6781097238
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (IJCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015
2.2.3 Security flaws in GPRS
The weak points of GPRS network are as follows.
1. The mobile terminal or SIM card:
Authentication algorithms are similar to those of GSM and similar kind of attacks may be initiated.
2. The GPRS radio link:
The encryption of radio link is based on KASUMI cipher it is deliberately simplified to perform well in resource limited devices.
3. The GPRS Application security:
The application security protocol proposed for GPRS is Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) maintained by WAP forum. The WAP gap is a serious security flaw.
2.3 Security enhancements in UMTS
The UMTS uses larger freąuency band and its objective is to provide high data and voice ratę. Since it has larger frequency band, a higher number of calls may be simultaneously serviced. The throughput for data communication has been increased significantly. Following Fig 5 illustrates UMTS inffastructure and its connecting elements.
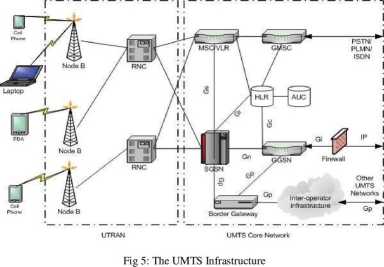
The UMTS network supports interoperability with GSM/GPRS network. The inffastructure includes GSM/GPRS specific and UMTS specific functionalities. The UMTS reuses GSM/GPRS functionalities for voice calls or data transmissions. It differs in the protocol layer for each interface with respect to radio technology [6]. The following two nodes replace those of GSM/GPRS.
a) Node B replaces BTS
b) RNC (Radio Network Controller) replaces BSC
The 3G Security system define a higher security management for UMTS networks. New security provisions have been added such that detection of rogue base stations, network mutual authentication, strict control over the transmission of secret keys, longer encryption keys etc.
35
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (IJCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 4.
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (IJCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 4.
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (IJCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 GS
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 sev
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 Fig
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 2.2
International Journal of Computer Science & Engmeenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 20157.
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 Th
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 co
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 Th
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 1.
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015 Fo
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April 2015?
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, April
International Journal of Computer Science & Engineenng Survey (UCSES) Vol.6, No.2, Apnl 2015Secu
IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 7, Issue 3, No 9, May 2010
12 IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 7, Issue 3, No 9, May 2010 www.IJCSI
IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 7, Issue 3, No 9, May 2010
14 IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues, Vol. 7, Issue 3, No 9, May 2010 www.IJCSI
więcej podobnych podstron