for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
Visit
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
Study guide by
Cisco PIX Firewall Fundamentals
Test Information
Exam
PIX Firewall Fundamentals
Certification
If all prerequisites are met: Security Specialist
Abstract
“This Study Guide will begin to guide you in preparing for the Cisco PIX Firewall
Fundamentals exam. This exam is part of a series of exams you will need to take to achieve
the “Security Specialist” designation from Cisco.
What to Know
What you need to know to be successful in obtaining the Security Designation:
Go over the necessary steps to obtaining the certification and what your steps will be
through the entire process. This will make your studying easier
You need a basic understanding of TCP/IP and a Valid CCNA
Then to obtain the “Security Specialist” Designation take the following exams:
640-442 MCNS
Managing Cisco Network Security (MCNS)
9E0-571 CSPFA
Cisco Secure PIX Firewall Advanced (CSPFA)
(See also prerequisite course Cisco Secure PIX Firewall Fundamentals CSPFF)
9E0-558 CSIDS
Cisco Secure Intrusion Detection System (CSIDS)
9E0-570 CSVPN
Cisco Secure VPN (CSVPN)
Note: Please take note where the PIX Fundamentals Sits in the line-up
for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
Study Tips
§ DO not take this test lightly. The test covers a lot of information mainly on HOW TO
configure something. Use this study guide to get the main idea of the topic and then
use the online resources to go through all the configs to familiarize your self with
HOW TO set these configs up
§ You need to be a CCNA prior to starting this track. The track is for the Security
Specialist designation. The designation is passing 4 out of 5 different exams. This
guide is half of the PIX firewall track. You can take the first exam but the second
exam for the Advanced track counts for credit. All the information from the
Fundamentals track is a prerequisite for the advanced track. Use them both to pass
the last exam.
§ You no longer have to be a CCNP for this (The CCNP+Security track will be
discontinued this year) You MUST have your CCNA.
§ Make sure you use the links provided to aid your studies. Like most of Cisco’s tests, a
lot of your information to study from is free and available on their web site. Use this
as a supplement to aid your studies.
§
Do not solely rely on this or any study guide alone.
Links and Resources
Everything you need to know about this topic can be found online.
This is one of the few exams and courses that have most of the information at your
disposal online
Make sure you use all the online resources you can for this exam
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
Configuring for MS-Exchange Use
o
o
Go through the above information and it should be all you need. Hands on
experience will make the above information stick harder and you will understand it
better

for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
PIX Fundamentals
PIX Firewall
•
The PIX Firewall, when properly configured, helps prevent unauthorized
connections between two or more networks
•
The PIX Firewall can protect one or more networks from an outer,
unprotected network
•
The PIX Firewall optionally supports multiple outside or perimeter networks
also known as demilitarized zones or DMZs
•
Connections between the networks can all be controlled by the PIX Firewall
•
To effectively use a firewall in your organization, you need a security policy to
ensure that all traffic from the protected networks passes only through the
firewall to the unprotected network - You can then control who may access
the networks with which services, and how to implement your security policy
using the features PIX Firewall provides
•
Within this architecture, the PIX Firewall forms the boundary between the
protected networks and the unprotected networks
•
All traffic between the protected and unprotected networks must flow through
the firewall to maintain security
•
The unprotected network is typically accessible to the Internet
•
PIX Firewall lets you locate servers such as those for web access, SNMP,
electronic mail (SMTP) in the protected network and control who on the
outside can access these servers
•
The PIX Firewall also lets you implement your security policies for connection
to and from the inside network
•
Typically, the inside network is an organization's own internal network, or
intranet, and the outside network is the Internet, but the PIX Firewall can also
be used within an intranet to isolate or protect one group of internal
computing systems and users from another
for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
Visit
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
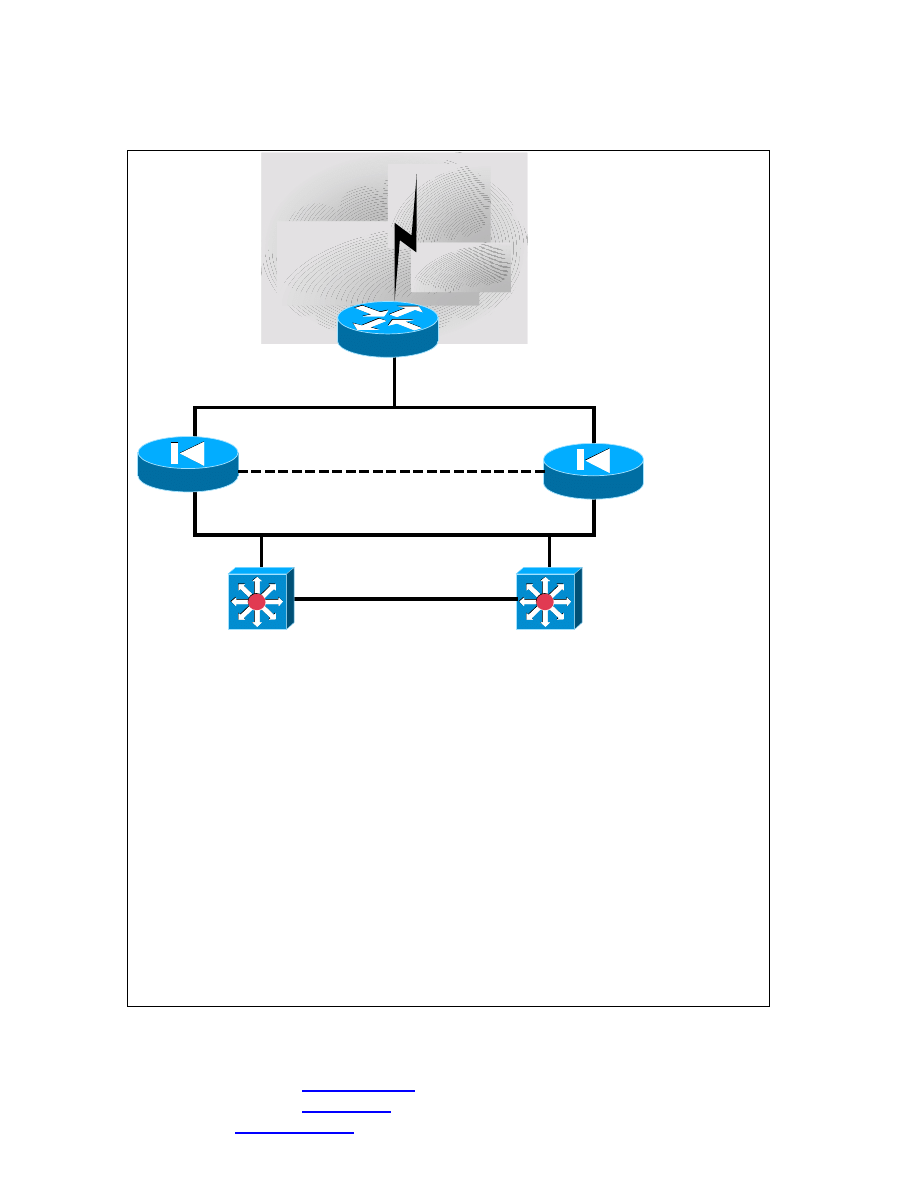
Basic Firewall setup
INTERNET
1
2
3
In this diagram we can see the 3 major portions of a DMZ setup:
1. The Outside Filtering router with the Firewall feature set on it. This is generally
used to connect your company to the Internet and has major filtering going on at
this portion.
2. As you come into the DMZ, we see the first segment and that’s where you DNS,
FTP and web servers sit. This is an Isolated segment. After this segment, we now
go through a set of PIX firewalls setup in a Failover situation with a Failover cable
in between them.
3. This is your internal network and anything can be here. You could put another
Firewall or nothing at all. This is where you protected network lies and all your
clients should be located here.
Note: This is very flexible and every setup will be different based on what you
need to implement. This is just a common setup.

Visit
for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
How Data Moves Through the Firewall
•
When an outbound packet arrives at a PIX Firewall higher security level
interface (security levels are set with the nameif command), the PIX Firewall
checks to see if the packet is valid based on the ASA or Adaptive Security
Algorithm, and then whether or not previous packets have come from that
host
•
If not, then the packet is for a new connection, and PIX Firewall creates a
translation slot in its state table for the connection
•
The information that PIX Firewall stores in the translation slot includes the
inside IP address and a globally unique IP address assigned by Network
Address Translation (NAT), Port Address Translation (PAT), or Identity (which
uses the inside address as the outside address)
•
The PIX Firewall then changes the packet's source IP address to the globally
unique address, modifies the checksum and other fields as required, and
forwards the packet to the lower security level interface
•
When an inbound packet arrives at an unprotected interface, it must first pass
the PIX Firewall Adaptive Security criteria
•
If the packet passes the security tests, the PIX Firewall removes the
destination IP address, and the internal IP address is inserted in its place. The
packet is forwarded to the protected interface
•
The PIX Firewall permits all outbound connections from the protected
networks to the unprotected networks, and rejects any connections inbound
from the unprotected network
PIX Firewall Connections
Maximum number of connections you can have on your PIX Firewall
Installed RAM
Maximum Number of Connections
16 MB
32,768 connections
32 MB
65,536 connections
128 MB
Approx 260,000 connections with the optional memory upgrade
Access Lists
•
Can control which inside systems can establish connections to the outside
network
•
The default security policy can be modified to be consistent with the site
security policy by limiting outgoing connections based on inside source
address, outside destination address, or protocol
•
Configure access lists carefully if your security policy limits outgoing
connections

for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
ActiveX Blocking
•
ActiveX controls, formerly known as OLE or OCX controls, are components
you can insert in a web page or other application
•
The PIX Firewall ActiveX blocking feature blocks HTML <object> </object>
commands and comments them out of the HTML web page
Adaptive Security Algorithm (ASA)
•
Implements stateful connection control through the firewall
•
Allows one way (inside to outside) connections without an explicit
configuration for each internal system and application
•
Always in operation monitoring, return packets to ensure they are valid.
•
Actively randomizes TCP sequence numbers to minimize the risk of TCP
sequence number attack
Conduits
•
Conduits allows connections from the outside network to the inside network
•
For some applications or business requirements, it is desirable to establish
connections to the inside or perimeter networks
•
Each conduit is a potential hole through the PIX Firewall and their use should
be limited as your security policy and business needs may require
•
Make conduits as specific as possible
•
Be aware that as the PIX grows up – the conduit command will be replaced by
IOS features like access lists. This is what new forms of PIX images are
offering
Failover
•
PIX Firewall failover allows you to configure two PIX Firewall units in a fully
redundant topology to provide fault tolerance
•
Both PIX Firewall units must be configured identically; failover does not
provide stateful redundancy. You need to set up specific cabling to provide
this failover as well
Java Filtering
•
Lets an administrator prevent Java applets from being downloaded by an
inside system (This is kind of the same as ActiveX Blocking except ActiveX is
pretty specific to Microsoft technologies)
•
Java applets are executable programs and can provide a vehicle through
which an inside system can be invaded. These attacks are VERY common and
any firewall implementation should provide applet blocking

for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
Visit
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
Mail Guard
•
Provides a safe conduit for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) connections
from the outside to an inside electronic mail server
•
Allows a single mail server to be deployed within the internal network without
it being exposed to known security problems
•
Avoids the need for an external mail relay system (this is very cool!)
•
Enforces a safe minimal set of SMTP commands to avoid an SMTP server
system being compromised
•
Also logs all SMTP connections which is also a big plus
Multiple Interfaces
•
Additional network interfaces can be added to the PIX Firewall and this is
common with any firewall setup. You want multiple Ethernet interfaces so you
can separate many different segments
•
PIX Firewall supports up to six interfaces, four of which are on the optional 4-
port Ethernet card
•
Can provide a mixed Token Ring and Ethernet environment
Conditions for interface use
o
Each interface has a unique security level that you specify with the
nameif command in your configuration:
§ The inside is always the highest at level 100 and the outside is
always 0
§ The perimeter interfaces can have a unique number between 1
and 99
o
When users on a higher security level interface need to access a host
on a lower security interface, you use the nat command:
§ If you are using Network Address Translation to specify which
lower security level interface can accept translated addresses,
use the global command
o
When users on a lower security level interface need to access a server
on a higher security interface, you use the static command:
§ To specify which services users can access, use the conduit
command in conjunction with the static command
o
It is easier to add nat and global commands to the configuration than
static and conduit commands:
§ The static command can specify one host or a network access to
a specific host or network

Visit
for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
o
Interfaces with the same security level:
§ If you set the perimeter interfaces to the same security level, the
two interfaces are completely isolated from each other, but each
could access the inside and outside interfaces
§ Locate servers on the lowest security level perimeter interface,
because if compromised, the attacker could only easily attack an
interface with a lower security level, the outside
§ The only exception to putting servers on the lowest perimeter
interface is the TFTP server where you download configurations
from the TFTP server must be on the inside interface
o
Telnet:
§ Access to the console via Telnet is available on the inside and
third interfaces. The third interface is the network connecting to
the third usable slot in the PIX Firewall
§ You can view the third interface with the show nameif
command
§ The third entry from the top of the listing is the third interface
•
With these conditions and the needs of your security policy, you can decide
which network to connect to each interface
Network Address Translation (NAT)
•
For inside systems, translates the source IP address of outgoing packets per
RFC 1631
•
Allows inside systems to be assigned private addresses or to retain existing
invalid addresses
•
Hides the real network identity of internal systems from the outside network
Port Address Translation (PAT)
•
By using port re-mapping, a single valid IP address can support source
IP address translation for up to 64,000 active xlate objects
•
PAT minimizes the number of globally valid IP addresses required to support
private or invalid internal addressing schemes
•
Will not work with multimedia applications that have an inbound data stream
different from the outgoing control path
•
Hides the real network identity of internal systems from the outside network

for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
Syslog Server
•
Provides syslog server for use on Windows NT system that accepts TCP and
UDP syslog messages from PIX Firewall
•
Syslog server can provide time stamped syslog messages, accept messages
on alternate ports, and be configured to stop PIX Firewall traffic if messages
cannot be received
•
Can stop PIX Firewall connections if Windows NT syslog server log disk fills or
server goes down
URL Filtering
•
The PIX Firewall URL filtering is provided in partnership with the NetPartners
WebSENSE product. PIX Firewall checks outgoing URL requests with the policy
defined on the WebSENSE server, which runs either on Windows NT or UNIX
•
Based on the response from the NetPartners WebSENSE server, which
matches a request against a list of 17 Web site characteristics deemed
inappropriate for business use, PIX Firewall either permits or denies the
connection
•
Because URL filtering is handled on a separate platform, no additional
performance burden is placed on the PIX Firewall
•
Check
for more information
Security Policy
•
The PIX Firewall separates the details of implementing a security policy from
providing network services such as Web, FTP, Telnet, and SMTP
•
A security policy provides:
o
Much better scalability and performance
§ The PIX Firewall is dedicated to the security role and does not
incur the substantial overhead required to offer server
connections
o
Greater security
§ Unless configured to do so, the PIX Firewall does not accept
connections from the outside network and is implemented using
a proprietary embedded system, rather than the full operating
system necessary to support server applications
o
Reduced complexity
§
Each device performs a dedicated function

for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
Visit
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
•
Use the Following links to find more information:
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
Making Image Backups
•
You should back up your configuration to both Flash memory and diskette
after making changes to the configuration
•
Use the write memory command to store your configuration in Flash
memory
•
You can enter this command from configuration mode
•
Flash memory is a special type of memory card that stores images without
the need for a battery or power source to maintain the image
•
Use the write floppy command to store the configuration on diskette
•
Each image you store overwrites the last stored image in either Flash memory
or diskette
•
Should the need arise, you can restore your configuration from Flash memory
with the configure memory command, or from diskette with the configure
floppy command
for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
Default configuration commands
nameif
Identifies the interface name and specifies its security level.
If you have more than two interfaces, you need to add a nameif
command to the configuration for each interface
enable
password
Lists the encrypted privileged mode password
passwd
Lists the encrypted password for Telnet access to the PIX Firewall
console
hostname
Sets the PIX Firewall system name to "pixfirewall."
You can change this name or leave it as is
fixup
Specifies service port numbers at which the PIX Firewall listens
names
Lets you rename IP addresses with names from your native language
to add clarity to your configuration
It is best to ignore this command until you have established network
connectivity
logging
Disables Syslog messages from displaying at the console or being
sent to a server
The logging command lists information about each connection that
starts and ends, whether pings through the PIX Firewall are
successful and additional information useful when troubleshooting
network connectivity
Set this command to logging buffered debugging
To view the messages, use show logging
interface
Identifies the speed of the interface or whether the network interface
card can automatically sense its speed and duplex
If you have Token Ring interfaces, you need to add these commands
by hand
For Ethernet interfaces, the default configuration provides interface
commands for every interface
mtu
Sets maximum packet size to 1500 bytes for Ethernet or to the
appropriate size for Token Ring interfaces
ip address
Identifies the IP addresses of the each interface
failover
Sets Failover
The no failover command disables the failover feature
for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
Visit
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
IP Addresses (Public and Private)
Class A The first octet is between 1 and 127 (127 Loopback)
Class B The first octet is between 128 and 191
Class C The first octet is 192 to 223
Use RFC 1918 IP addresses for inside and perimeter addresses:
o
Class A: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
o
Class B: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
o
Class C: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Supported Protocols
o
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
o
Archie
o
Berkeley Standard Distribution (BSD)-rcmds
o
Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)
o
Domain Name System (DNS)
o
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
o
Generic Route Encapsulation (GRE)
o
Gopher
o
Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP)
o
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
o
Internet Protocol (IP)
o
NetBIOS over IP (Microsoft Networking)
o
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
o
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
o
Sitara Networks Protocol (SNP)
o
SQL*Net (Oracle client/server protocol)
o
Sun Remote Procedure Call (RPC) services, including (NFS)
o
Telnet
o
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
o
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
o
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)

for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
Terminology
Conduits
Use of the PIX Firewall conduit command to identify what
services can be accessed from a global address (kind of like a
route statement)
DNAT address
An IP address that has been translated by the alias command
Global address
An IP address that is visible on an unprotected network
Local addresses are translated into global addresses as they
pass through the PIX Firewall to protect the local addresses from
outside detection
Global addresses are created with the global and static
commands
Local address
An IP address on the PIX Firewall's inside network
Protected network One or more networks that you are protecting from intrusion
A protected network is also known as an internal network
On a PIX Firewall with two interfaces, the protected network is
the inside network
Unprotected
network
One or more networks that feed into the PIX Firewall that
connect the protected networks with access to the rest of your
organization and to the Internet
An unprotected network is also known as an external network
On a PIX Firewall with two interfaces, this is the outside network
Translation
When a connection moves through the PIX Firewall from a
protected network, PIX Firewall translates the originating local
IP address to a global address so that the local address is
protected from scrutiny on the outside address
Course Information from Cisco
Course Content
Cisco Secure PIX Firewall Fundamentals (CSPFF) course is a new, two-day,
instructor-led, lab-intensive course, which will be delivered by Cisco Training
Partners. This course provides an introduction to network security, focusing on how
the PIX Firewall functions within network security. This course teaches the
knowledge and skills needed to install, configure, and operate the Cisco Secure PIX
Firewall version 5.0(1)
NOTE: This course will be followed by the Advanced Cisco Secure Firewall
Technologies course (ACSFT) in Q2 CY 2000
Course Objectives
Upon completion of this course, students will be able to do the following:
•
Identify PIX Firewall features, models, and components.
•
Install the PIX Firewall, upgrade software images and perform general
commands.
•
Configure PIX Firewall firewalling capabilities.
•
Configure inbound and outbound access through the PIX Firewall
•
Configure multiple interfaces on the PIX Firewall.

for all your certification needs.
for the best online practice exams.
– most powerful IT certifications search engine.
•
Configure syslog and routine maintenance procedures.
•
Configure PIX Firewall IPSec VPN features in a PIX-to-PIX topology.
•
Test and verify PIX Firewall operations
The CSPFF 1.1 course is an introductory course for LAN or network administrators. It
introduces the Cisco Secure PIX Firewall and teaches the basic features needed to
get the PIX operational on a production network. Security professionals working at
all levels of the enterprise will gain knowledge from this class.
Course Outline
•
Network Security Fundamentals (Lecture)
•
PIX Firewall Security Features and Options (Lecture)
•
Installing the PIX Firewall (Lecture)
•
Upgrading the PIX Firewall Software Image (Lecture/Lab)
•
Configuring Basic PIX Firewall Commands (Lecture/Lab)
•
PIX Translation Overview
•
Configuring Access through the PIX Firewall (Lecture/Lab)
•
Configuring Multiple Interfaces (Lecture/Lab)
•
Configuring Syslog and Performing Maintenance (Lecture/Lab)
•
PIX Firewall Advance Features
•
Configuring Virtual Private Networks (VPN) using the PIX Firewall
Last Tips
All you need to know to pass this exam is to have hands on experience if possible
and to read the online documentation at this URL:
Go through every piece of this documentation!
This is the PIX Firewall documentation on HOW TO set up a PIX firewall from scratch
It goes Systematically through everything. There really are no books or study guides
available for this topic but all you need are on the Cisco Documentation home page
Make sure you go through the step by step and do the hands on if possible
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
clad exam preparation guide
AutoCAD 2013 Certification Exam Preparation Roadmap
Cisco PIX Firewalle cispix
Opis materiału wymienionego w CLAD Exam Preparation Guide
Cisco PIX Firewalle cispix
Cisco PIX Firewalle cispix
Cisco PIX Firewalle cispix
Cisco PIX Firewalle
Cisco PIX Firewalle 2
clad exam preparation guide
Cisco PIX Firewalle cispix
Cisco PIX Firewalle cispix
Cisco PIX Firewalle
Cisco PIX Firewalle cispix
02 cisco semestr 3 v31 module 2 exam
01 cisco semestr 2 v31 module 1 exam
08 cisco semestr 2 v31 module 8 exam
05 cisco semestr 2 v31 module 5 exam
więcej podobnych podstron