UI Department of Accounting Writing Tutorials
Reference Materials Sheet #1
Parts of Speech: A Brief Primer
This page is designed to help you remember the definitions and uses of various parts of
speech. If you get stuck at any point in the writing tutorials, you can return to this page
to be reminded of the basics.
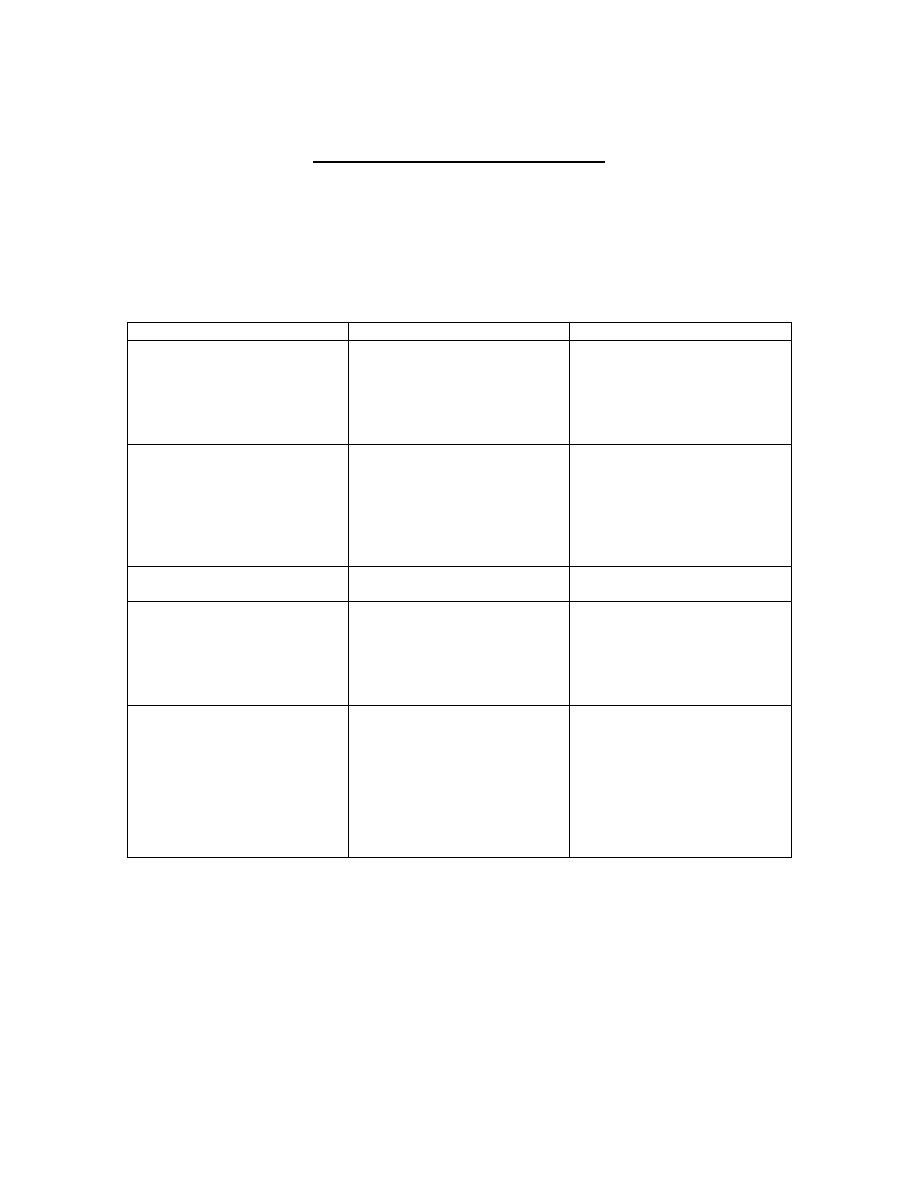
Parts of Speech and Their Uses
Part of Speech
How It Is Used
Examples of Usage
Noun
A noun is the name of a person,
place, or thing. Proper nouns are
capitalized; common nouns are
not.
Proper nouns: God, Mother
(used as a name), University of
Iowa, Japan
Common nouns: dog, woman,
university (used in the generic),
country
Verb
A verb is a word that expresses
action or being. Verbs may be a
single word or a small group of
words that work together. Verbs
come in a variety of tenses,
indicating the relative time at
which an action is performed.
Action verbs: jump, run, sit
Being verbs: is, was
Multiple-word verbs: is sitting,
was jumping, can help, could do
Pronoun
A pronoun is a word that stands
in place of a noun.
I, me, you, we, us, he, she, they
Adjective
An adjective is a word that
modifies (tells something about) a
noun or pronoun. Adjectives
usually answer questions like,
“Which one?” “What kind of?”
“How many/how much?”
the bluetick hound
a frantic golfer
nineteen giraffes
horrible-tasting ice cream
Adverb
An adverb is a word that
modifies (tells something about) a
verb, adjective, or adverb.
Adverbs often end in “-ly.” They
usually answer questions like,
“When?” “Where?” “How?”
“Why?” “Under what
conditions?” “To what degree?”
Walking slowly
Walking very slowly
Walking unusually slowly
Walking ridiculously slowly

Preposition
A preposition is a word placed
before a word or group of words,
to form a phrase modifying
(telling something about) another
word in the sentence. In other
words, prepositions are
connecting words that show the
relationship among words in a
sentence. Prepositions often
have to do with a noun’s location
in time or space, or with the time
at which an action is performed.
Some common prepositions are:
about, above, across, after,
against, along, among, around, at,
before, behind, below, beside,
besides, between, beyond, by,
down, during, except, for, from,
in, inside, into, like, near, next,
of, off, on, onto, out, outside,
over, past, since, than, through,
to, toward, under, unlike, until,
up, with, without.
Conjunction
A conjunction is a joining word;
it links words or groups of words
in a sentence, and shows the
relationship between them.
While prepositions tend to tell
something about a group of
words in a sentence (where is the
cologne? How did Rabbit run?),
conjunctions tell more about the
way in which the sentence itself
should be read. Which idea
depends on other ideas? Which
idea stands alone?
Common conjunctions are: and,
but, either, or, neither, nor, after,
although, as, because, before,
how, if, since, than, that though,
unless, until, what, when, where,
which, while, who/whom.
Article
An article is a word used to mark
and define a noun.
A floppy-eared bunny rabbit.
The snarling Doberman.
Ask Mr. Language Person
Q. Please explain how to diagram a sentence.
A. First spread the sentence out on a clean, flat surface, such as an ironing board. Then, using a
sharp pencil or X-Acto knife, locate the "predicate," which indicates where the action has taken
place and is usually located directly behind the gills. For example, in the sentence: "LaMont never
would of bit a forest ranger," the action probably took place in a forest. Thus your diagram would be
shaped like a little tree with branches sticking out of it to indicate the locations of the various
particles of speech, such as your gerunds, proverbs, adjutants, etc.
__
Dave Barry
Document Outline
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
PARTS OF SPEECH
02 Parts of Speech DVD
parts of speech chart
Academic Studies English Support Materials and Exercises for Grammar Part 1 Parts of Speech
Parts of speech (for students)
02 Parts of Speech DVD
~$Production Of Speech Part 2
Red?dge of Courage Brief Analysis
The Top Figures of Speech Smutek
Parts of the body 2
parts of the body
activity-animals-and-parts-of-the-body, Filologia angielska, Praktyki
Production Of Speech Part 1
The hierarchy of words, the parts of
23)21 09 Parts of the animal body VIa
Prioress & parts of Thopas, Melibee, Monk
Production Of Speech Part 2
PARTS OF THE BODY
więcej podobnych podstron