
Prepared by
National Research Center
Safety and Occupational Health Committee
2
Contents
pag
e
Subject
s.
2
Introduction
1
3
Occupational health hazards due to handling of
laboratory animals
2
3
Factors affecting the occurrence of occupational
health hazards in personnel handling laboratory
animals
3
4
Prophylactic measures to reduce occupational health
hazards due to handling of laboratory animals
4
5
1- General precautions
5
5
2- Application of safety measures in animal house
6
10
- 3-Application of personal hygienic measures
7
1
1
Some zoonotic diseases due to handling of
laboratory animals
8
11
a- General diseases
9
14
b-In case of handling of rats and rabbits
10
17
c- In case of handling of dogs and cats
11
21
d- In case of handling of monkeys
12
22
e- In case of handling poultry
13
27
Conclusion
14

3
Introduction
Laboratory animals are mainly used to carry out scientific researches for
the benefit and welfare of man and animals. Therefore, scientific
institutions and organizations are interested to use modern technology
for constructing animal houses to keep, bred and manage good quality
laboratory animals and to produce purebred standard stains. Moreover,
it is well known that any defect in keeping of these animals may affect
the economy, the progress and the obtained results of an experiment.
The most commonly used laboratory animals in animal houses are rats,
mice, guinea pigs and hamsters, however, monkeys, cats, dogs and
poultry may be sometimes used.
Laboratory animals are mainly used for:
1- Testing and evaluation of newly produced drugs, antibiotics and
chemical compounds before usage for human being.
2- Diagnosis of diseases either infectious or non infectious.
3- Production of vaccines, antisera and antitoxins.
4- As models for surgical training in experiments of organ transfer in
man.
The current guide was designed to throw lights on some aspects of safe
handling with laboratory animals and their welfare in animal houses.

4
Occupational health hazards due to handling of
laboratory animals
Handling of laboratory animals may be associated with some
occupational health hazards, therefore it is of prime importance to
review the most commonly occurred hazards to find the suitable
prophylactic measures.
Hazards due to handling of laboratory animals may be:
1- Physical hazards due to the direct contact with the animal such as
biting, scratching and also, due to the use of sharp utensils.
2- Chemical hazards due to the use of some chemical materials
during experimentation with laboratory animals such as
formaldehyde, phenol, solvents, anesthetics, biological
preparations and other relevant chemicals according to the nature
of the experiment.
3- Zoonotic diseases, which may transfer from animal to man during
non careful handling.
Factors affecting the occurrence of occupational health
hazards in personnel handling laboratory animals
There are some factors, which influence the occurrence of occupational
hazards during handling of laboratory animals such as:

5
1- Animal species:
The most important occupational health hazard that can occur due to
handling of rats and rabbits is allergy, with great individual variations
among personnel deal with laboratory animals, ranging from 10 – 44 %,
while , in persons deal with dogs and cats, these hazards are represented
by biting, scratching and allergy.
2- Duration of the experiment:
The incidence of occurring of occupational health hazards increase as
the duration of the experiment becomes longer as compared with the
short duration experiment.
3- The nature of the experiment:
The incidence of occurring of occupational health hazards is larger in
experiments, whereas, infectious agents, radioactive isotopes and
poisonous materials are used than in experiments deal with nutritional
treatments for example.
Prophylactic measures to reduce occupational
health hazards due to handling of laboratory
animals
Responsible persons for application of prophylactic measures to
reduce occupational health hazards:

6
Who is responsible to apply prophylactic measures to reduce
occupational health hazards originate from handing of laboratory
animals?
It is:
- The supervisor of the animal house
- The researcher
- Animal house staff
- Workers
- Visitors
In fact this is the responsibility of all of the above mentioned persons
and for avoid these hazards the following aspects must be strictly
followed:
1- General precautions:
It is easy to avoid occupational health hazards due to handling of
laboratory animals in animal houses through:
1- Determination of the hazard sources
2- Availability of some protective and safety utensils
3- Enforcement of safety and occupational health laws and
instructions in this respect
4- Continuous training of personnel
5- Application of personal hygienic health measures
2- Application of safety measures in animal house
a- General measures:
• Building used for animal housing must be located in an isolated place
and far away from other buildings.

7
• Animal house should be provided with a good ventilation system to
avoid spreading of unfavorable odor.
Fig. (1): Animal house in an isolated place and far away from
other Buildings
• Inside temperature should be automatically controlled to be ranged
between 18 – 22 C° and relative humidity to be ranged between 45 –
55% and air should be changed 10 – 15 times in an hour.
• A good system of registration, including complete information about
all running experiments should be available.
• Instruction labels must be posted in clear sites and on doors of rooms.
• Working areas should be kept clean continuously.

8
• Entrance of visitors, especially children must be regulated and
recorded in special record and must by associated with a staff
member and wear protective clothes.
• Floors and walls must be washed continuously and disinfected,
especially between experiments.
Fig. (2): Area used for breeding rats should be continuously
clean
• Cages and feeding and drinking utensils must be in a good condition,
have no defects and cleaned twice weekly at least and between
experiments using hot water and soap and light disinfectant. Excess
number of cages should be available to transfer animals during
cleaning processes.
• Eating, drinking or smoking inside animal rooms are forbidden.

9
• Avoid crowdness inside the room or cages.
• Ectoparasites like cockroaches, flays, mosquitoes and flees must be
periodically combated, especially in breeding rooms, bedding and
cracks should be sealed and doors and windows must be provided
with additionally silk covers.
• Animal should be properly restrained during dealing with it.
• Injuries must be recorded in special record.
• Workers should be informed about the nature of the experiment and
how to properly deal with these animals, cages and bedding by safe
methods.
• Animals used for carrying out dangerous experiments such as
infecting agents, radioactive isotopes or toxins must be kept in
separate rooms and labeled by different obvious color.
• Dead and condemned animals at the end of experiments as well as
bedding of animals used in dangerous experiments and all biological
wastes should be collected in special plastic bags labeled by the name
of the animal house and kept in deep freezers tell disposal and
incineration.
• All used sharp utensils such as razors, scalpels and glasswares must
be collected in special tight plastic containers before disposal.
• In case of dealing with rats and rabbits, attention should be paid that
these animals must obtain from known trusted sources and free from
diseases of man and animals.
• In case of using dogs or cats, these animals should be obtained from
trusted good reputation source and specialized in breeding of research

10
animals. The animals must be in good health and it is prefer to be
associated with health certificate indicating its freedom from diseases.
Dogs must be rabies free and cats must be toxoplasma free.
Fig (3): A container used for collecting sharp utensils.
b- Animal welfare:
• Laboratory animals should be kept in comfortable clean places and
provided with good quality feed and clean water to ensure good
health conditions.
• Cages must be in a good condition, easy to clean and permits no
contaminations of feed and drinking utensils to avoid spreading of
diseases.
• Bedding must be clean and not contaminated with excretory
products of animals.
• In case of large laboratory animals such as dogs and monkeys, it is
necessary to permit a suitable time for daily exercise.

11
• On using birds as laboratory animals, the specific vaccination
program for each species must be applied.
3- Application of personal hygienic measures
• Every researcher intends to deal with laboratory animals, should have
a training course for safety management of this species.
• Every person deal with laboratory animals must wear a special
protecting clothes during the existence in animal house, these clothes
should not be wear in other places or taken to clean at home.
• Protective masks, gloves and boats with long neck must be used in
accordance with the nature of the experiment.
• Hands should be continuously washed with water and soap and light
disinfectant and dry by air dryer or disposable towel.
• In case of accidentally contamination with blood, urine, feces or hairs
of laboratory animals on hand, face, eyes or mouth of a person, such
contaminant should be rapidly remove and wash the contaminated
part by water and soap.
• Staff members of laboratory animals should be subjected to periodical
medical examination every 6 months and taking blood, urine and tool
samples for analysis and diseased person must be treated before
contact animals again.
• Persons deal with animals experimentally infected with contagious
infectious diseases such as rabies, tuberculosis and tetanus, pox
should be vaccinated by the specific vaccine.

12
Fig. (4): Protective clothes and utensils worn in animal house
Some zoonotic diseases due to handling of
laboratory animals
a- General diseases:
The most important occupational health hazards that may be occurred
for persons deal with laboratory animals includes:
1- Allergy:
Some symptoms of allergy may be appear due to handling of
laboratory animals in animal houses such as increased nasal and eye
discharges - sneezing, especially in persons who deal with these
13
animals for the first time and these symptoms increased by time of
exposure and even asthma may by occurred.
Prophylaxis :
This disorder can be overcome by :
- Use of masks- gloves - protective clothes.
- Work in well ventilated area.
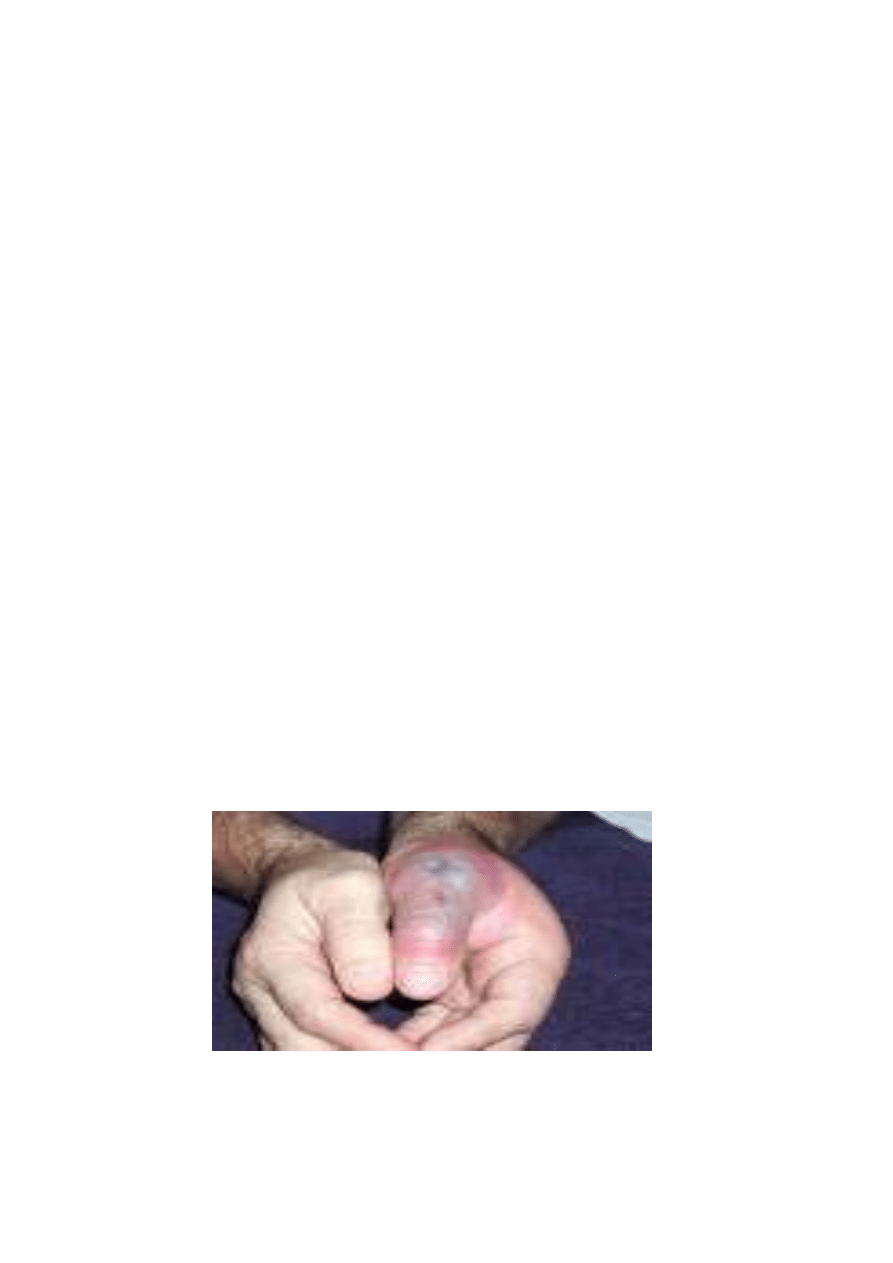
2-Bite and Scratch:
Bites and scratches cause pain, discomfort, wounds, infection and
transfer of some dangerous microorganisms such as pasturella,
Clostridium teteni, staphylococcus, streptococcus, especially in
persons deals with rats, cats and dogs.
Prophylaxis:
- Use of gloves – protective clothes.
- Wounds and scratches must be immediately washed by water and
soap and disinfected by tincture iodine
Fig (5): A rat bite
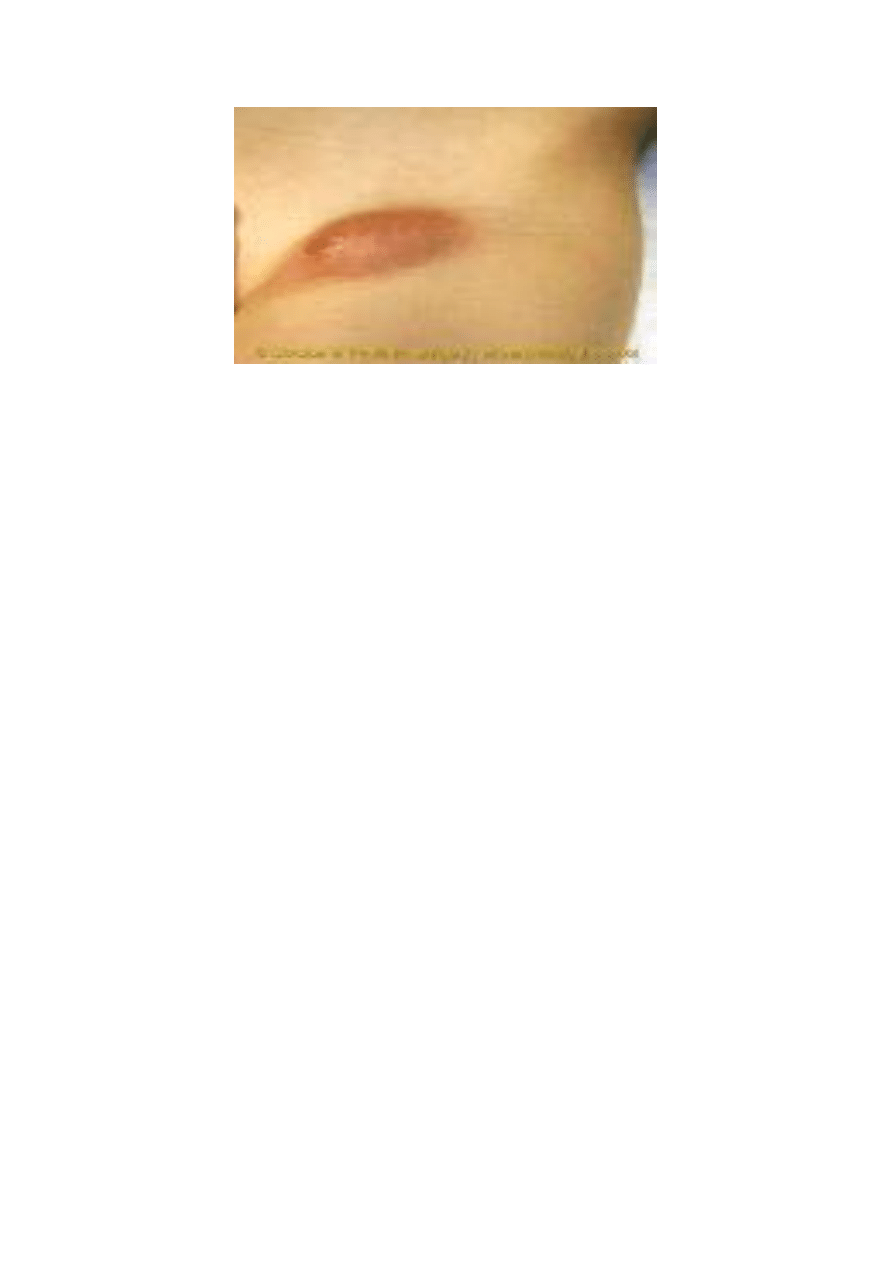
14
Fig,(8): A cat scratch
3-Gastrointestinal syndrome:
Laboratory animals are carriers for many microorganism such as
salmonella, shigella, campylobacter which cause vomiting, diarrhea
and abdominal pain for dealing person.
Prophylaxis:
- Protective clothing
- Fellow proper personal hygienic measures
4- Dermatomycosis( Ring worm):
Some laboratory animals may carry germs of some skin diseases
such as ring worm and transfer it to contact person either by direct
method or by indirect method through contaminated bedding and
utensils.
Prophylaxis:
- Protective clothes.
- Fellow proper personal hygienic measures.

15
5- Leptospirosis:
Infection by this disease occurred due to contact with urine of
infected rats or via inhalation of dust during cleaning of cages used
for breeding of infected animals, also the organism can penetrate
through wounded skin and mucous membranes leading to symptom
like ordinary flu with back pain and the infection may be extends to
the nervous and urinary systems.
Prophylaxis:
- Use animal from trusted sources.
- Use vaccines.
- Do not make any contact with urine of animals.
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures
b- In case of handling of rats and rabbits:
The most important diseases that can transmit due to contact with
rats and rabbits include:
1- Hantavirus:
Rats are carrier for this disease without appearance of any clinical
signs and the virus is shed in saliva, urine and feces, get mixed
with bedding and dust. Contact persons can infected by inhalation
of virus contaminated dust leading to pneumonia and collection of
serous fluid in lungs and difficult breathing.
Prophylaxis:
- Use animals from known trusted sources.

16
- Use of protective masks.
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures.
2- Rat bite fever( Streptobacillus moniliformis):
Bacterial disease transmitted by rat bite or by skin cracks after
contamination with the microorganism which occurred in the pharynx
of 50% of rats. The disease appears in the form of fever, vomiting,
headache, skin eruptions on joint and muscles together with arthritis.
Prophylaxis:
- Use animals from known trusted sources
- Use of protective clothes
- Use of masks
3-Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis :
Viral disease, carried by mice, rats and guinea pigs in dormant form. It
infect contact person leading to either mild or severe signs in the
form of fever, headache and muscular fatigue.
Prophylaxis:
- Use animals from known trusted sources
- Use of protective gloves
- Proper washing of hand following contact with rats
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures
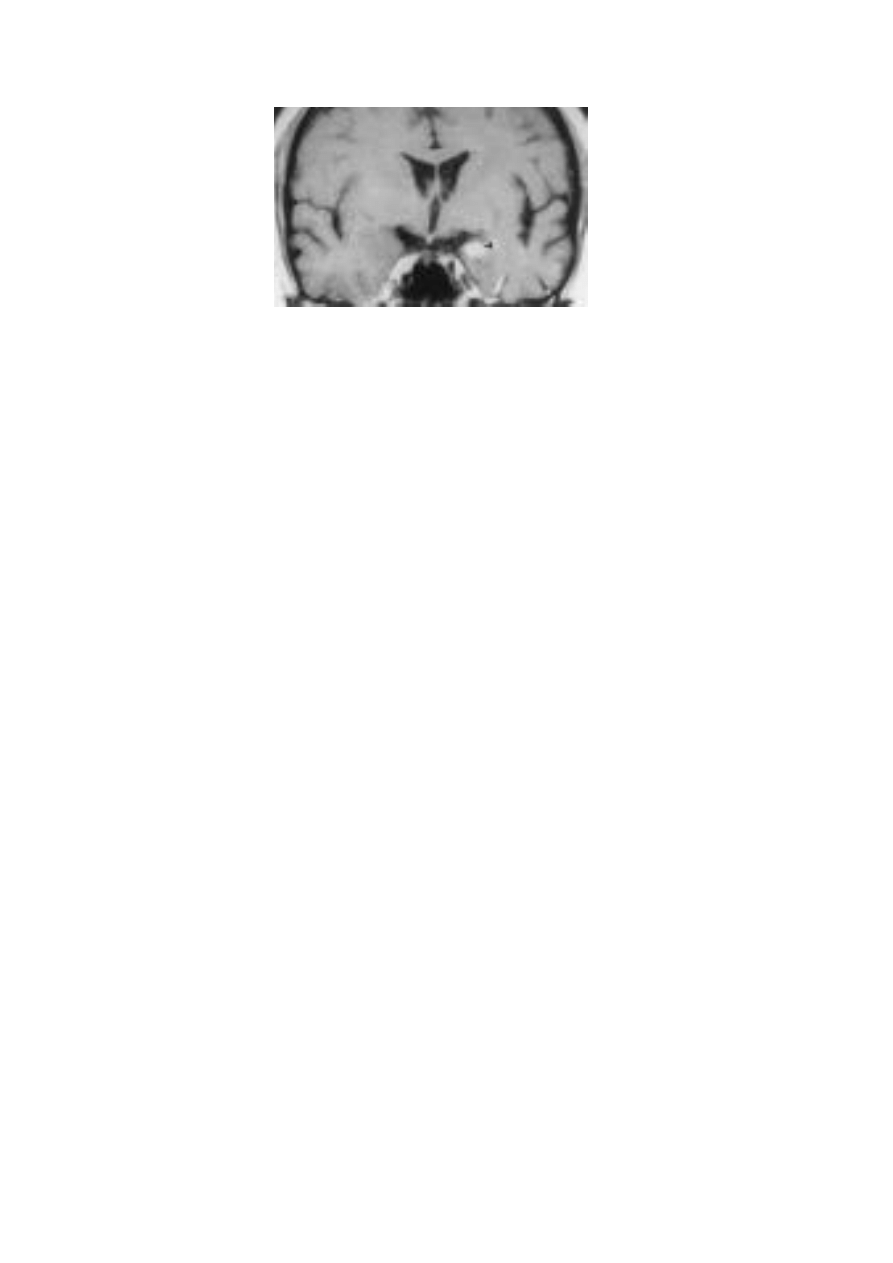
17
Fig. ( 6): C.S. on brain in case of Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis
4-Leptospirosis:
5-Salmonellosis:
The causative bacteria is carried by rats and excreted in feces without
appearance of any clinical signs. The organisms propagate in intestine
after contamination of food and water cause food poisoning in form
of diarrhea, vomiting, headache and muscular fatigue.
Prophylaxis:
- Proper washing of hands after contact with rats.
- Use of protective gloves.
- Protective clothes.
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures.
6- Campylobacteriosis:
Bacterial disease, the organism discharged in the excreta of
infected animals, causing diarrhea, especially during summer
season.

18
Prophylaxis:
- Proper washing of hands after contact with rats
- Use of protective gloves
- Protective clothes
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures
7- Dermatomycosis( Ring worm):
c- In case of handling of dogs and cats
ِAmong the most important diseases that can transmitted to
contact person:
1-Rabies:
Viral disease, transmitted through contact with saliva of infected
dogs or after scratching. Symptoms appear after an incubation period
of hours to days to years from infection. Clinical signs appear in the
form of fatigue, headache, irritability, worry and fear from water, air
or light. The organism may reach to the nervous system and end by a
comma and complete paralysis.
Prophylaxis:
- Consider any non vaccinated animal to be positive for rabies
and deal with it with great care.
- Dogs exposed person must be vaccinated.
- Notification of authority after any dog bits.

19
- Proper washing of the site of bit with water and soap and
disinfected with tincture iodine
- Protective clothes
- Proper washing of hands after contact with dogs.
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures
Fig.(7): Rabies infected Dog.
2-Toxoplasmosis:
Infection occurred due to contamination of food and water with this
protozoan parasite shaded in feces of infected cats. The disease is more
dangerous in immune depressed persons such as pregnant women and
elder persons. Clinical signs appear in form of general fatigue in all the
body and recurrent habitual abortion in ladies.
Prophylaxis:
- Daily changing of cats bedding.
- Use of protective gloves.
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures.

20
3- Pasteurella(Capnocytophaga):
These bacteria are present in the mouth cavity of dogs and cats and
contaminated wounds after biting leading to cellulitis at the biting site,
pain and fever
Prophylaxis:
- Use of animals from trusted sources.
- Proper washing of hands after contact with dogs.
- Use of protective gloves.
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures.
4- Cat scratch fever(Bartonella henselae):
Bacterial disease with a history of dealing with cats, biting, scratch
leading to fever and lymphadenitis.
Prophylaxis:
- Cutting of cats claws.
- Use of protective gloves.
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures.
5-Brucellosis:
The causative bacteria are found in the genital organs of male and
female animals. It induced abortion and may infect contact persons,
especially those interested in reproductive aspect and contact workers
who dispose abortion products. It induced severe pathological changes
in the liver and joints.

21
Prophylaxis:
- Proper disposal and avoid contact with abortion products,
discharges and dead fetuses.
- Periodical testing of dogs and positive animals must be culled
and not used for breeding purposes.
- Positive cases must be condemned and valuable animals must be
surgically spayed .
- Fellow the proper personal hygienic measures.
6 - Ring Worm
7 - Leptospirosis
8 - Salmonellosis
9 - Campylobacteriosis
10-Echinococcosis:
Parasitic disease, induced by contamination of food, water and air by
eggs of tape warms present in dog feces. When get enter into human
body, it develops into large water filled cysts and cause symptoms differ
according to its situation in the host body.
Prophylaxis:
- Proper washing of hands after contact with dogs.
- Use of protective clothes.
- Fellow the proper personal hygiene measures.

22
d- In case of handling of monkeys:
1- Cercopithecine herpesvirus 1-(Monkey B- virus):
This disease is characterized by the presence of vesicles and ulcers on
mouth and genital organs of infected monkeys. It may infect contact
persons by contamination or biting leading to similar lesions in addition
to fever, headache and muscular fatigue.
Prophylaxis:
- Regular exercise.
- Protecting clothes.
- Apply proper personal hygienic measure.
2- Tuberculosis:
Chronic bacterial disease, infection occurred after feeding or drinking
contaminated materials or after inhalation of contaminated air by these
germs. The disease is characterized by formation of granuloms in
different body organs, especially lungs leading to cough, severe weight
losses and diarrhea.
Prophylaxis:
- Use of animals from known trusted sources.
- Regular periodical examination of animals using x rays and
immunological tests.
- Application of quarantine measure after experimental induction.
- Apply proper personal hygienic measure.
3-Hepatitis A&E:

23
Infection occurred due to contamination of food and water with feces of
infected animals in case of type A , while infection occurred by contact
with blood of infected animals in B type.
Prophylaxis:
- Use animal from known trusted source.
- Proper washing of hands after any contact with animals.
4- Shigellosis:
Animals usually carry Shigella that cause bloody diarrhea in man,
vomiting and gastritis.
Prophylaxis:
- Proper washing of hands after any contact with animals.
-Apply proper personal hygienic measure.
5- Salmonellosis
6- Campylobacteriosis
7- Ring Worm
e- In case of handling of poultry
1- Chlamydiosis:
Bacterial disease affect all poultry species and birds can carry the
disease without showing clinical symptoms. Infect man, especially those
who are dealing with pigeon, turkeys and colored birds. The organism
secreted in the excreta of infected birds, contaminated man food and

24
water leading to flu like clinical symptoms, diarrhea, inflammation of
eyes and throat.
Prophylaxis:
- Use birds from trusted sources.
- Use protecting clothes.
- Apply proper personal hygienic measure.
Fig. (9): Chlamydia infected cock
2- Salmonellosis
3-Allergic alveolitis:
Some persons have allergy for birds feathers and contact dust, especially
that of pigeon and showed coughing, difficult breathing and fever when
they deal with these birds for a long period.
Prophylaxis:
- Daily cleaning of cages.
25
- Avoid birds overcrowding.
- Keep ventilation in a proper manner usually
- Apply proper personal hygienic measure
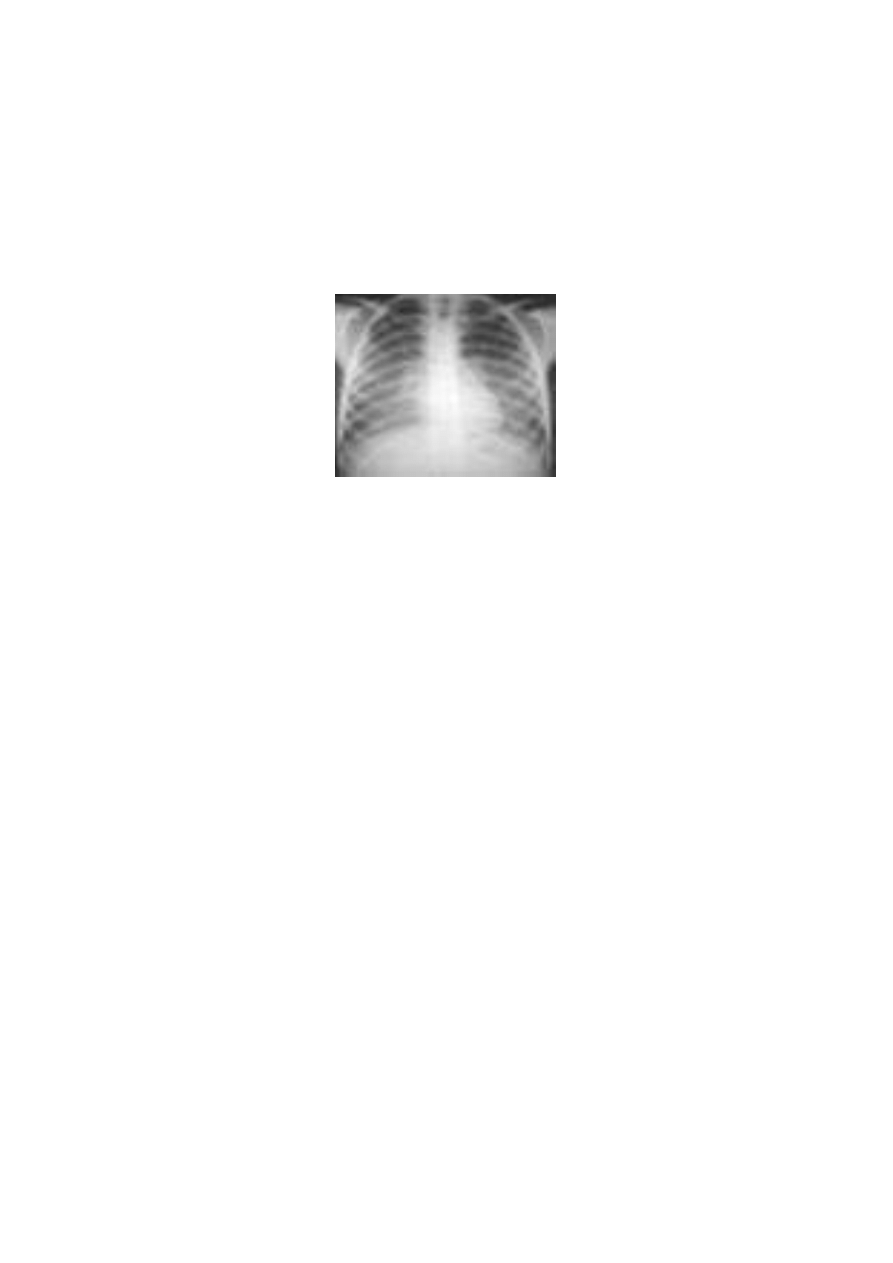
Fig( 10): X ray plate shows water distention in chest due to Allergic
alveolitis
4- Campylobacteriosis:
:
5- New castles disease
Viral disease affects all species of poultry. The virus shad with the
excreta of the infected bird and cause reparatory symptoms,
characteristic white diarrhea, inflammation of the eyes and nervous
symptoms in head and neck region. Man gets infected through inhalation
of contaminated dust and develop flu signs with characteristic red eyes.
Prophylaxis:
- Regular periodical vaccination of birds.
- Continuous cleaning of cages.
- Apply proper personal hygienic measure.

26
Fig (11): New castle disease in fowl
6- Avian tuberculosis
Fig (12): A duck suffered from tuberculosis

27
7- Giardia:
Protozoon parasite live in intestine of infected birds. Infection occurred
due to use of contaminated food and water, leading to abdominal pain
and diarrhea.
Prophylaxis:
- Use of birds from trusted sources.
- Avoid overcrowdings of poultry.
- Isolate newly purchased birds for a period of time to be sure that
they are healthy.
- Apply proper personal hygienic measure.
8- Avian influenza:
Group of infectious viral diseases affecting all species of poultry. Wild
and water poultries are the original factor of disease transfer due these
birds are carriers for the disease without the appearance of any clinical
symptoms. The disease mostly spreads by reparatory route after
inhalation of waste of infected birds by direct and indirect means. The
infected person has flu like symptoms, fever and difficult breathing.
Prophylaxis:
- Avoid overcrowdings.
- Work usually in good ventilated area.
- Frequently proper washing of hand.
- Use protective masks.
- Use protected clothes.
- Regular vaccination.
28
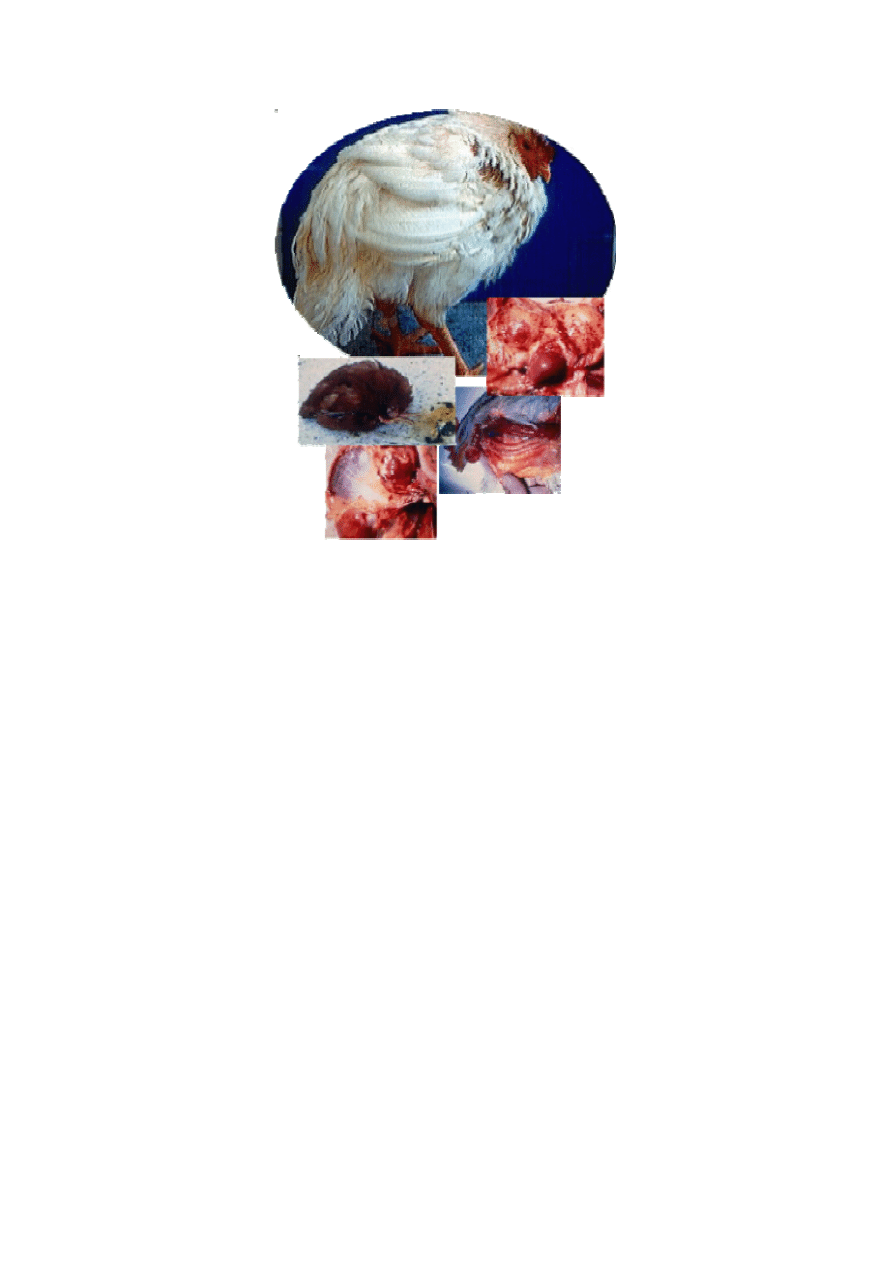
Fig (13): ِAvian influenza
Conclusion
For safe handling with laboratory animals and to avoid exposure to some
occupational heath hazards:
- Everybody in animal house is responsible.
- Use protective clothes and utensils.
- Fellow safety instructions.
- Apply proper personal hygienic measure.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
APA practice guideline for the treatment of patients with Borderline Personality Disorder
Guidelines for the Management of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
GUIDELINES FOR THE APPROVAL OF FIXED WATER BASED LOCAL APPLICATION
ESTRO BOOKLET 5 Practical guidelines for the impletation of in vivo dosimetry with diodes in extern
guidelines for the content of rig move procedures sept 2008
Guidelines for Persons and Organizations Providing Support for Victims of Forced Migration
Guidelines for Persons and Organizations Providing Support for Victims of Forced Migration
AMENDMENTS TO THE REVISED GUIDELINES FOR APPROVAL OF SPRINKLER SYSTEM
Guidelines For Decontamination of Equipment for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Guidelines for coordinated human and animal brucellosis surveillance
EASE Guidelines for Authors and Translators of Scientific Articles to be Published in English june20
Development of mental health first aid guidelines for deliberate NSSI
The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty
GUIDELINES FOR WRITING AND PUBLISHING SCIENTIFIC PAPERS
Party Games for Large Groups of Teenagers
więcej podobnych podstron