372596150
112
HIKEN Accel Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)
111-5-15. Detector System for Secondary Reactions of Unstable Nuclei
T. Nakamura, S. Shimoura, T. Kubo, N. Inabe, I. Tanihata, and M. Ishihara
The radioactive beam linę RlPSn is expected to open a way of the study of unstable nuclei through secondary nuclear reactions. One of our interests is the observation of a soft giant dipole resonance of light neutron-rich nuclei such as nLi or nBe.2) Another interest is the study of a variety of excited States of exotic nuclei by using inverse reactions of (d,p) or (n,p) as secondary reactions. To study the excited States of unstable nuclei, invariant mass spectroscopy provides a powerful and direct method because the excited States of these nuclei are often particie unbound and the resolution of excitation energies dose not suffer from the energy broadening of radioactive nuclear beams. A detector system including an analyzing magnet is now being designed and will be constructed at the end of the beam linę R1PS to facilitate the experiments by the invariant-mass-reconstruction method. Here we summarize the outline of the system.
Figurę 1 shows a schematic view of the system,
NELT
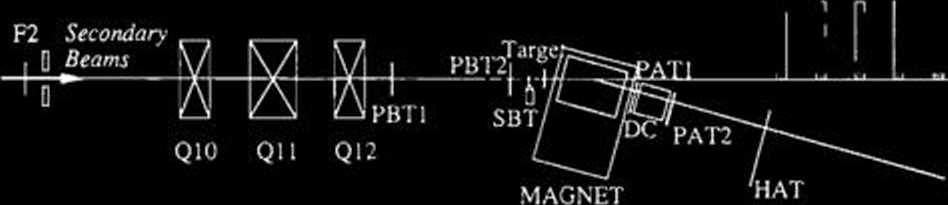
Fig. 1. Detector system for secondary nuclear reaction experiments. PBT1, PBT2, MWPCs before targets; SBT, Scintillator before targets; PAT1, PAT2, MWPCs after targets; DC, a drift chamber; HAT, a hodoscope for charged particles; Neut, a hodoscope for neutrons.
which consists of an analyzing magnet, MWPCs (PBT1, PBT2, PAT1 and PAT2), a plastic scintil-lator (SBT), a drift chamber (DC), a hodoscope for charged particles (HAT), and a hodoscope for neutrons (NEUT).
The analyzing magnet is of a C-type with a gap of 250 mm; its poles are detennined to be 850 mm in length and 700 mm in width. The maximum bending power B L is 1.3 T-m, where B denotes the maximum magnetic field and L the effective length of the magnet. Under the condition, one can bend 100-A-MeV 10Be up to 20 degrees. The angu-lar acceptance for charged particles is determined to be 200 mrad in the horizontal direction and 150 mrad in the vertical direction.
PBT1 and PBT2 are 2-dimensional readout type MWPCs with a 1 mm wire spacing. They are used for determining reaction points by measuring the positions and angles of incident radioactive nuclear beams.
SBT is used to define incident radioactive beams and as a TOF counter.
PAT1 and PAT2 are 1-dimensional (horizontal) readout type MWPCs with a 1.5 mm wire spacing. They are located at the exit of the magnet and the exit of DC for excluding beam events from trigger events.
DC is used as a tracking chamber of the analyzing magnet and has 5 planes for determining the horizontal position and 4 planes for determining the vertical position.
HAT is used as the start counter for I)C and for measuring the time of flights of charged particles.
NEUT is composed of 5 walls of 940x980 mm2 sensitive areas, each of which includes 16 plastic scintillators (BC-408) (see Fig. 2). It observes
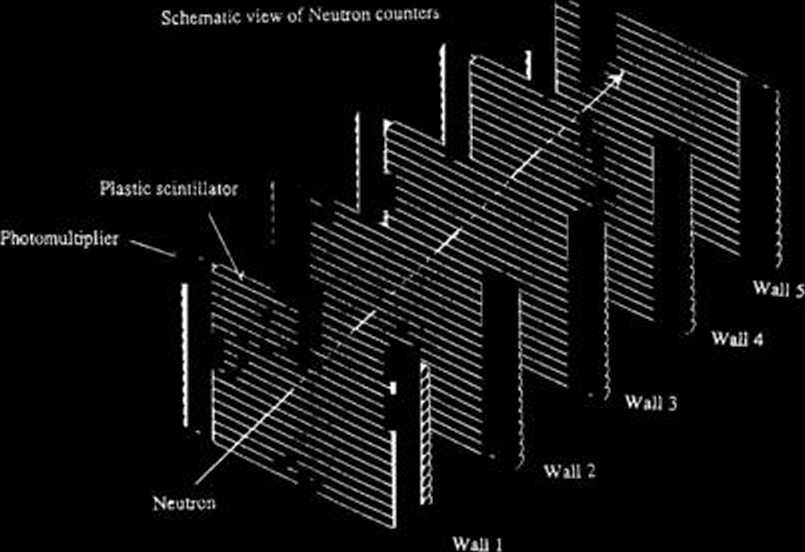
Fig. 2. System for detecting neutrons (NEUT) composed of 5 walls, each of which has 16 plastic scintillators with 32 photomultipliers.
energies of neutrons by a TOF method and observes the tracks as well. The resolution of position detection is expected to be less than 6 cm (FWHM), which corresponds to the angular resolution of 10 mrad.
We estimated the resolution of the excitation energy. As an example, for 80-A-MeV 11 Be with excitation energy of 5.5 MeV decaying into 10Be and a neutron, the resolution of the excitation energy is estimated as less than 700 keV.
References
1) T. Kubo et al.: This Report p. 96.
2) T. Kobayshi, S. Shimoura, I. Tanihata, K. Katori, K. Matsuta, T. Minamisono, K. Sugimoto, W. Mueller, D.L. Olson, T.J.M. Symons, and H. Wieman; Phys. Lett., B232, 51 (1989).
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
48 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-2-15. High Resolution L X-Ray Angular Distribution Measureme
92 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5. Instrumentation1. Design of a Microbeamline for a Compact
94 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-2. Design of a Decay Muon Channel Using an Axially Symmetr
102 RIKEN Accel Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-8. Performance of Isotopic Separation in RIPS T.Nakamura,
103 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-9. Test Experiment of the GARIS/IGISOL K. Morita, T. Nomu
105 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-10. Velocity Distribution of IGISOL lon Beams M. Koizumi,
108 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-12. Status Report of the RIKEN Swinger-Magnetic Analyzer
110 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-14. Test for Dispersive-Mode Beam Transportto the SMART
116 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-19. Responses of Large Position-Sensitive Detectorsto Hea
RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-25. High Speed Serial Data Link for PC-9801 J. Fujita > PC
11 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-1-2. Three a Disintegration of 12C in the Field of208Pb Nucl
12 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-1-3. Coulomb Breakup Reaction of 90 MeV/u 140 T. Takei, T. M
29 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-1-19. Dissociation Cross Sections of nLiK. Soutome, S. Yamaj
RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-1-20. Induced Fission Studied with a Multi-DimensionalLangevin
56 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-2-22. Electron Spectra from Doubly Excited Boroń lonsProduce
63 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-2-28. Development of Nuclear Track Microfilters N. Nakanishi
72 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111*3-8. Dry Separation of Radioactive Nuclides from a Gold Targ
więcej podobnych podstron