6781097326
Estimation of Horizontal Accuracy of the Large-Scale Digital Maps 41
points in respect of which the length of vector of shift of point differed signifi-cantly from the remaining lengths of vectors were discarded (vector lengths of: 0.37 m, 0.54 m and 0.87 m, where AL < 0.10 m in 93% of control points). At next stage, based on the formula (1), the accuracy of position of type B and U topo-graphic details and other topographic points was estimated, and the accuracy of digital technical map data in object A was estimated together in view of the entire set of 478 control points.
Estimation of the Accuracy of the Object B
Topographic data acquired through the recalculation of the results of direct measurements conducted in the course of 30 years (recorded in technical reports) cannot be regarded as highly uniform due to the variety of the applied topographic survey methods and differences in the applied control networks. For this reason, the accuracy of the object B was estimated by comparing the coordinates of lst group topographic details (type B, G and U) which have been entered into the database of the analyzed map with their model co-ordinates determined in the direct control survey. The error of position of control point was computed based on a simplified formula (2)
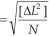
(2)
where:
- error of position of a point in the estimated digital map,
AL=^(Xn —Xj )2 +(Yn -Yj)2 - length of vector of shift of control point,
Xn, Yn - co-ordinates of the control point obtained from the database of the estimated map,
X,, Y, - model co-ordinates of the control point,
N - number of control points.
3.2. Determination of the Accuracy of Maps
Produced by Means of Graphical-and-Digital Processing
In case of object C and object D, topographic data were acquired with the use of the graphical-and-digital processing technology. This technology is an advanced process, and in the case of object D it is even morę complex and susceptible to a larger number of sources of potential errors. The problem of estimating the accuracy of each stages of graphical-and-digital processing has been discussed by
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Estimation of Horizontal Accuracy of the Large-Scale Digital Maps 47 [2] Burmanje
Estimation of Horizontal Accuracy of the Large-Scale Digital Maps 39 dundant observations for the ri
Estimation of Horizontal Accuracy of the Large-Scale Digital Maps 43 lyzed topographic points obtain
45 Estimation of Horizontal Accuracy of the Large-Scale Digital Maps Table 1.
Modeling Large-Scale Computing Systems Practical Approaches in MERPSYS Edited by Paweł Czarnul
14 A. ajczak large-scale morphological mapping of selected stretches of the floodplain, analysis of
00075 (2b96bc67222a673a4490d97d7317e6 74 Hembree & Zimmer We define the actual covariance of a
EN 12354-2(2000). Building acoustics. Estimation of acoustic performance in buildings from the perfo
4. KRUK M., KUREK J, BILSKI P„ RABARIJOELY S„ 2014: Automatic estimation of the&nb
Inne projekty badawcze COST: Advanced Methods for the Estimation of Humań Brain Activity and
968 A. Edorh et al. tumors were associated with advanced clinical and histological markers. The esti
211 Ocena noźliwości kompensacji niepożądanych.#» ESTIMATION OF THE POSSIBILITY OF THE COMPENSATION
Figurę 2: Estimation of constants mt/nij and s The parameters mi/mj and i are related to changes in
15 The socioeconomic conditions of saving behaviours in Polish households Table 3. The results of es
Large Scalę Machinę Learning • Large n. largo p. largo k (numbcr of Inne zależności (largo p.
DSC04806 403 Section 5.2 Exercises (b) The sample result x is an unbiased estimator of the populatio
ms were delivcred at 25-100 Hz in a row-by-row scquencc stimulating motion of a horizontal bar along
więcej podobnych podstron