9058009748
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica. Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004
SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERISATION AND CATALYTIC APPLICATION FOR WET PHENOL OMDATION OF AN IRON-CONTAINING PILLARED CLAY
TIMOFEEVA. M. N..1 KHANKHASAEVA, S. TS.,2 BAD.\1AEVA, S. V.,3 RYAZANTSEV, A. A.3
Boreskov institute of Catalysis [Miicnnyr learajiina hm. T. K. Bopecłcosa], pr. akademika Lavrent’eva 5, Novosibirsk, 630090, Russia ‘ Baikal Inslitute ofNaiure Management [EaftKanbCKHH MHCTHTyT npMpoaonojib30BaHHfl], Sahyanovoy 8, Ulan-Ude, 670047, Russia Water Supply Department, Siberian Transport University [Kanapa nupaBJWKH h BOAOCHaóweHHM, CnóiipcKHH ymiBepcHTeT nyieft coo6uichhji], D. Koval’chuk 191, Novosibirsk, 630049, Russia E-mail: timofeeva@catalysis.nsk.su
Microporous solids synthesised by intercalating volumi-nous metallic comp!exes between structural layers of swell-ing clays, such as montmorillonites, are an ongoing subject for research in heterogeneous oxidation catalysis.
High surface area pillared clays (PILC) were prepared from naturally occurring montmorillonites by exchanging inter-layer ions with polyoxocations containing a) iron (Fe-PILC), b) aluminium (Al-PILC), c) iron adsorpted onto Al-PILC, and d) iron and aluminium located within the same complex (AlFe-PILC). Polyoxocations Ali3_xFeN04o (x = 0 /1.5) with like Keggin structure were prepared by base-hydrolysed AlCh-FeClj Solutions. The obtained AlFe-PILCs and Fe-PILCs were characterised by far FTIR spectroscopy, ESR. ‘ Al NMR, scanning electron microscopy and BET surface area measurements.
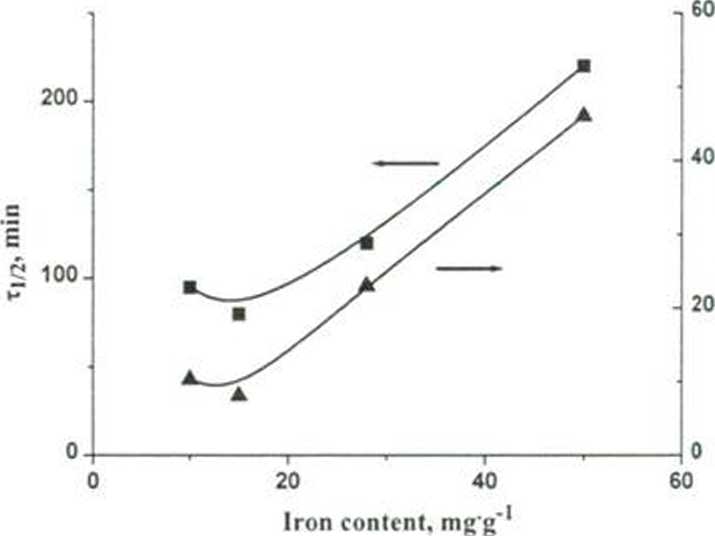
Fig. 1: Influence of the iron content in the Fe-PILCs and leaching of iron from samples on catalyst activity ([PhOH] = I mM, [HA] = 14 mM, [catalyst] = I g-P1, pH = 6.2, 50°C)
Catalytic properties of AlFe-PILCs and Fe-PILCs were studied in the wet peroxide oxidation of phenol. It was found that catalytic activities of Fe-PILCs correlated with the iron initially contained in the catalyst and the total amount of dis-solved iron by the reaction (Fig. 1).
The induction period which observed on AlFe-PILCs and Fe-PILCs is not produced by diffusion limitations. Probably the induction period account for a) the necessity to reduce ferric into ferrous ions, b) diflerences in the accessibility to the active sites in the solids and c) differences in the naturę of iron in the solids. From ESR characterisation, it was de-duced that on AI-PILCs, iron is present as isolated species, probably located on the clay and as oxide clusters, whereas on AlFe-PILCs, an other isolated species was detected, probably located on the pillars. From the catalytic results, it can be concludcd that this latter species catalyses morę cfficient-ly the total phenol oxidation than the others do.
Important factors affecting catalyst activity and phenol removal efficiencies were studied, i.e. the effect of pil, temperaturę, catalyst concentration and the stability of the catalyst. It was established that AlFe-PILCs allows a total elimi-nation of phenol without significant leaching of iron ions. It was also obsened that by using this catalyst, it is possible to extend the rangę of pH value (pH = 3.5 - 6.2) for which Fenton-type oxidations can occur. The optimum pil value for AlFe-PILCs is around 3.5-4.0.
The stability of AlFe-PILCs was studied. It was shown that during three cycles AlFe-PILCs can be used without lost catalytic activity and iron leaching.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Grant of the Federal Program “Integration” no. 33216 and Russian Foundation for Basic Research under Grant 01-05-97254.
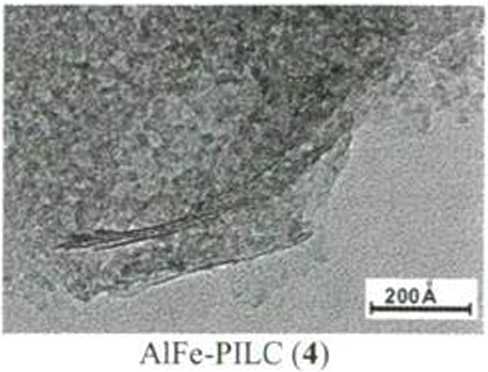
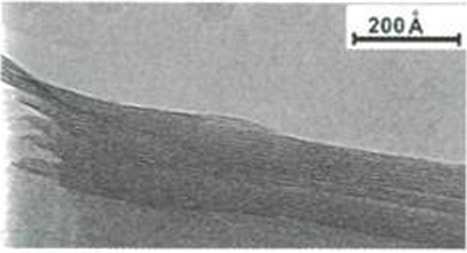
PILC
Fig. 2: According to SEM data the natural clay are lath shaped, but air heating AlFe-PILCs have the house of cards structure. In flocculated clays both face-to-face (lamellar) and delaminated (edge-to-face and edge-to-edge) layers occur.
104
www.sci.u-szeged.hu/asvanytan/acta.htm
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004STRUCTURAL, THERMAL AND SURFACE FORCE
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4. Szeged, 2004ZEOLITE AND CLAY MINERALS AT THE CONT
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4. Szeged. 2004ANKARA CLAY: ITS GEOLOGY, MINERALOGY,
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004THE CRYSTAL CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF TALC: XRD AND SP
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004TEMPERATURĘ AND PRESSURE EFFECTS ON
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004CLAY PIGMENTS AS INDICATORS OF PAINT
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004TEM-STUDY OF MUSCOVITE-CHLORITE MIXED
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004CHEMICAL RESISTANCE OF CEMENT-BENTONI
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004EFFECT OF THE Ni-Al HYDROTALCITE-LIKE
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004REACTIONS OF ORGANIC MOLECULES WITH S
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004EVOLUTION OF CLAY MINERALOGY OF PALAE
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004ELASTIC NETWORK OF LAMELLAR PARTICLES
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004NANO AND MICRO PARTICLES ON BENTONITE
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004MINERALOGICAL AND CRYSTAL CHEMICAL AS
Acta Mineralogica-Petrographica, Abstract Senes 4, Szeged, 2004FACTORS AFFECTING THE REACTION PROGRE
więcej podobnych podstron