SCOTLAND
GEOGRAPHY
Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the southwest.
Scotland includes over 790 islands, including Orkney Islands, Shetland Islands and the Hebrides.
SCOTTISH REGIONS
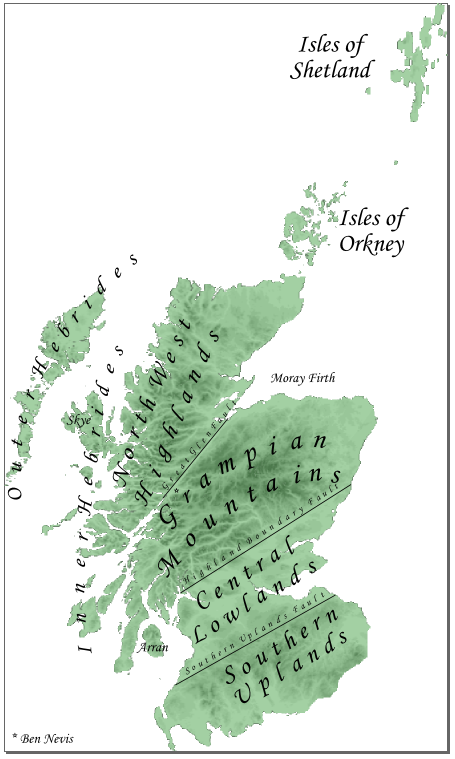
Northwest Highland
The Grampian Mountains or Grampians are one of the three major mountain ranges in Scotland.
Ben Nevis is the highest mountain in the British Isles. It is located at the western end of the Grampian Mountains in the area of the Scottish Highlands.
Loch Lomond is a freshwater Scottish loch. It is the largest lake in Great Britain by surface area.
Loch Ness is a large, deep, freshwater loch in the Scottish Highlands extending for approximately 37 km (23 mi) southwest of Inverness. Its surface is 15.8 m (52 ft) above sea level. Loch Ness is best known for the alleged sightings of the cryptozoological Loch Ness Monster, also known affectionately as "Nessie".
Central Lowlands
Arthur's Seat the largest of the extinct volcanoes in Edinburgh and the hill domination the city (823 feet above sea level). It's Edinburgh's most prominent landmark, which resembles a huge, crouched lion.
The Campsie Fells are a range of hills in central Scotland, stretching east to west in Stirlingshire.
Southern Uplands
The Southern Uplands are a range of hills almost 200 kilometres (124 mi) long, interspersed with broad valleys.
FAMOUS PLACES AND BUILDINGS
Edinburg it's the capital of Scotland. It's the second largest city in Scotland. Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Parliament.
The Old Town is the medieval part of the city. Together with the 18th-century New Town, it is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It has preserved its medieval plan and many Reformation-era buildings.
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh. It is often considered to be a masterpiece of city planning, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Although still referred to as the New Town, it was built in stages between 1765 and around 1850, and retains much of the original neo-classical period architecture.
The Royal Mile is a succession of streets which form the main thoroughfare of the Old Town of the city.
The Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the monarch in Scotland. The palace stands at the bottom of the Royal Mile at the opposite end to Edinburgh Castle. Holyrood Palace is the setting for state ceremonies and official entertaining. Queen Elizabeth II spends one week in residence at Holyrood Palace at the beginning of each summer, where she carries out a range of official engagements and ceremonies.
Edinburgh Castle is a fortress which dominates the skyline of the city of Edinburgh, Scotland, from its position atop the volcanic Castle Rock.
Calton Hill a hill in central Edinburgh just to the east of the New Town. Calton Hill is the headquarters of the Scottish Government, which is based at St Andrew's House, on the steep southern slope of the hill. The hill also includes several iconic monuments and buildings: the National Monument, Nelson's Monument,the Dugald Stewart Monument, the New Parliament House (the Royal High School), the Robert Burns Monument, the Political Martyrs' Monument and the City Observatory.
Dean Village is a former village immediately northwest of Edinburgh.
The Scott Monument - one of Edinburgh's most famous landmarks and historic buildings. It's 200 feet high. It's the largest monument in the world to a man of letters.
Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland. The city is situated on the River Clyde in the country's west central lowlands. Glasgow has an impressive heritage of Victorian architecture: the Glasgow City Chambers, the main building of the University of Glasgow and the Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum.
Other famous cities in Scotland are Dundee and Aberdeen.
Balmoral Castle is a large estate house in Royal Deeside, Aberdeenshire. It is located near the village of Crathie. Balmoral has been one of the residences of the British Royal Family since 1852.
SCOTTISH INDUSTRY
Scottish industry is premised on agriculture and forestry, oil and gas, fishing, energy, manufacturing, whisky, textiles and tourism.
Bagpipes - national instrument of Scotland.
Kilt - is the traditional dress of men and boys in the Scottish Highlands of the 16th century. It is most often made of woollen cloth in a tartan pattern.
Haggis - a traditional Scottish dish made of a sheep's stomach stuffed with spiced liver, oats and onions, now also available in a vegetarian version.
Whisky - the `water of life' (in Gaelic), produced since the 15th century, available in a number of varieties (single malt, grain, blended), and carrying various brand names such as `Johnny Walker', `The Famous Grouse' and `Glenfiddich'.
Ceilidh - a social gathering involving traditional Scottish dances and sometimes singing and story-telling.
Highland Games - a range of events held all over Scotland encouraging traditional dress, music dance and sports (e.g. tossing the caber, putting the stone, throwing the Scottish hummer).
Robert Louis Stevenson - one of the best-loved writers of his generation, born in Edinburgh, the author of the world famous short story `Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde' and such novels as `Kidnapped', `Catriona' and `Treasure Island'.
Sir Walter Scott - a poet and novelist remembered for the extensive knowledge of Scottish history and folklore which is revealed in his works. The author of `Ivanhoe', `Rob Roy' and `Waverley'.
Robert Burns - the national poet of Scotland who wrote in Scots vernacular. The author of `Tam o' Shanter' and `Auld Lang Syne'. Today groups of people all over the world mark the anniversary of his birth with a special supper featuring haggis, whisky and bagpipe music.
John Knox - the fiery 16th century religious reformer who laid the foundations of the Presbyterian movement. He is remembered for his tract `First Blast if the Trumpet Against the Monstrous Regiment of Women'.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
The Culture of Great Britain The Four Nations
The History of Great Britain - Chapter One - Invasions period (dictionary), filologia angielska, The
The History of Great Britain - Chapter Two - The Middle Ages (dictionary), filologia angielska, The
The History of Great Britain Chapter One Invasions period
The history of Great Britain
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
The History of Great Britain Chapter Three The English Renaissance
the united kingdom of great britain
History of Great Britain exam requirements
History of Great Britain exam requirements
History of Great Britain
History of Great Britain
LECTURE 3 ATTACHMENT 1 PMs of Great Britain
History of Great Britain exam requirements
United Kingdom of Great Britain
[Hay] The spirituality of adults in Great Britain recent research
Summaries of the Four Arab Israeli Conflicts in the th?n
The Special Relationship?tween the United States and Great Britain
więcej podobnych podstron