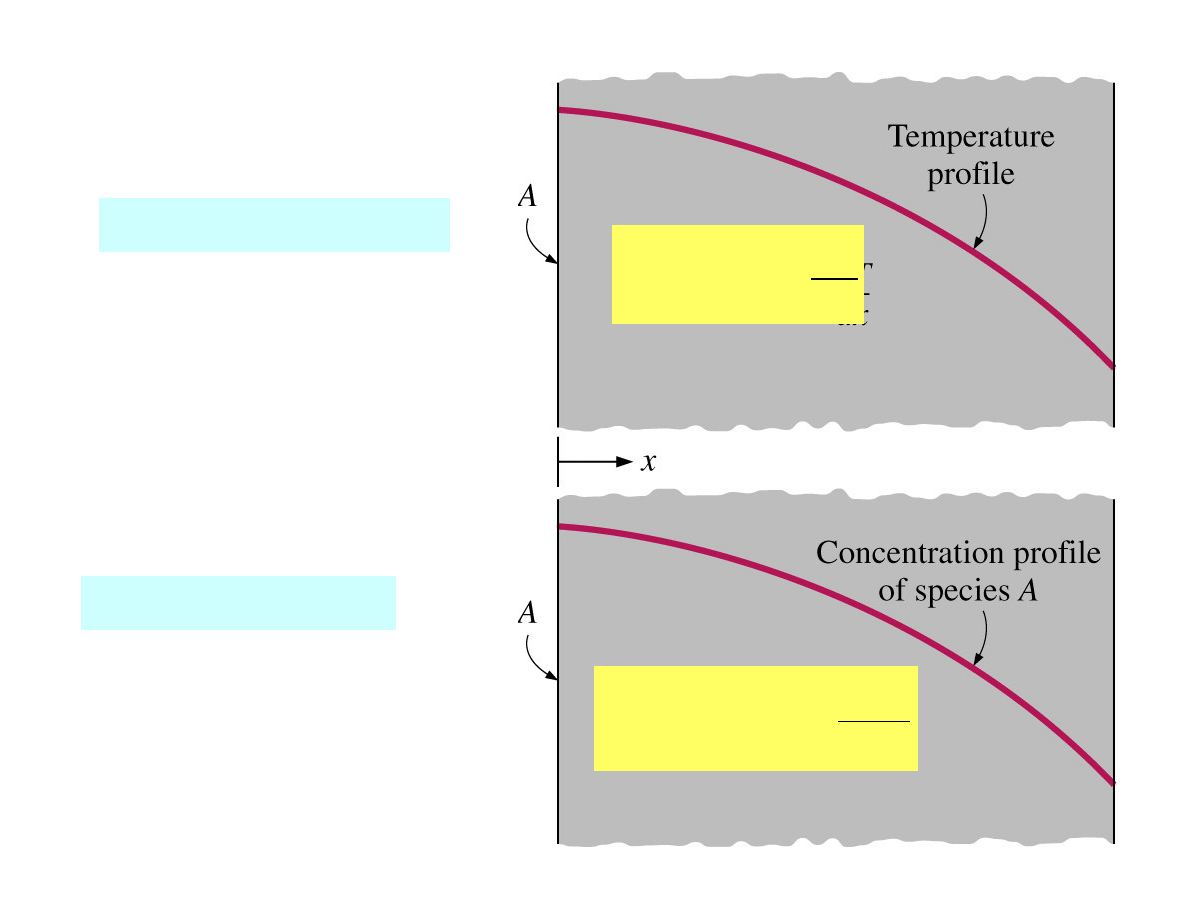
Analogy Between Heat and Mass Transfer
Mass and heat – two
different forms of energy,
according to the
Einstein`s formula:
2
mc
E =
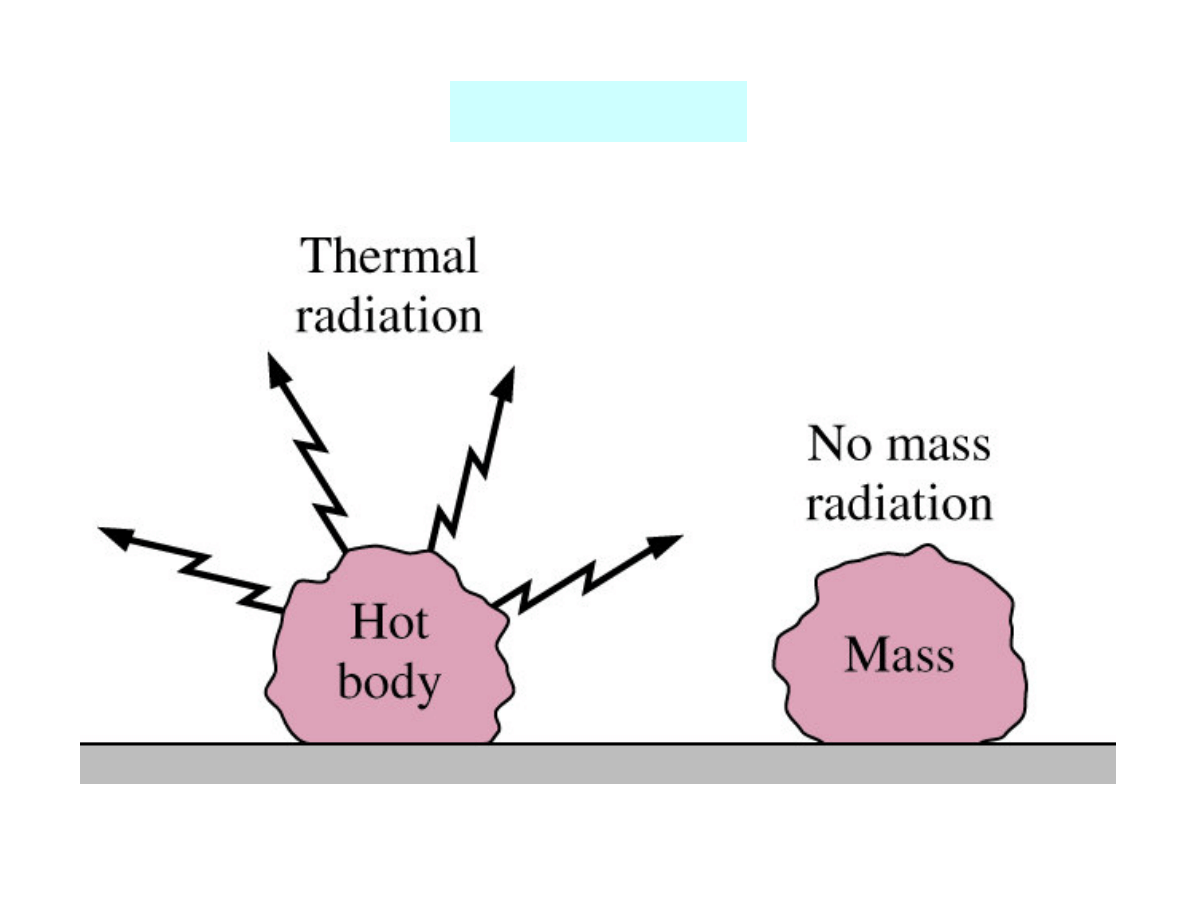
Radiation
dx
dT
A
cond
Q
Λ
−
=
•
dx
dC
A
D
A
AB
diff
m
−
=
•
Heat conduction
Mass diffusion
Concentration difference
is the driving force for
mass transfer
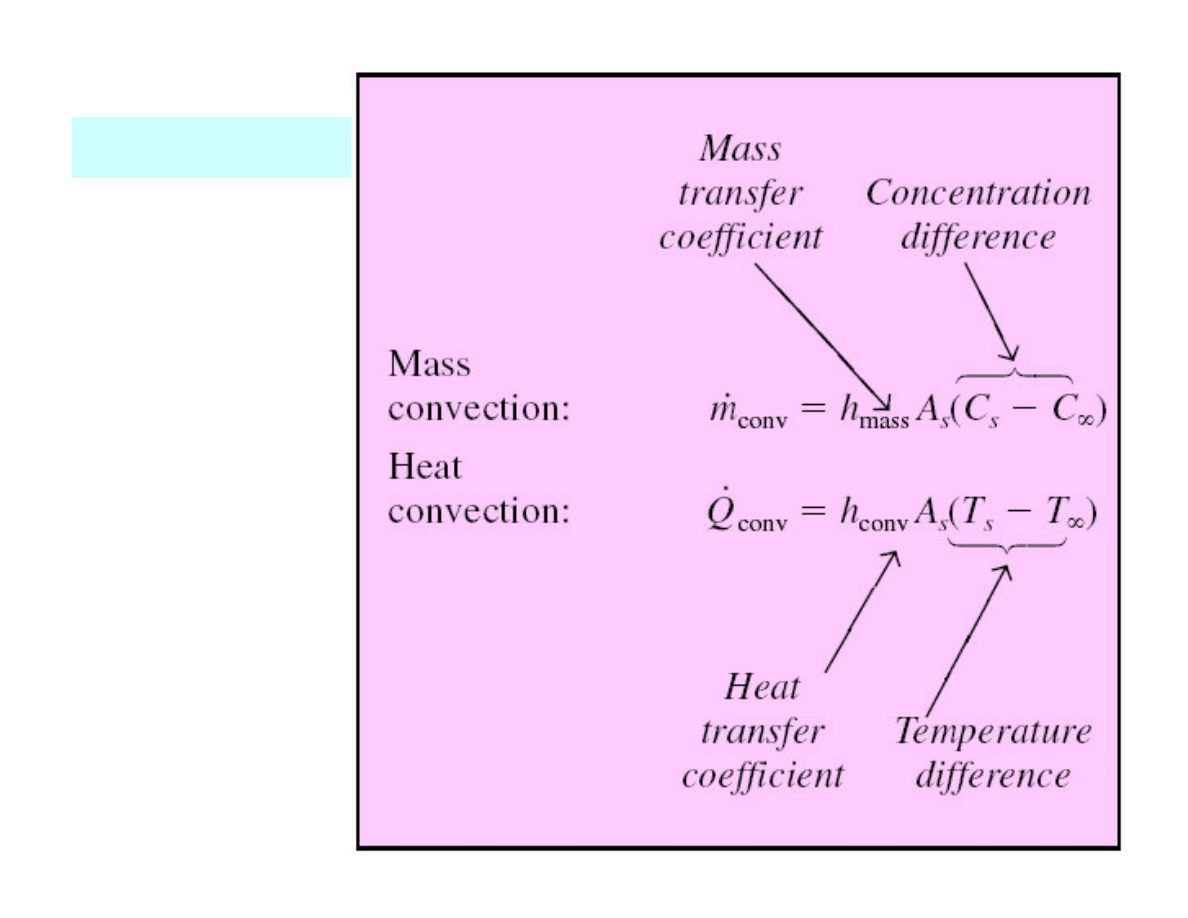
Convection
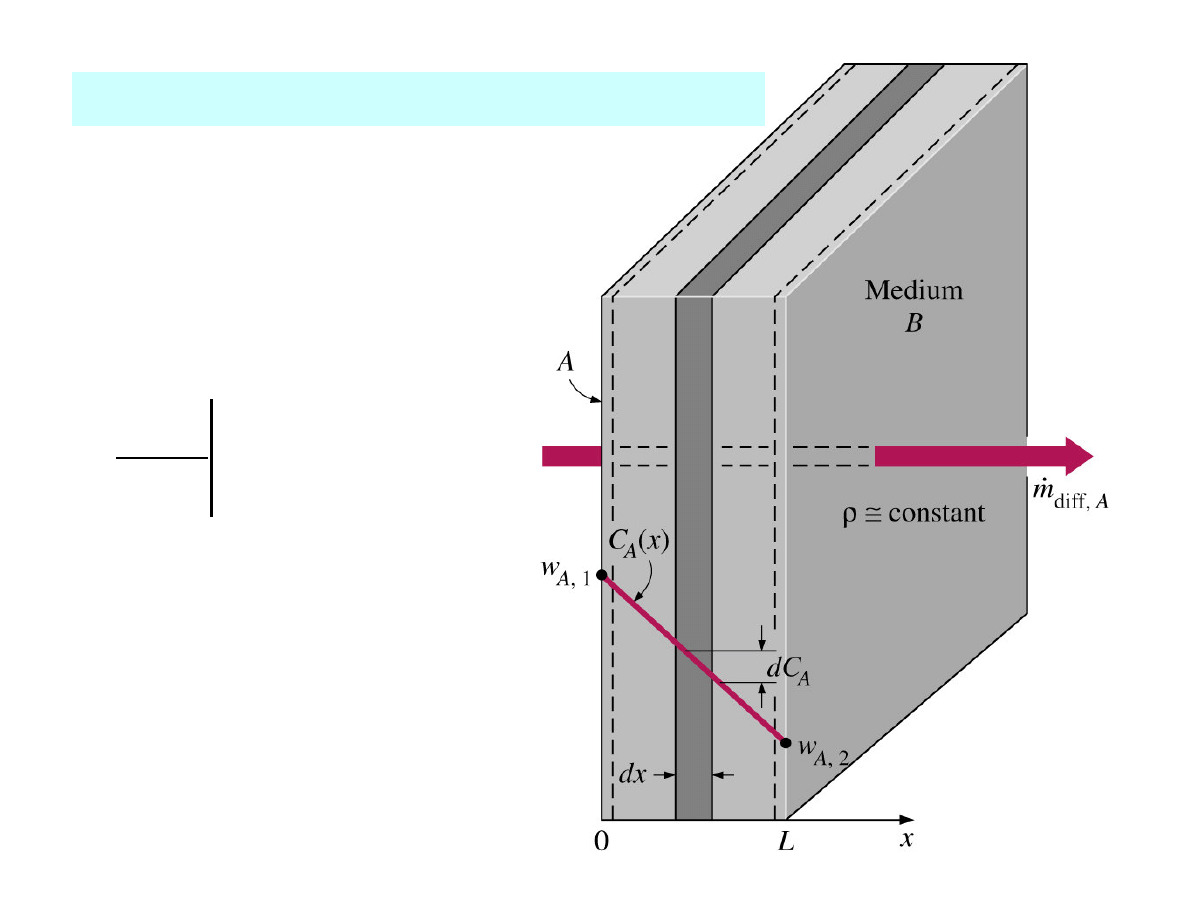
Steady mass diffusion through a wall
dw
dx
A
x =
=
0
0
An impermeable surface is a
surface that does not allow
any mass to pass through.
Thus at x = 0:
→
→
→
→
Analogy to an insulated
surface in heat transfer.
where
w
is the mass fraction.
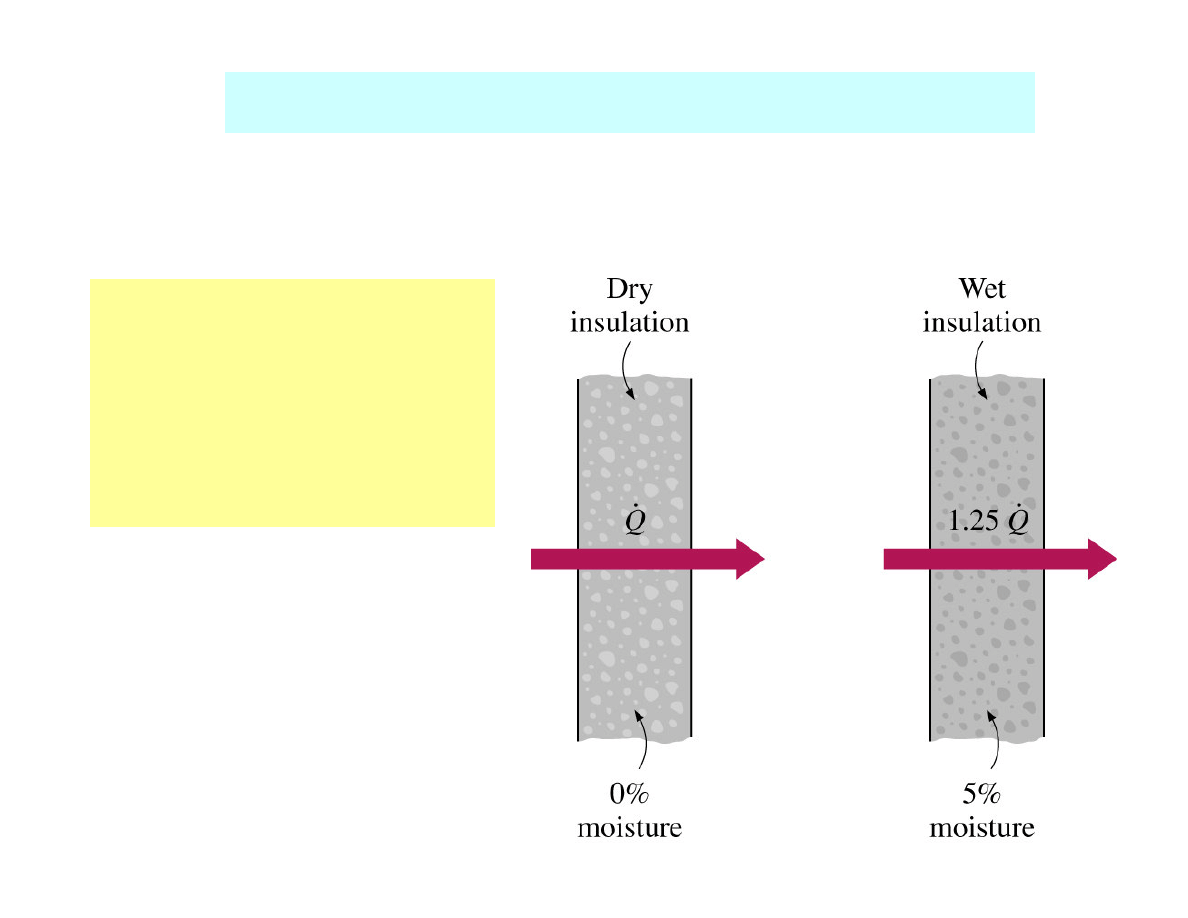
Water vapour migration in buildings
Moisture – influence on the performance and durability of
building materials →
→
→
→
importance of moisture transmission
Example:
A 5% moisture content
can increase heat
transfer through wall
insulation by 25 %.
Moisture
– affects the
effective thermal
conductivity of porous
building materials →
→
→
→
linear increase of heat
transfer
Negative effects due to excess moisture – changes in the
appearance and physical properties of materials:
- corrosion and rusting in metals
- rotting in woods
- peeling of paint on the interior and exterior wall surfaces
- molds grow on wood surfaces at relative humidities above 85%
- damage of the porous material structure due to freezing
The effects of moisture in buildings
– migration of water vapour
through the walls and condensation on the inner side, releasing
the heat of vaporisation.
The vapour barriers (thick metal and plastic layers) and retarders
(thin metal, paper and plastic layers)
– control of moisture
migration in the walls, floors and ceilings.
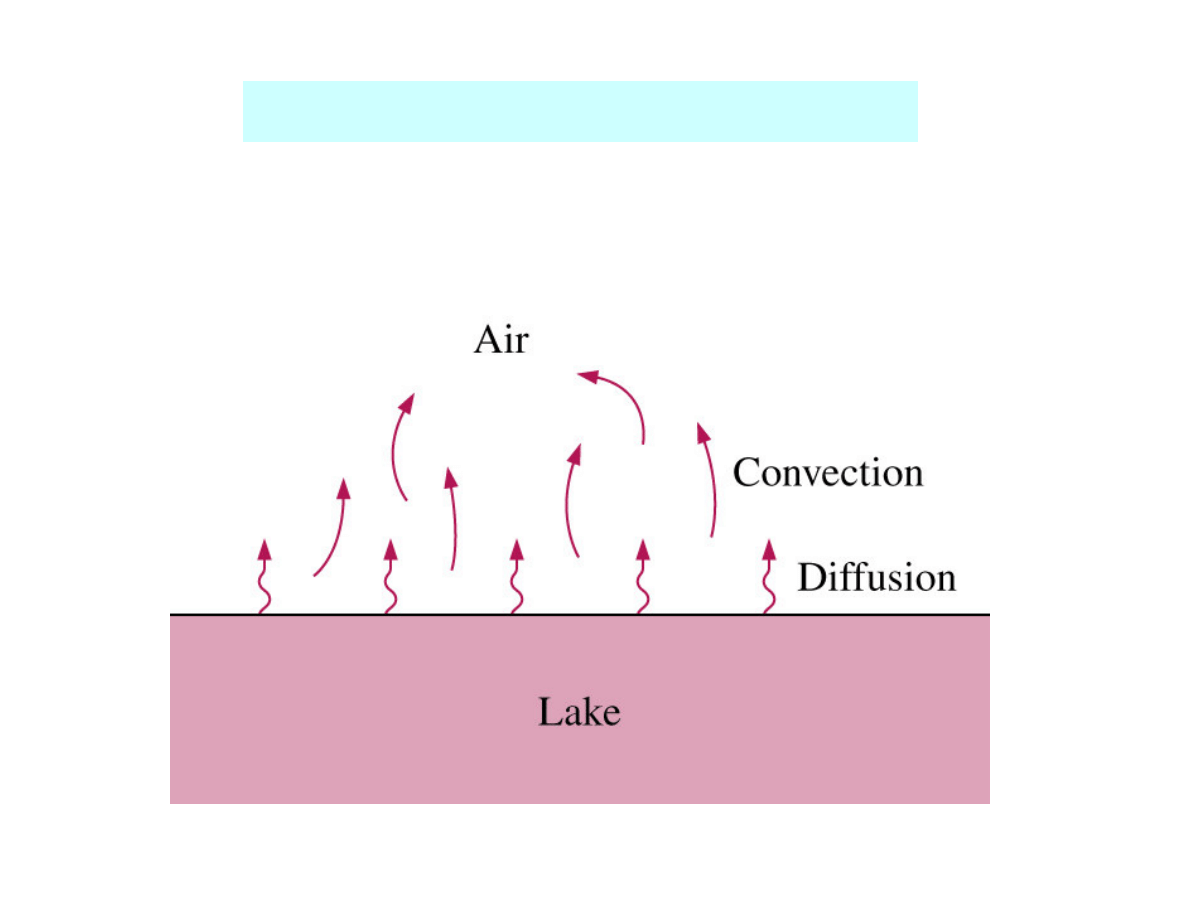
Diffusion in a moving medium
Mass transfer - due to both diffusion and convection
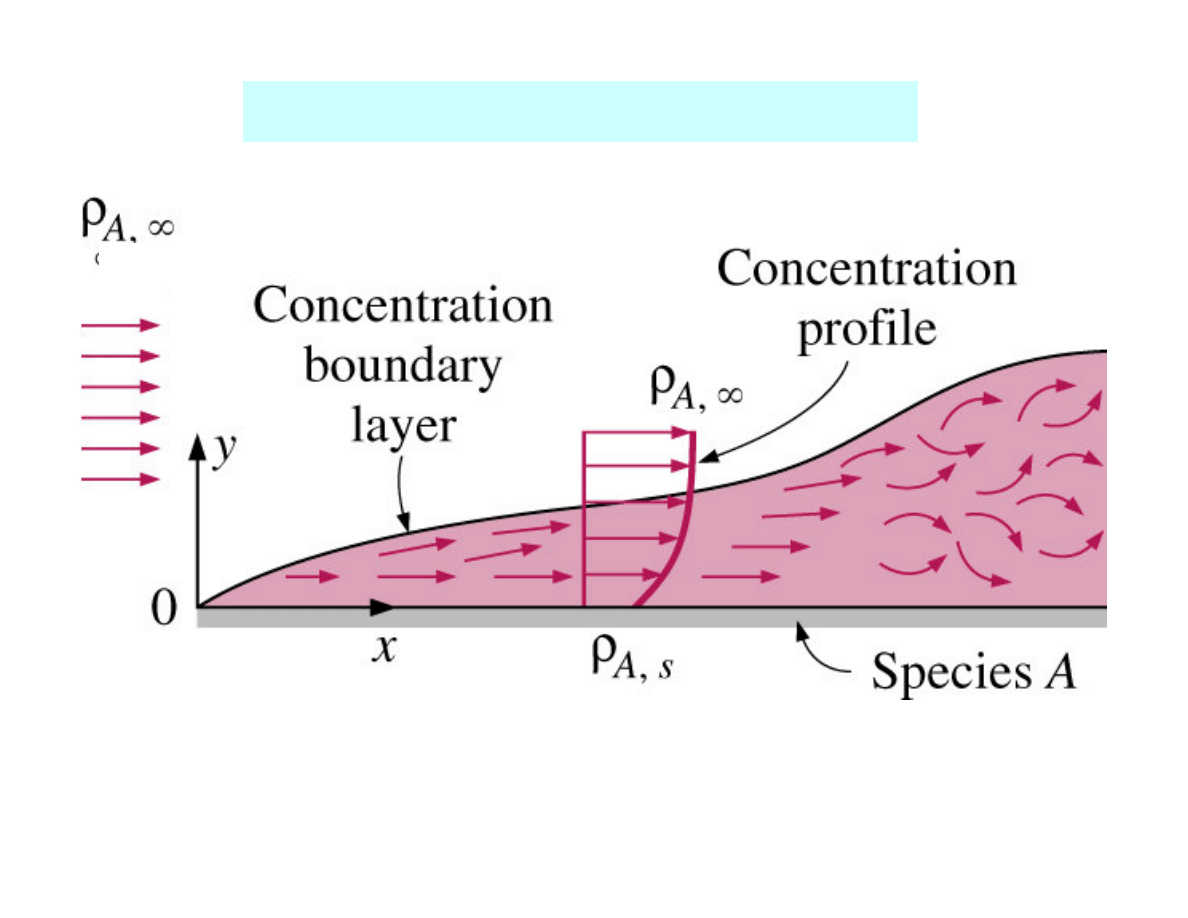
Mass convection
∞
v
∞
v
Concentration boundary layer for species A during
external flow on a flat surface.
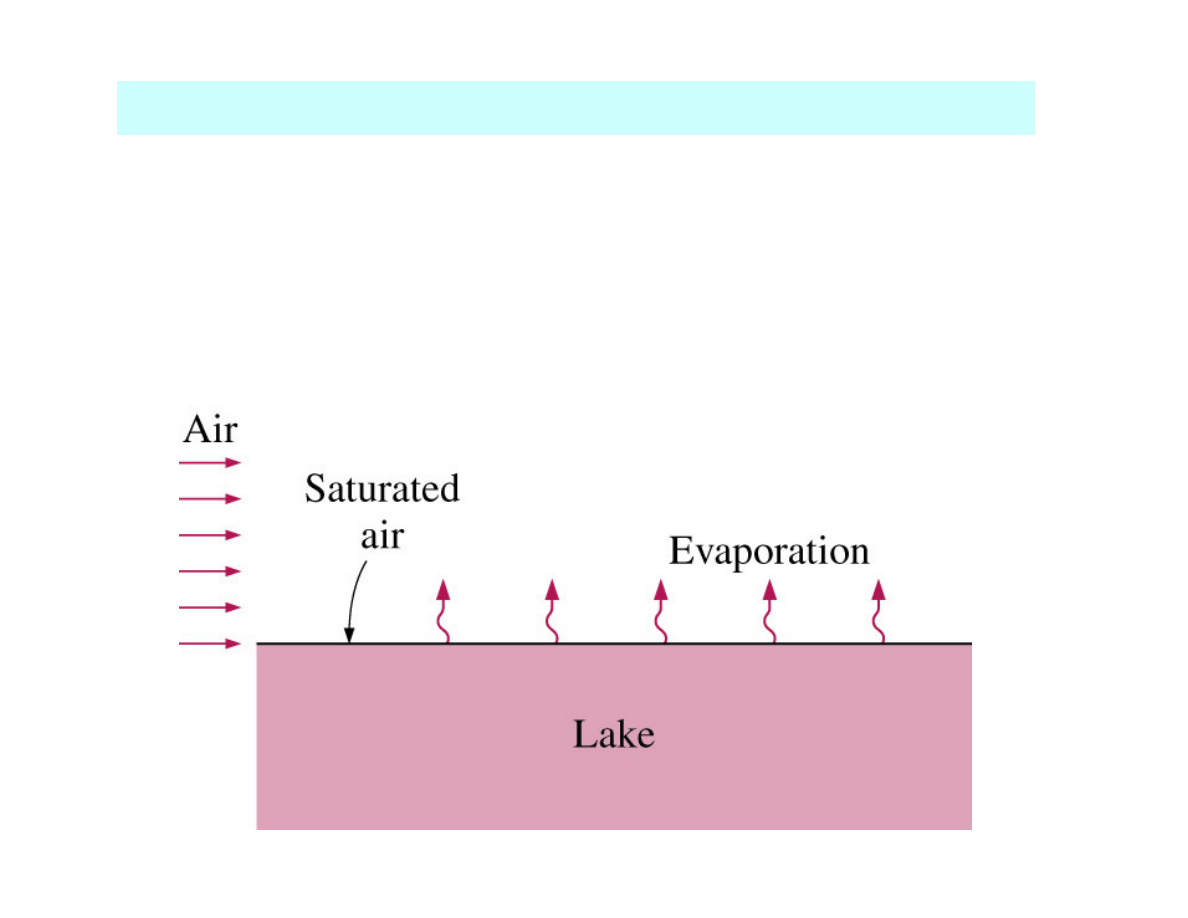
Evaporation from the free surface of water into air
Heat-mass convection analogy is not applicable when
the rate of mass transfer of species is high relative to
the flow rate of that species (boilers, condensers...)
Example of the fulfilled mass-heat analogy
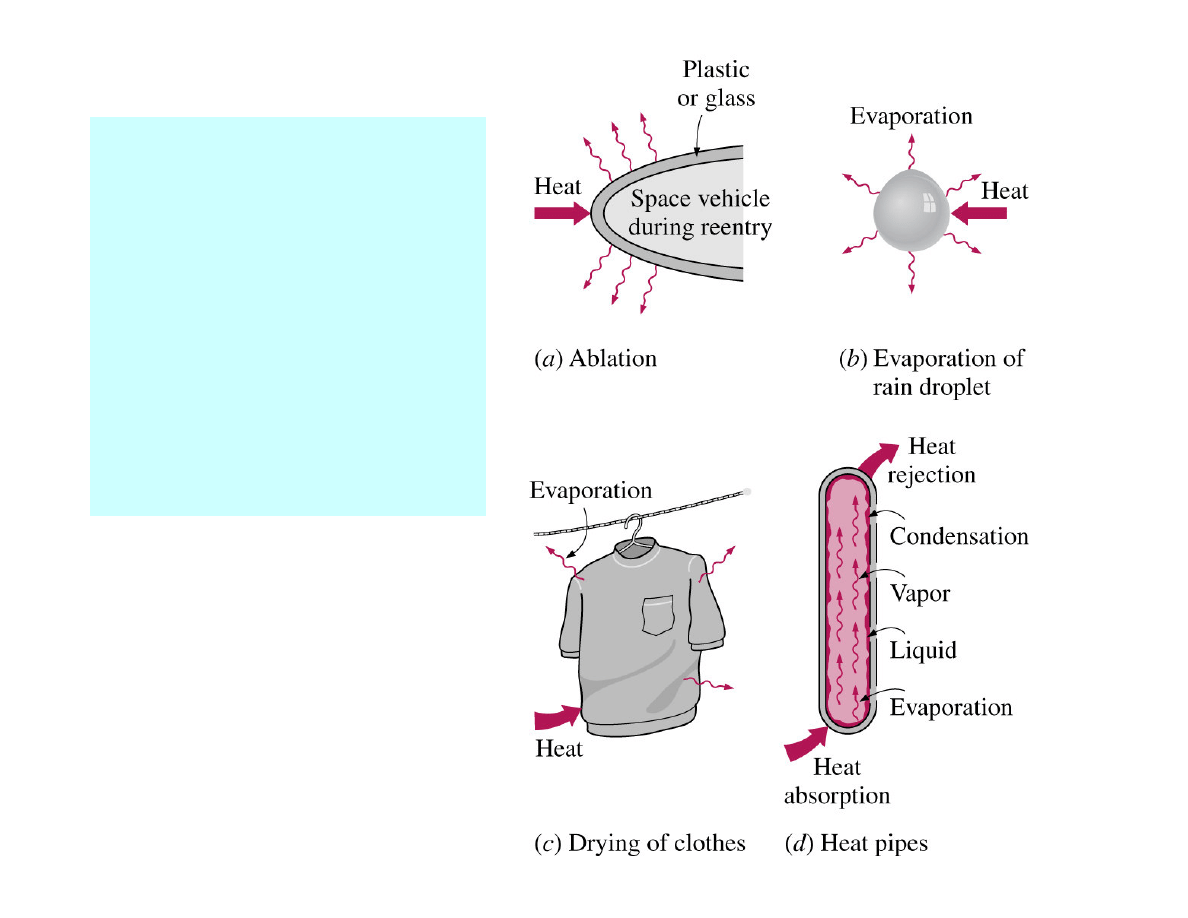
Simultaneous heat
and mass transfer
(drying, evaporative
cooling, cooling by
dry ice, combustion
of fuel droplets,
transpiration cooling,
rain, snow) →
→
→
→
complex problem.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
14 Stacje transformatorowe
14 wschodnia transformacja kulturowa Justynian
14 Stacje transformatorowe
14 transformacjeid 15566
MODUL 14 Ogolna%20struktura%20umow%20dotyczacych%20transferu%20technologii
14 transformacjeid 15566
T7 Transformacja układu odniesienia
wyklad 14
Vol 14 Podst wiedza na temat przeg okr 1
11 BIOCHEMIA horyzontalny transfer genów
Metoda magnetyczna MT 14
Transformacje91
wyklad 14 15 2010
5 Algorytmy wyznaczania dyskretnej transformaty Fouriera (CPS)
TT Sem III 14 03
więcej podobnych podstron