15223 skanuj0024 (169)
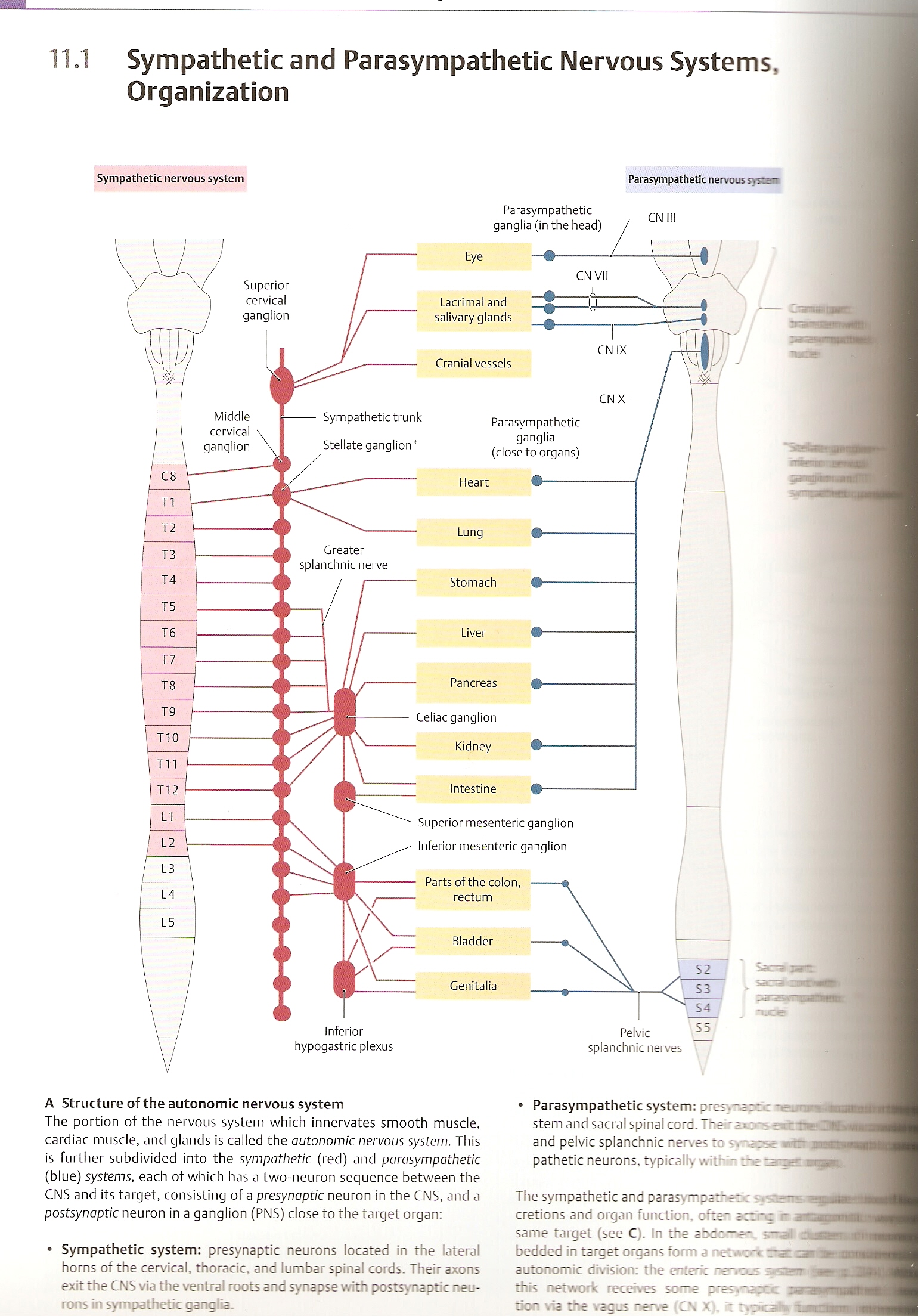
11.1 Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems, Organization
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nen/ous syst^-
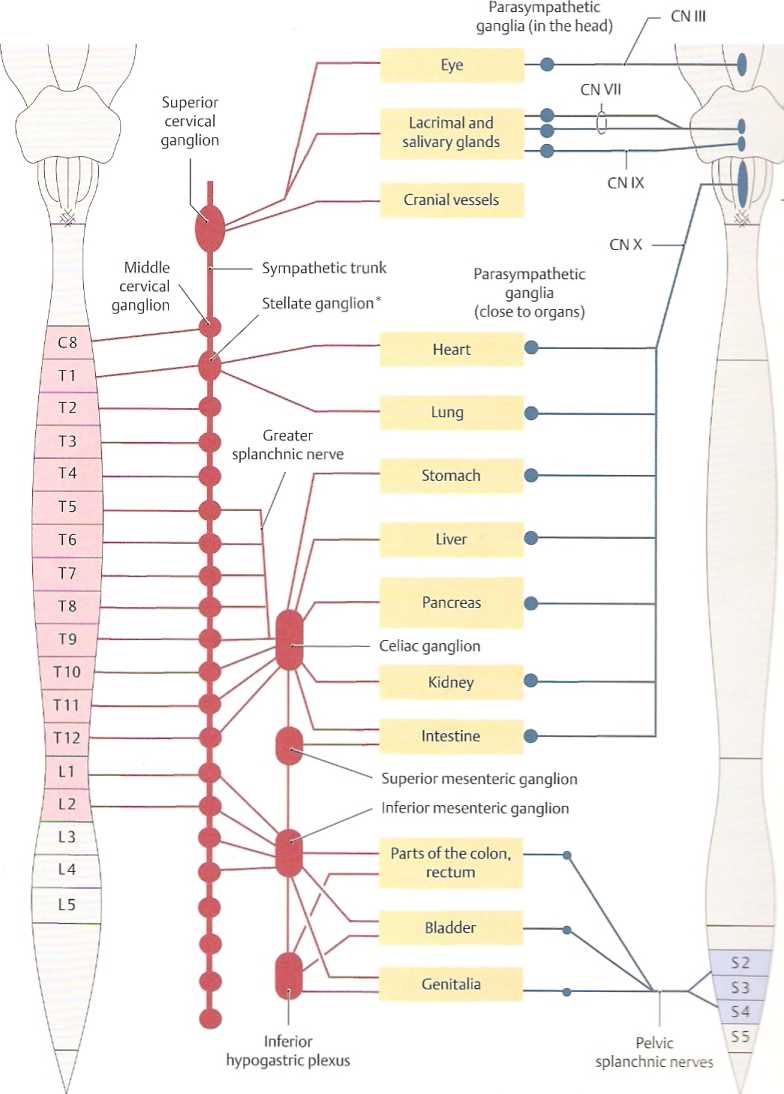
• Parasympathetic system: presynaptic ~em1 stem and sacral spinał cord. The' sions sritAM and pelvic splanchnic nerves to syar^r t : pathetic neurons, typically with - re w
The sympathetic and parasympatr-eiic 51saeHM| cretions and organ function. often aerrę rai same target (see C). In the abdo-ich. ~ =. ra. bedded in target organs form a netwofc rraccei autonomie division: the enteńc nermms | this network receives some >"es>,~^ccc asa tion via the vagus nerve (CN X). ~ ry=»cahr%f
LlALAłM ŁkŁ
A Structure of the autonomie nervous system The portion of the nervous system which innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands is called the autonomie nervous system. This is further subdivided into the sympathetic (red) and parasympathetic (blue) systems, each of which has a two-neuron sequence between the CNS and its target, consisting of a presynaptic neuron in the CNS, and a postsynaptic neuron in a ganglion (PNS) close to the target organ:
Sympathetic system: presynaptic neurons located in the lateral horns of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spinał cords. Their axons exit the CNS via the ventral roots and synapsę with postsynaptic neurons in sympathetic ganglia.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
skanuj0021 (169) 11.3. Gospodarka łowiecka 11.3. Gospodarka łowiecka 639 Prawa i obowiązki dzie
skanuj0033 (89) 11.5. Gospodarka wodna Ryby oraz inne organizmy wodne stanowią pożytki, a do korzyst
IMAG0371 (5) Anatomical Differences in Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions CHS Proganglionlc
skanuj0011 (169) >fy<7nAuęJ(y rM Wlyrc/^J/lrM/> I yyJfrpfe^ IffT TO Jf 1
skanuj0011 (266) L) 11 & P P ( <vt y^ & b
więcej podobnych podstron