8342936729

PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY
^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ
It should be noticed that the interval of conduction is prolonged close to 6m where the phase inductance is maximum. As mentioned above, at high speeds the phase turn-on angle 0on is advanced and so is the tum - off angle 9C.
SRM control is often described in terms of ”low-speed” and ”high-speed” regimes. Low-speed operation is typically characterized by the ability to arbitrarily control the current to any desired value. Fig. 1.10 illustrates waveforms typical of low-speed SRM operation. As the motor’s speed increases, it becomes increasingly difficult to regulate the current because of a combination of the back EMF effects and a reduced amount of time for the commutation interval. Eventually a speed is reached where the phase conducts (remains on) during the entire commutation interval. This modę of operation, depicted by Fig. 1.11, is called the single-pulse modę.

idealized induclance
current
z\.
-Ir-Or
Fig. 1.11. Single-Pulse Modę - Motoring, High Speed
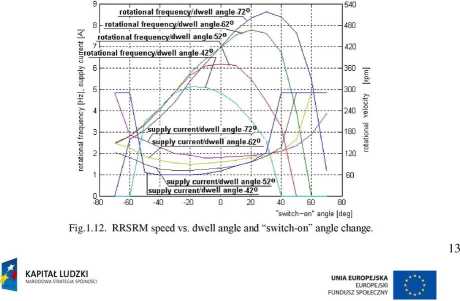
When this occurs, the motor speed can be increased by increasing the conduction period (a greater dwell angle) or by advancing the firing angles, or by a combination of both. Example of experimental change of RRSRM (rolling Rotor Switched Reluctance Motor) speed by using both above technique is presented in Fig. 1.12.
Materiały dydaktyczne dystrybuowane bezpłatnie.
Projekt współfinansowany ze środków Unii Europejskiej w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ It should be noticed that the interval of conduction i
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Eąuation (1.14) may be written as: transformation rota
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Eąuation (1.14) may be written as: transformation rota
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY ^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ dr inż. Adam BiernatElectrical Machines in the Power
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Only for the linear case (no magnetic saturation) the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ phase conducts), and maximum torąue is achieved by max
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ a = Ua — The maximum value of #w, for Qon = 0 (zero ad
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ By adjusting the turn-on and turn-off angles so that t
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ To solve above eąuation one must find transient curren
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Fig. 1.15. Instantaneous value of voltage and current
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Fig. 1.17. a) One key switch. b) Unipolar current
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY ^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJPROGRAM ROZWOJOWY 2. PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS MOTOR
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ SRMs do, however, offer some advantages along with pot
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ 2-phase. 4-phase. 4 stator poles i 2
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ The symmetry of magnetic Circuit leads to the almost z
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Using eąuations (1.3) to (1.5), the incremental mechan
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ 1) The torque is proportional to the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ EAM - laboratoriumLaboratorium Elektroniczna Aparatura
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ 1. Cel ćwiczenia Celem ćwiczenia jest zapoznanie z badan
więcej podobnych podstron