
Studia Quaternaria, vol. 31, no. 1 (2014): 31–37.
DOI: 10.2478/squa-2014-0003
DE VEL OP MENT OF THE KUB£OWO PALAEOLAKE, CEN TRAL
PO LAND, DUR ING THE EEMIAN INTER GLA CIAL AS AGAINST
SUBFOSSIL CLADOCERA ANAL Y SIS – PRE LIM I NARY RE SULTS
Monika Niska
1
, Ma³gorzata Roman
2
1
In sti tute of Ge og ra phy and Re gional Stud ies, Pom er a nian Uni ver sity in S³upsk, Partyzantów 27,
76-200 S³upsk, Po land, e-mail: monikaniska@wp.pl
2
De part ment of Geo mor phol ogy and Palaeo ge ogra phy, Fac ulty of Geo graph ical Sci ences, Uni ver sity of £ódŸ,
Narutowicza 88, 90-139 £ódŸ, Po land , e-mail: mroman@geo.uni.lodz.pl
Ab stract
The re sults of anal y sis of Cladocera oc cur rence in lac us trine sed i ments from the Kub³owo site have been pre sented.
Lac us trine and peat de pos its found there have been pre vi ously an a lyzed for pol len con tent (depth of 11.1–3.8 m) and
rep re sent a lon gest con tin u ous Eemian–Vistulian suc ces sion in cen tral Po land (Ro man and Balwierz, 2010). Clado-
cera anal y sis was car ried out on 25 sam ples from the depth of 9.20–10.5 m of an Eemian age sec tion. The sec tion con -
sists of fine or ganic sand, silt with or ganic mat ter and gyttja. Iden ti fied were 19 spe cies of subfossil Cladocera and five
zones of fauna de vel op ment were dis tin guished. In the early and mid-Eemian low fre quency zoo plank ton in the
palaeolake has been found. Best con di tions for zoo plank ton de vel op ment oc curred in the late Eemian (R PAZ E6, E7).
At the end of the Eemian a sig nif i cant change of cli mate in a de te ri o ra tion of en vi ron men tal con di tions and de creased
pres ence of zoo plank ton has been noted. Cladocera re sults and the pol len data en able a re con struc tion of the cli ma tic
and en vi ron men tal changes in the Kub³owo palaeolake.
Key words: Cladocera anal y sis, Eemian Inter gla cial, palaeoenvironment, cen tral Po land.
Mansuscript re ceived 15 September 2013, ac cepted 23 May 2014
IN TRO DUC TION
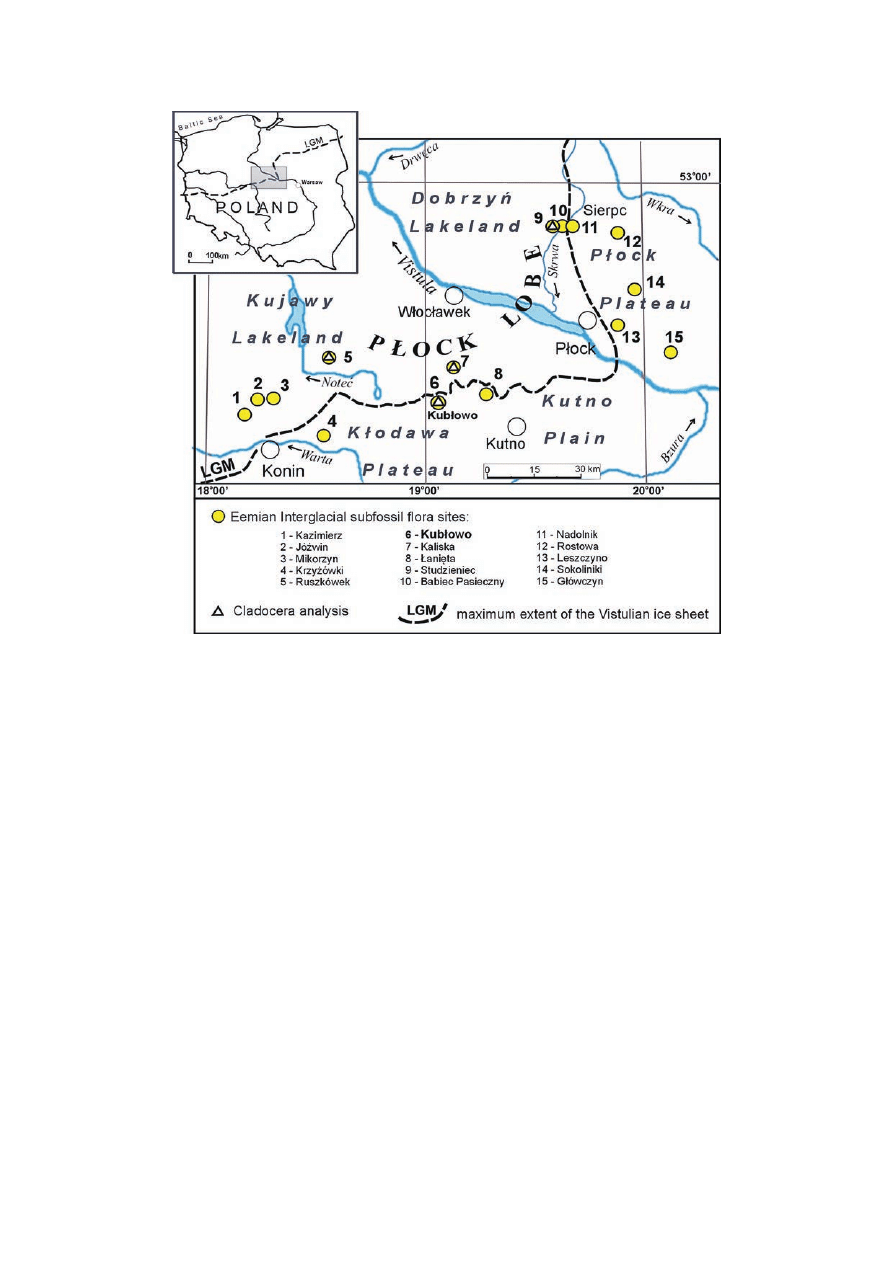
Nu mer ous lo cal i ties with lac us trine de pos its of Eemian
Inter gla cial age have been found in cen tral Po land, par tic u -
larly in the P³ock Lobe area and its sur round ings (Fig. 1). The
area, was a wide lakeland dur ing the Eemian. Lake sed i ments
of that age have well been doc u mented in palynology. At
some sites (Ruszkówek, Kaliska and Studzieniec) a suc ces -
sion of Cladocera has also been re corded (Miros³aw-Gra-
bowska and Niska, 2007a; Miros³aw-Grabowska and Niska,
2007b; Miros³aw-Grabowska et al., 2009; Niska, 2008).
Gen er ally, Cladocera an or gan isms group dom i nant
within zoo plank ton and their subfossil re mains are well pre -
served in sed i ments (cf. Szeroczyñska, 2002). Small size of
Cladocera, their ap ti tude to pro duce ephippia which may be
trans ported by birds to col o nize new wa ter bod ies, and abil ity
to re pro duce by par the no gen e sis, caused Cladocera much
more ex pan sive and mo bile than larger aquatic fauna. Thus,
their re sponse to cli ma tic and en vi ron men tal changes may be
faster and more rad i cal than in the case of larger or gan isms.
Subfossil Cladocera have been stud ied for al most 90
years. In Po land, first stud ies were con ducted in the 1980s
and 1990s (Czeczuga et al. 1970, Mikulski, 1976, Szero-
czyñska, 1984, 1985, 1991, 1998; Biñka et al. 1991). The
high use ful ness of Cladocera in re con struc tion of en vi ron -
men tal con di tions has led to a con sid er able in ter est in its po -
ten tial ap pli ca bil ity in stud ies of older sed i ments pre ced ing
the last gla ci ation. Frey (1962) ini ti ated in ves ti ga tions of
Cladocera from Eemian de pos its. Since 2001 sim i lar stud ies
have been taken up in Po land by Niska (Kupryjanowicz,
2005; Miros³aw-Grabowska and Niska, 2005; Niska, 2002,
2003). Cladocera subfossils de pos ited dur ing the Eemian
Inter
gla
cial, com
pared to those from the Ho
lo
cene sed
i
-
ments, are thin ner, have a more dam aged struc ture and of ten
lack char ac ter is tic fea tures en abling spe cies de ter mi na tion.
subfossil Cladocera re mains ex am ined in the Eemian sed i -
ments did not ex hibit sub stan tial dif fer ences in ap pear ance
and size com pared to the pres ent-day re mains. De spite the
sub stan tial de struc tion of the Cladocera re mains, the ob -
tained re sults are fully cred i ble and may be used in the re con -
struc tion of en vi ron men tal con di tions from the pe riod prece-
ding the last gla ci ation
The aim of the ar ti cle is to pres ent re sults of Cladocera
anal y sis and zoo plank ton suc ces sion, em pha siz ing the pa-
laeolake en vi ron men tal changes dur ing the Eemian Inter gla -
cial at Kub³owo.
STUDY SITE
The Kub³owo site is lo cated in the north ern part of the
K³odawa Pla teau within the area of the Warta Stadial, the fi -
nal stadial of the Odranian (Late Saalian) Gla ci ation (for -
Brought to you by | Uniwersytet Lodzki
Authenticated
Download Date | 6/12/15 3:48 PM
merly Wartanian Gla
ci
ation) (Lindner, 2005; Ber et al.,
2007) and slightly to the south of the max i mum limit of the
Vistulian (Weichselian) Gla ci ation ice sheet (Fig. 1). The
K³odawa Pla teau is a mo not o nous morainic plain at 120–130
m a.s.l., mainly com posed of till. There are no postglacial
lakes, how ever, in fos sil de pres sions at Kub³owo can be
found biogenic de pos its which ac cu mu lated through out the
Eemian Inter gla cial and the older part of the Vistulian, and
were sub se quently cov ered by glaciofluvial sed i ments dur -
ing the last ice sheet ad vance (Ro man and Balwierz, 2010).
The or ganic de pos its at Kub³owo have been found to be as so -
ci ated with mar ginal forms of the max i mum ex tend of the
Vistulian Gla ci ation ice sheet in the P³ock ice lobe (Ro man
2007, 2010). Lac us trine and peat de pos its found there have
been an a lyzed for their pol len con tent (depth of 11,1 – 3,8 m)
and rep re sent a lon gest con tin u ous Eemian–Vistulian suc -
ces sion in cen tral Po land (Ro man and Balwierz, 2010). The
pres ently examinated de pos its from 10.50 to 9.20 m do not
con tain car bon ates and their li thol ogy is shown be low:
Depth (m)
9.20–9.40
lam i nated silt and silty clay, gray to brown -
ish-gray,–HCl
9.40–10.10
gyttja, highly com pressed, dark gray, –HCl
10.10–10.35
silt with or ganic mat ter, dark gray, –HCl
10.35–10.50
very fine or ganic sand, light gray, –HCl
METH ODS
The Cladocera anal y sis was car ried out on 25 sam ples
from the depth of 9.20 to 10.50 m. The sam ples of 1cm
3
were
pre pared ac cord ing to the stan dard pro ce dure (Frey, 1986),
slightly mod i fied. Af ter re moval of car bon ates us ing 10%
HCl, each sam ple was heated to 80°C in 10% KOH for 20
min utes. Af ter wash ing with dis tilled wa ter, the res i due was
sieved through a 40-µm mesh. The fine ma te rial was trans -
ferred into a polycarbone test-tube. Be fore count ing, the re -
mains were col oured with safranine. A min i mum num ber of
200 re mains of Cladocera (3–5 slides) were ex am ined in each
sam ple. All the re mains from each slide were counted (head-
shield, shell, postabdomen, postabdominal claws, an ten nules
and other), and next, the cladoceran spec i mens were as sem -
bled. Iden ti fi ca tion and eco log i cal in ter pre ta tion of the Cla-
docera re mains were car ried out ac cord ing to Duigan (1992),
Frey (1958, 1962), Goulden (1964), Hofmann (1986, 2000),
Korhola (1990), Flössner (2000) Szeroczyñska (1985), and
Szeroczyñska and Sarmaja-Korjonen (2007). Re sults of the
quan ti ta tive and qual i ta tive anal y sis are shown in the con cen -
tra tion di a gram, and the to tal num ber of Cladocera spec i -
mens in 1cm
3
of de
pos
its and the spe
cies di
ver
sity was
as sessed ac cord ing to the Shan non-Wiener Biodiversity In -
dex to see on Fig ure 2, 3 (PolPal com puter pro gram, Walanus
and Nalepka, 1999) .
32
M. NISKA & M. RO MAN
Fig. 1.
Lo ca tion of Eemian subfossil flora sites in Cen tral Po land.
Brought to you by | Uniwersytet Lodzki
Authenticated
Download Date | 6/12/15 3:48 PM
DE VEL OP MENT OF THE KUB£OWO PALAEOLAKE
33
.
2 .
gi
F
.e
li
f
or
p
o
w
o³
b
u
K
f
o
st
ne
m i
de
s
e
ht
ni
sl
a
u
di
vi
d
ni
ar
ec
o
da
l
C
f
o
re
b
m
u
n
et
u l
o s
ba
e
ht
f
o
ma
r
g a
i
D
Brought to you by | Uniwersytet Lodzki
Authenticated
Download Date | 6/12/15 3:48 PM

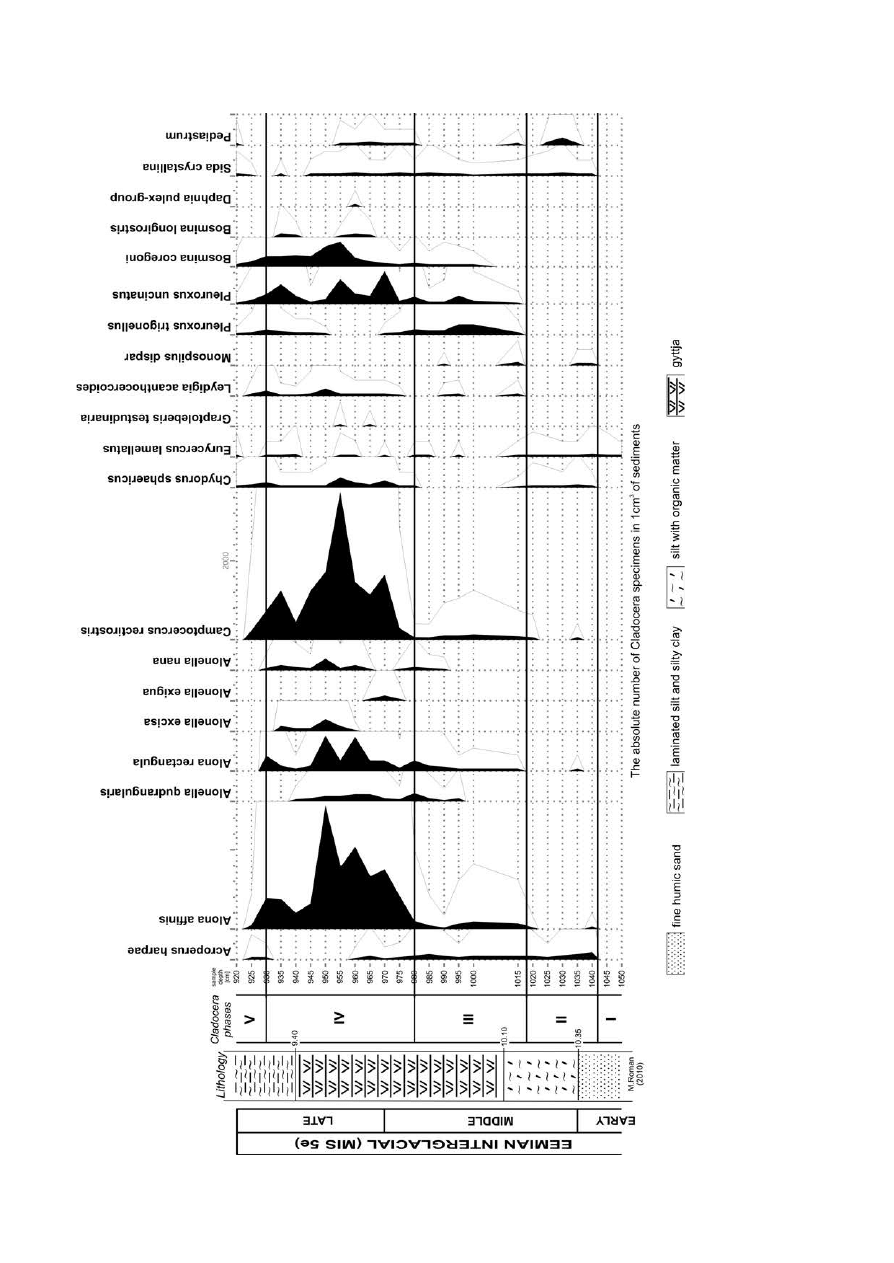
RE SULTS
Subfossil cladoceran fauna from the Kub³owo palaeo-
lake is rep re sented by 19 spe cies be long ing to four fam i lies:
Bosminidae, Chydoridae, Sididae, Daphnidae. Most of the
re mains are of the Chydoridae and Bosminidae fam i lies.
Dom i nant were two spe cies of Chydoridae – Alona affinis
and Camptocercus rectirostris be long ing to a group in hab it -
ing the lit to ral zone in clear and calm wa ter, de pend ing on the
pres ence of aquatic plants (Flössner, 1972). Con sid er ing the
age of the re mains from over 100 ka BP (128,000–118,000
years BP, Shackle ton, Opdyke 1976), they are well pre served
and came in large num bers. The quan ti ta tive and qual i ta tive
com po si tion of fauna has en abled to dis tin guish five phases
of the Cladocera de vel op ment (Fig. 2).
Phase I (10.50 m – 10.42 m): at that phase only one spe -
cies has been iden
ti
fied, namely, Eurycercus lamellatus
which was tol
er
ant to low wa
ter tem
per
a
tures (Poulsen,
1944) and inhabs the lit to ral zone in clear wa ters. E. lamella-
tus sug gests the ex is tence of macrophytes (Flössner, 1972).
Phase II (10.42 m – 10.17 m): at that phase oc curred spe -
cies pre fer ring wa ter with low con tent of nu tri ents and tol er -
ant of cold wa ter, such as Acroperus harpae, Eurycercus
lamellatus, Sida crystalina, Alona affinis, (White side, 1970)
and eurybiont – Chydorus sphaericus (Alhonen, 1970).
Through out this phase the pres ence of eight spe cies of Cla-
docera was noted (above 400 spec i mens/1 cm
3
in the sed i -
ments, Fig. 3). Within the du ra tion of this phase oc curred
Monospilus dispar, a spe cies con nected with sand in the bot -
tom. The oc cur rence of the Camptocercus rectirostris sug -
gested a lit tle warmer wa ter con di tions (Poulsen, 1944). At
that phase there are spe cies char ac ter is tic for a lit to ral zone
and the ab sence of spe cies from the open wa ter was noted.
Phase III (10.17 m – 9.80 m): at that phase spe cies tol er -
ant to cooler wa ter (Eurycercus lamellatus) give way to spe -
cies pre fer ring wa ter of higher tem per a ture. In the lake found
were Camptocercus rectirostris – pre fer ring warmer, clean
and calm wa ter, dwell ing in the macrophyte zone, and Pleu-
roxus uncinatus and Pleuroxus trigonellus – pre fer ring wa ter
that is warmer and richer in nu tri ents (Frey, 1958). This may
in di cate a rise in wa ter tem per a ture and an in crease in nu tri -
ents in the lake. Im prove ment of liv ing con di tions in the lake
caused a greater biodiversity, 14 spe cies oc curred (above
1500 spec i mens/1cm
3
of sed i ments, Fig. 3).
Phase IV (9.80 m – 9.30 m): the be gin ning of phase IV
was ex pressed by an in crease of both di ver sity of taxa (18
spe cies) and fre quency of Cladocera re mains up to 8000
spec i mens/cm
3
of a de posit. It in di cates an im prove ment of
the en vi ron men tal con di tions (warmer wa ter, more nu tri ents)
in the lake. The con vic tion of the warm con di tions in this
palaeolake is sup ported by the pres ence of Camptocercus
rectirostris, Pleuroxus trigonellus, Pleuroxus uncinatus and
Graptoleberis testudinaria. Higher at ten dance of the Leydi-
gia acanthocercoides, Alona rectangula, Pleuroxus uncina-
tus spe cies sug gests a higher con tent of nu tri ents in the wa ter
(Korhola, 1990). The ap pear ance of Graptoleberis testudi-
naria may in di cate nu tri ent-rich wa ter (Duigan, 1992). In the
mid dle of that phase there was an in creased pres ence of spe -
cies pre
fer
ring open wa
ter: Bosmina coregoni, Bosmina
longirostris and Daph nia pulex-group. This may sug gest a
rise of the wa ter level in the lake. In the mid dle of that phase
(9.50 m) Alonella excisa have been re ported, spe cies that can
be re lated to the de crease of pH of the wa ter in the lake
(Krause-Dellin and Steinberg, 1986). That phase ends the pe -
riod of fa vor able con di tions for the de vel op ment of Clado-
cera. Dur ing that phase, two short pe ri ods of lower Cladocera
fre quency were re corded (9,65 m and 9.40 m). This could be
due to the fluc tu a tions in ther mal con di tions in the res er voir
and the oc cur rence of short cold cli mate pe ri ods.
Phase V (9.30 m – 9.20 m): at the be gin ning of that phase
12 spe cies of Cladocera were iden ti fied in sed i ments. The
sig nif i cant de crease in the pres ence of Cladocera in di vid u als
of all spe cies (max 3000 in di vid u als/1cm
3
) along with low er -
ing num
ber of spe
cies was ob
served. In the palaeolake
Acroperus harpae spe cies re ap peared. In that phase pre -
sented were spe cies with di verse con di tion pref er ences but a
de crease in con cen tra tion of re mains in the sed i ment may in -
di cate de te ri o rat ing liv ing con di tions in the lake prob a bly
con nected with wa ter low er ing and cli mate cool ing.
DE VEL OP MENT OF THE KUB£OWO
PALAEOLAKE
The stra tig ra phy of the sed i ments of the Kub³owo pa-
laeolake was de ter mined on the ba sis of the dis tin guished
pol len zones. Ac cord ing to the pol len data, the lac us trine de -
pos its from 11.00m to 9.20m were ac cu mu lated dur ing the
Eemian Inter gla cial (Ro man and Balwierz, 2010).
Early Eemian, Pol len zone K1 – Pinus-Ar te mi sia-Juni-
perus; K2 – Pinus–Betula-Quercus
Sed i men ta tion of or ganic de pos its at Kub³owo com -
menced when in the neigh bor hood were open pine for ests
with a dis tinct birch share (L PAZ K1), while scarce open ter -
rains were grassy (Ro man and Balwierz, 2010). The ame lio -
ra tion of the cli mate led to a vis i ble re duc tion in heliothytes,
re placed by dense birch-pine for ests (L PAZ K2) (Ro man
and Balwierz, 2010). At the begining of the pe riod cor re lated
with L PAZ K2 in the lake ap peared cladocerans rep re sented
by a sin gle spe cies tol er at ing cold wa ter (Cladocera Phase I).
The wa ter level was prob a bly low. At the bot tom of the lake
sand was de pos ited. The con di tions in the lake were not fa -
vor able for the de vel op ment of zoo plank ton.
Eemian op ti mum, Pol len zone K3 – Quercus, K4 –
Corylus-Tilia-Almus, K5 – Carpinus-Alnus-Corylus-Tilia
The inter gla cial cli ma tic op ti mum be gan with oak for -
ests and some elm and ash (L PAZ K3). At that time in the
lake dom i nated spe cies pre fer ring wa ter with a low con tent
of nu
tri
ents and tol
er
ant to cold wa
ter. In the zone the
Cladocera spe cies pre fer ring warmer wa ter ap peared for the
first time, which sug gested slightly warmer wa ter con di tions
(Cladocera phases II). At that zone pre dom i nated spe cies
from the lit to ral zone. The pro gress ing warm ing re sulted in
changes in the dom i nant tree stands. The dom i nant spe cies –
oak, elm and ash trees were re placed by multi-spe cies de cid -
u ous for ests with ha zel and lin den trees, as well as al ders (L
PAZ K4), pre vail ing in wet hab i tats. With time, horn beams
be gan to spread and at the end of L PAZ K5 they be came
34
M. NISKA & M. RO MAN
Brought to you by | Uniwersytet Lodzki
Authenticated
Download Date | 6/12/15 3:48 PM
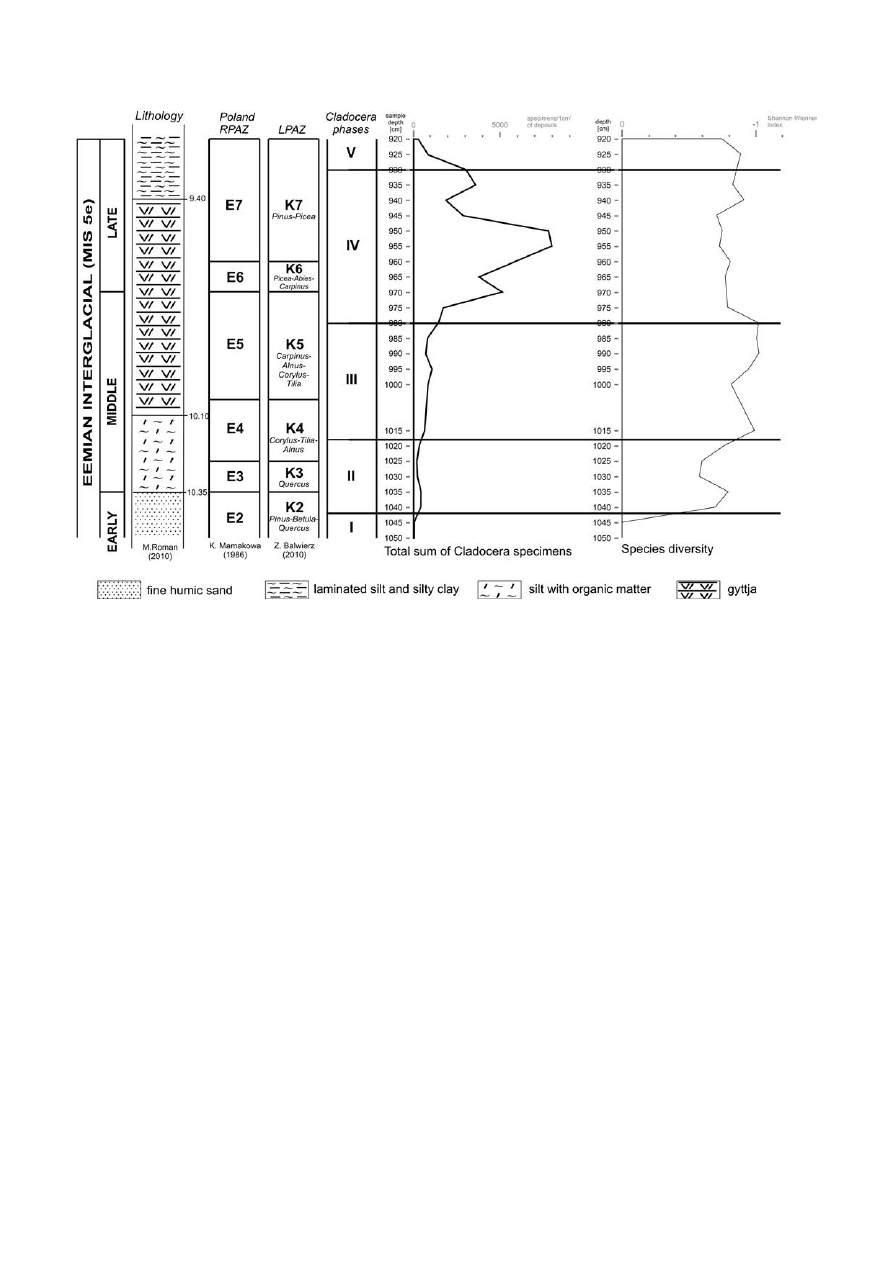
dom i nant (Ro man and Balwierz, 2010). In the lake from L
PAZ E4 (Cladocera Phase III) there was an in creased fre -
quency of spe cies pre fer ring warmer wa ter richer in nu tri -
ents. Im prove ment of liv ing con di tions in the lake caused a
greater di ver sity of spe cies. From the be gin ning of the K5
zone the wa ter level in the res er voir be came slightly higher.
Eemian post-op ti mum, Pol len zone K6 – Picea-Abies-
Carpinus, K7 – Pinus-Picea
The de cline of the cli ma tic op ti mum was marked by the
pre-em i nence of horn beam for est. The grad ual cool ing of the
cli mate led to a re ces sion of thermophilous trees and the ap -
pear ance of spruce, fir and yew (L PAZ K6). De spite the pro -
gress ing cool ing, the fauna in hab it ing the lake reached its
max i mum de vel op ment. The cli ma tic con di tions oc cur ring
in the L PAZ K6 and at the be gin ning of the K7 zone were op -
ti mal for the de vel op ment of zoo plank ton, which re sulted in
the in crease of the Cladocera spe cies and re spec tive in di vid -
u als, in clud ing thermophilic spe cies (Cladocera phase IV). A
larger num ber of spe cies pre fer ring more fer tile wa ter as well
as a pres ence of or ganic mat ter were noted. At the be gin ning
of L PAZ K7 the in creased num ber of spe cies pre fer ring open
wa ter sug gests ris ing of the wa ter level in the lake. Then,
Alonella ex cise was re ported. This may in di cate the de crease
of pH. The sed i ments changed into silt. At the end of L PAZ
K7 there was a dec re ment in both the num ber of the Clado-
cera spe cies and the num ber of spec i mens of par tic u lar spe -
cies (Cladocera phase V). At that time the spread of pine trees
with some spruce and ini tially also fir (L PAZ K7) marked
the de cline of the Eemian Inter gla cial (Ro man and Balwierz,
2010). In the lake the most un fa vor able con di tions for the de -
vel op ment of zoo plank ton oc curred prob a bly due to the pro -
gress ing cool ing of the cli mate.
Dur ing the late Eemian Inter gla cial there were re corded
short pe ri ods of lower fre quency of Cladocera (9.65m, 9.40m
– Cladocera phase IV), which could have been due to fluc tu a -
tions in the ther mal con di tions in the lake and the oc cur rence
of short cool ing pe ri ods.
DIS CUS SION
The re con struc tion of the Cladocera suc ces sion dur ing
the Eemian Inter gla cial at Kub³owo is com pa ra ble with the
re cords from the ad ja cent Eemian sites: Ruszkówek (Jan-
czyk-Kopikowa, 1997; Miros³aw-Grabowska and Niska,
2007b) and Kaliska (Janczyk-Kopikowa, 1965, Miros³aw-
Grabowska and Niska, 2007b). These palaeolakes are lo -
cated no fur ther than 40 km from each other. The clos est to
Kub³owo is the Kaliska palaeolake. The Cladocera suc ces -
sion in the Kaliska palaeolake be gan with the outstart of the
ha zel zone (R PAZ E4). How ever, in the Ruszkówek palaeo-
lake an in di vid ual Cladocera spe cies ap peared at the turn of R
PAZ E2/E3 like in the Kub³owo palaeolake. The Cladocera
spe cies oc cur ring dur ing the early Eemian Inter gla cial be -
long to the so-called arc tic spe cies (Alona affinis, Acroperus
DE VEL OP MENT OF THE KUB£OWO PALAEOLAKE
35
Fig. 3.
Di a gram of the to tal num ber of Cladocera spec i mens and spe cies diversit at the Kub³owo pro file.
Brought to you by | Uniwersytet Lodzki
Authenticated
Download Date | 6/12/15 3:48 PM

harpae), tol er ant of cold wa ter with a low con tent of or ganic
mat ter (Eurycercus lamellatus).
Dur ing the pe riod cor re lat ing with R PAZ E4 (Corylus)
in the palaeolakes of Ruszkówek and Kub³owo fauna de vel -
op ment and in creased amount of thermophilic spe cies were
re corded. How ever, at the end of the ha zel zone (E4) and in
the horn beam zone (E5) at two sites – Kaliska and Rusz-
kówek an ab sence of fau nal re mains was ob served. The ex -
pla na tion of that phe nom e non is dif fi cult. One rea son could
have been the high con tent of CaCO
3
in those sed i ments. The
car bon ate might have ac cel er ated the de cay of chitin shells,
which have not pre served till now. The sec ond rea son could
have been a short age in nu tri ents and/or un fa vour able con di -
tions in the res er voir con nected with a higher wa ter level
(Miros³aw-Grabowska and Niska, 2007b). There is no sig -
nif i cant drop in Cladocera fauna fre quency in the pro file of
Kub³owo prob a bly due to lack of cal cium car bon ate in the
sed i ments. This re sulted in a con tin u ous suc ces sion of Cla-
docera in the mid dle of the Eemian. In the palaeolakes the be -
gin ning of the late Eemian was as so ci ated with the de vel op -
ment of the Cladocera fauna. Es pe cially clearly marked was
the increase in the frequency of fauna in the profiles of
Kaliska and Kub³owo.
In the palaeolakes spe cies from the lit to ral zone dom i -
nated. Bosmina longirostris was a com mon mi grant spe cies
which, with in creas ing tro phy, could move be tween open
wa ter and the lit to ral zone (Frey, 1986). Only from Kub³owo
the pres ence of the Bosmina coregoni, the spe cies con nected
with open wa
ter zone was repoted, which may in
di
cate
greater depth in the Kub³owo palaeolake than in the others
lakes.
The end of the Eemian Inter gla cial is con nected with a
strong drop in fre quency of Cladocera in the stud ied palaeo-
lakes. The grad ual cool ing re sulted in an in hi bi tion of life in
all the lakes.
In the neigh bor ing palaeolakes, there was a sim i lar de -
vel op ment of the Cladocera suc ces sion re sult ing from re -
gional cli mate changes tak ing place in the Eemian Inter-
gla cial. The dif fer ences in the de vel op ment of the fauna be -
tween lakes are the re sult of dif fer ences in the lo cal con di -
tions un der which lakes ex isted and of their or i gin, cha-
racteristics and the location of the lake basin.
The stud ies of the Kub³owo palaeolake will be con tin ued
for the pur pose of trac ing the Cladocera suc ces sion and lake
de vel op ment through out the Vistulian. The re search will also
be sup ple mented by de ter mi na tion of sta ble iso topes in the
sediments.
CON CLU SION
1. In the Kub³owo palaeolake most dom i nant and most
di verse group of spe cies was the lit to ral group – the Chydo-
ridae fam ily.
2. The de vel op ment of zoo plank ton in the res er voir be -
gan as in other res er voirs in the re gion be fore the L PAZ K3
(R PAZ E3).
3. The en vi ron men tal con di tions in the palaeolake dur -
ing the early Eemian Inter gla cial have not pro vided fa vor able
con di tions for the de vel op ment of zoo plank ton, which could
be as so ci ated with a low con tent of nu tri ents in the water.
4. In
crease wa
ter fer
til
ity oc
curred in the mid
dle of
Eemian Inter gla cial (Cladocera Phase III).
5. Based on the in crease in the num ber of Cladocera
found that the most fa vor able en vi ron men tal con di tions for
the fauna de vel
op ment pres ent in the end of the mid dle
Eemian Inter gla cial and the be gin ning of the late Eemian
Interglacjal.
6. The high est fre quency of the Cladocera re mains in the
sed i ments oc curred at the end of the Eemian Inter gla cial (K6
and K7 L PAZ) sim i larly to other sites, the Kaliska and the
Ruszkówek.
7. The Cladocera spe cies found in the ex am ined palaeo-
lake cor re spond to the pres ent-day spe cies in hab it ing the
area of Po land and Europe.
8. Cladocera subfossils de pos ited dur ing the Eemian
Inter
gla
cial, com
pared to those from the Ho
lo
cene sed
i
-
ments, were thin ner, had a more dam aged struc ture and they
of ten lacked char ac ter is tic fea tures en abling spe cies de ter-
mination.
9. Cladocera phases show a good cor re la tion with the lo -
cal pol len as sem blages zones dis tin guished by Balwierz (Ro -
man and Balwierz, 2010).
The re search pro ject was sup ported by the Foun da tion
for Pol ish Sci ence, Bridge Pro gram 2012 – pro ject: “Re con -
struc tion of the de vel op ment of lake en vi ron men tal in the
Eemian inter gla cial based on subfossil Cladocera (Crusta-
cea) analysis”.
REF ER ENCES
Alhonen, P., 1970. The paleolimnology of four lakes in south-west -
ern Fin land. Ann. Acad. Sci. Fenn. A. III, 105: 1–39.
Biñka, K., Cieœla A., £¹cka, B., Madeyska, T., Marciniak, B.,
Szeroczyñska, K., Wiêckowski, K., 1991. The de vel op ment of
B³êdowo Lake (Cen tral Po land) Stud. Geol. Polon, 100: 1–86.
Ber, A., Lindner L., Marks, L., 2007. Propozycja podzia³u straty-
graficznego czwartorzêdu Polski. Prz. Geol., 55(2): 115–119.
Bruj, M., Ro man M., 2007. The Eemian Lakeland ex tent in Po land
ver sus strati graphi cal po si tion of the Mid dle Pol ish Glacia-
tions (in Pol ish with Eng lish sum mary). Biul. Pañstw. Inst.
Geol., 425: 27–34.
Cheddadi, R., Mamakowa, K., Guiot, J., de Beaulieu J. L., Reille,
M., Andrieu, V., Granoszewski, W., Peyron, O., 1998. Was the
cli mate of the Eemian sta ble? A quantitive cli mate re con struc -
tion from seven Eu ro pean pol len re cords. Paleogeogr., Paleo-
climat., Paleoecol., 143: 73–85.
Czeczuga, B., Go³êbiewski, Z., Kossacka, W., 1970. The his tory of
Lake Wi¿ajny in the ligth of chem i cal in ves ti ga tions of the sed -
i
ments and Cladocera fos
sils. Schweiz. Z. Hydrobiol. 25:
75–86.
Duigan, C.A., 1992. The ecol ogy and dis tri bu tion of the litoral
fresh wa ter Chydoridae (Branchiopoda, Anomopoda) of Ire -
land with tax o nomic com ments on some spe cies. Hydrobio-
logia 241: 1–70.
Flössner, D., 1972. Branchipoda, Branchiura. Tierwelt Deutschl.,
60: 1 – 501.
Flössner, D., 2000. Die Haplopoda und Cladocera (ohne Bosmi-
nidae) Mitteleuropas. Backhuys Pub lish ers, Leiden: 1–428.
Frey, D.G., 1958. The Late Gla cial cladoceran fauna of a small lake.
Ar chives of Hydrobiology 54: 209–275.
Frey, D.G., 1962. Cladocera from the Eemian Inter gla cial of Den -
mark. Jour nal of Pa le on tol ogy 36: 1133–1154.
Frey, D.G., 1986. Cladocera anal y sis. In Berglund B. E. (ed.),
36
M. NISKA & M. RO MAN
Brought to you by | Uniwersytet Lodzki
Authenticated
Download Date | 6/12/15 3:48 PM

Hand book of Ho lo cene Palaeo ec ol ogy and Palaeohydrology.
Wiley, Chichester, UK 667–692.
Goulden, C.E., 1964. The his tory of the cladoceran fauna of Esth-
waite Wa ter (Eng land) and its lim no logi cal sig nif i cance. Ar -
chives of Hydrobiology 60: 1–53.
Hofmann, W., 1986. De vel op men tal his tory of the Grosser Plöner
See and the Schöhsee (north Ger many): cladoceran anal y sis,
with spe cial ref er ence to eutrophication. Ar chives of Hy dro-bi
ology. Stuttgart. Suppl., 74, 259–287.
Hofmann, W., 2000. Re sponse of the chydorid fau nas to rapid cli -
ma tic changes in four al pine lakes at dif fer ent al ti tudes. Pala-
eogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeo ec ol ogy 159(3–4):
281–292.
Janczyk-Kopikowa, A. Z., 1965. Eemian Inter gla cial flora at Ka-
liska near Chodecz in Kujawy (in Pol ish with Eng lish sum -
mary). Biul. Inst. Geol., 187: 107–118.
Janczyk-Kopikowa, A. Z., 1997. Analiza py³kowa osadów intergla-
cja³u eemskiego w Ruszkówku na Pojezierzu Kujawskim.
Prz.Geol., 45(1): 101–104.
Korhola, A., 1990. Paleolimnology and hydroseral de vel op ment of
the Katasuo Bog, South ern Finlad, with spe cial ref er ence to the
Cladocera. Ann. Acad. Sci. Fenn., 155: 5–40.
Krause-Dellin, D., Steinberg, C., 1986. Cladoceran re mains as in di -
ca tors of lake acid i fi ca tion. Hydrobiologia 143, 129–134.
Kupryjanowicz, M., 2005. Roœlinnoœæ i klimat Podlasiaw czasie
interglacja³u eemskiego oraz wczesnego i œrodkowego vistu-
lianu. Prace Komisji Paleogeografii Czwartorzêdu P AU, 3:
73–80.
Lindner, L., 2005. A new look at the num ber, age and ex tent of the
Mid dle Pol ish Gla ci ation in the south ern part of cen tral–east -
ern Po
land (in Pol
ish with Eng
lish sum
mary). Prz. Geol.,
53(2): 145–150.
Mamakowa, K., 1986. Lower bound ary of the Vistulian and the
Early Vistulian pol len stra tig ra phy in con tin u ous Eemian–
Early Vistulian pol len se quence in Po land. Quatern. Stud., 7:
51–63.
Mikulski, J.S. 1976. Fur ther in ves ti ga tions upon Ho lo cene his tory
of Lake Jeziorak. Part I. The Boy Moty. Acta Univ. Nicol.
Copernici. Limnol. Pa pers 9: 65–73.
Miros³aw-Grabowska, J., Niska M., 2005. Iso to pic and Cladocera
re cords of cli mate changes of Early Eemian at Besiekierz
(Cen tral Po land). Geo log i cal Quar terly 49: 67–74.
Miros³aw-Grabowska, J., Niska, M., 2007a. Iso tope and Cladocera
data and in ter pre ta tion from the Eemian op ti mum and postop-
timum de pos its, Kaliska palaeolake (Cen tral Po land). Qua ter -
nary In ter na tional 175: 155–167.
Miros³aw-Grabowska, J., Niska, M., 2007b. Re con struc tion of en -
vi ron men tal con di tions of Eemian palaeolake at Studzieniec
(Cen tral Po land) on the ba sis of sta ble iso tope and Cladocera
anal y ses. Qua ter nary In ter na tional 162–163: 195–204.
Miros³aw-Grabowska, J., Niska M., Sienkiewicz, E., 2009. Evo lu -
tion of the palaeolake at Ruszkówek (cen tral Po land) dur ing
the Eemian Inter gla cial based on iso to pic, cladoceran and di a -
tom data. Jour nal of Paleolimnology 42: 467–481.
Niska, M., 2002. Pres er va tion of Chydoridae (Cladocera) re mains
in the Ho lo cene and Eemian lake sed i ments. Book of Ab stracts
VI
th
ISC Po land, Wierzba.
Niska, M., 2003. Cladocera w osadach interglacja³u eemskiego na
przyk³adzie stanowiska Kuców C. W: Badania paleobota-
niczne jako podstawa rekonstrukcji zmian klimatu w czwarto-
rzêdzie Polski. I Polska Konferencja Paleobotaniki Czwar-
torzêdu, 22-25 maja 2003, Materia³y konferencyjne, Bia³o-
wie¿a: 31
Niska, M., 2008. Interpretacja zmian œrodowiska jeziornego w
interglacjale eemskim na podstawie analizy kopalnych Clado-
cera. Akademia Pomorska w S³upsku, s 128.
Poulsen, E., 1944. Entomostraca from a late-gla cial lac us trine de -
posit at Næstved, Den mark. Meddelelser fra Dansk Geologisk
Forening 10, 405–416.
Ro man, M., 2007. Zasiêg i formy glacimarginalne lobu Wis³y w ob-
szarze Pojezierza Kujawskiego i Kotliny P³ockiej. In: Plejs-
tocen Kujaw i dynamika lobu Wis³y w czasie ostatniego
zlodowacenia (eds. W. Wysota et al.): 23–31. XIV Konfe-
rencja “Stratygrafia Plejstocenu Polski, Ciechocinek”.
Pañstw. Inst. Geol.
Ro man, M., 2010. Rekonstrukcja lobu p³ockiego w czasie ostat-
niego zlodowacenia (Re con struc tion of the P³ock ice lobe dur -
ing the last gla ci ation). Acta Geographica Lodziensia, 96: 1 –
171.
Ro man, M. Balwierz, Z., 2010. Eemian and Vistulian pol len se -
quence at Kub³owo (Cen tral Po land): im pli ca tions for the limit
of the Last Gla cial Max i mum. Geo log i cal Quar terly, 54, 1,
55–68.
Shackle ton, N.J., Opdyke N.D. 1976. Ox y gen-iso tope and paleo-
mag netic stra tig ra phy of Pa cific core V., 28-239. Late Plio -
cene to Lat est Pleis to cene. Geo log i cal So ci ety of Amer ica
Mem oirs 145, 449–464.
Szeroczyñska, K., 1984. Analiza Cladocera w osadach niektórych
jezior tatrzañskich (Re sults of ex am i na tion of Cladocera re -
mains in lac us trine sed i ments of Dol ina Piêciu Stawów Pols-
kich). Pr. i Stud. Geogr., 5: 93–102.
Szeroczyñska, K., 1985. Cladocera jako wskaŸnik ekologiczny w
póŸnoczwartorzêdowych osadach jeziornych Polski Pó³noc-
nej (Cladocera as ecologic in di ca tor in late Qua ter nary lac us -
trine sed i ments in North ern Po land). Acta Palaeontologica
Polonica 30(1–2): 3–69.
Szeroczyñska, K., 1991. Im pact of pre his toric set tle ments on the
Cladocera in the sed i ments of Lakes Suszek, B³êdowo and
Skrzetuszewskie. Hydrobiologia, 225: 105–114.
Szeroczyñska, K., 1998. Palaeolimnological in ves ti ga tions in Po -
land based on Cladocera (Crustacea). Palaeo ge ogra phy, Pala-
eoclimatology, Palaeo ec ol ogy, 140: 335–345.
Szeroczyñska, K., 2002. Hu man im pact on lakes re corded in the re -
mains of Cladocera (Crustacea). Qua ter nary In ter na tional 95–
96: 165–174.
Szeroczyñska, K., Sarmaja-Korjonen, K., 2007. At las of Subfossil
Cladocera from Cen tral and North ern Eu rope. Towarzystwo
Przyjació³ Dolnej Wis³y, Œwiecie: 1–84.
Walanus, A., Nalepka, D., 1999. POLPAL. Pro gram for count ing
pol len grains, di a gram plot ting and nu mer i cal anal y sis. Pro -
ceed ings 5
th
EPPC. Acta. Paleobot. Suppl., 2: 659–661.
White side, M.C., 1970. Dan ish chydorid Cladocera: mod ern ecol -
ogy and core stud ies. Eco log i cal Mono graphs 40: 79–118.
DE VEL OP MENT OF THE KUB£OWO PALAEOLAKE
37
Brought to you by | Uniwersytet Lodzki
Authenticated
Download Date | 6/12/15 3:48 PM
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
01 [ABSTRACT] Development of poplar coppices in Central and Eastern Europe
Development of financial markets in poland 1999
Development of organic agriculture in Poland, Technologie
DEVELOPMENT OF FACTORING MARKET IN TURKEY
FIDE Trainers Surveys 2012 08 31 Uwe Bönsch The recognition, fostering and development of chess tale
Wójcik, Marcin; Suliborski, Andrzej The Origin And Development Of Social Geography In Poland, With
Did Shmu el Ben Nathan and Nathan Hanover Exaggerate Estimates of Jewish Casualties in the Ukraine D
Exergetic efficiency of high temperature lift chemical heat pump (CHP) based on CaO CO2 and CaO H2O
Development of Carbon Nanotubes and Polymer Composites Therefrom
Development of BBM turbine
Development of a highthroughput yeast based assay for detection of metabolically activated genotoxin
Development of vertical bulb turbine
Effect of caffeine on fecundity egg laying capacity development time and longevity in Drosophila
Aristoteles # Guthrie (The Development of Aristotle's Theology 1) BB
Development of wind turbine control algorithms for industrial use
An experimental study on the development of a b type Stirling engine
więcej podobnych podstron