26834 netter121
Anatomy of the Kidney: The Nephron
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY

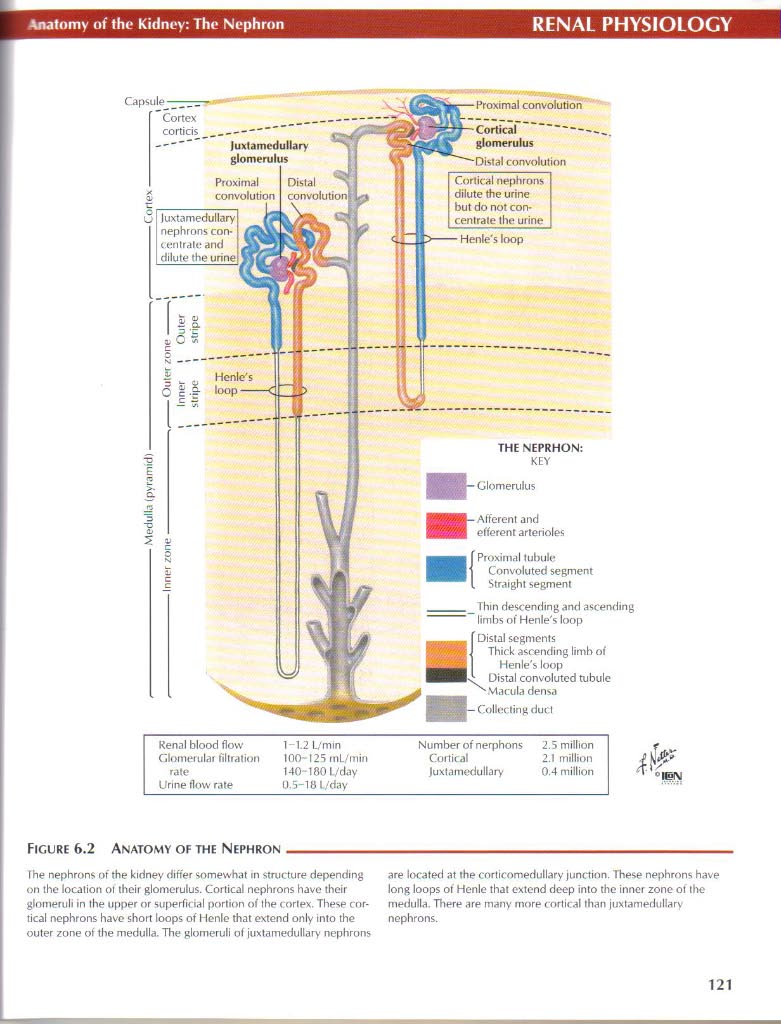
Cortical nephrons dilute the urine but do not eon-centrale the urine Henle's loop
)uxtamedullary nephrons eon-centrale and dilute the
Pro.yimal tubulc Convoluted segment Straight segment
__ Thin descendingand ascending limbs ot Henle's loop f Distal segments IJ Thick ascending limb of Henle's loop Distal convoluted tubulc rMacula densa 1— Collectingdud
|
Renal blood flow |
1-1.2 L/mm |
Number of nerphons |
2.5 million |
|
Glomerular filtration |
100-125 rnL/min |
Cortical |
2.1 million |
|
rale |
140 180 L/day |
Juxtame<lullary |
0.4 million |
|
Urine flow ratę |
0.5-18 l/day |
Figurę 6.2 Anatomy of the Nephron
Ihe nephrons of the kidney difter somewhat in structure depending on the location ot their glomcrulus. Cortical nephrons havc their glomeruli in the upper or superficial porlion of the cortex. These cortical nephrons have short loops of Henie that extend only into the outer zonę of the medulla. The glomeruli of juxtamedullary nephrons are located at the corticomedullary junction. These nephrons have long loops of Henie that extend deep into the inner zonę ot the medulla. There are many morę cortical ihan juxtamedullary nephrons.
121
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
skanuj0015 (279) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain -landtudinal Mrafcsure ■PHlfillilll
skanuj0016 (266) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain10.4 Coronal Sections: VII and VIII
SCAN0131 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 5-
SCAN0145 178 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System Epimysium Perimysium EndomysiumFIGURĘ 10-1 Connec
SCAN0125 44 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System mented melanocytes, fibroblasts, and collagen band
skanuj0016 (266) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain10.4 Coronal Sections: VII and VIII
więcej podobnych podstron