Funkcje trygonometryczne1
26
FUNKCJE TRYGONOMETRYCZNE
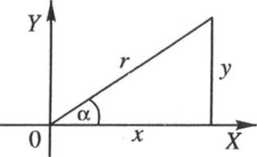
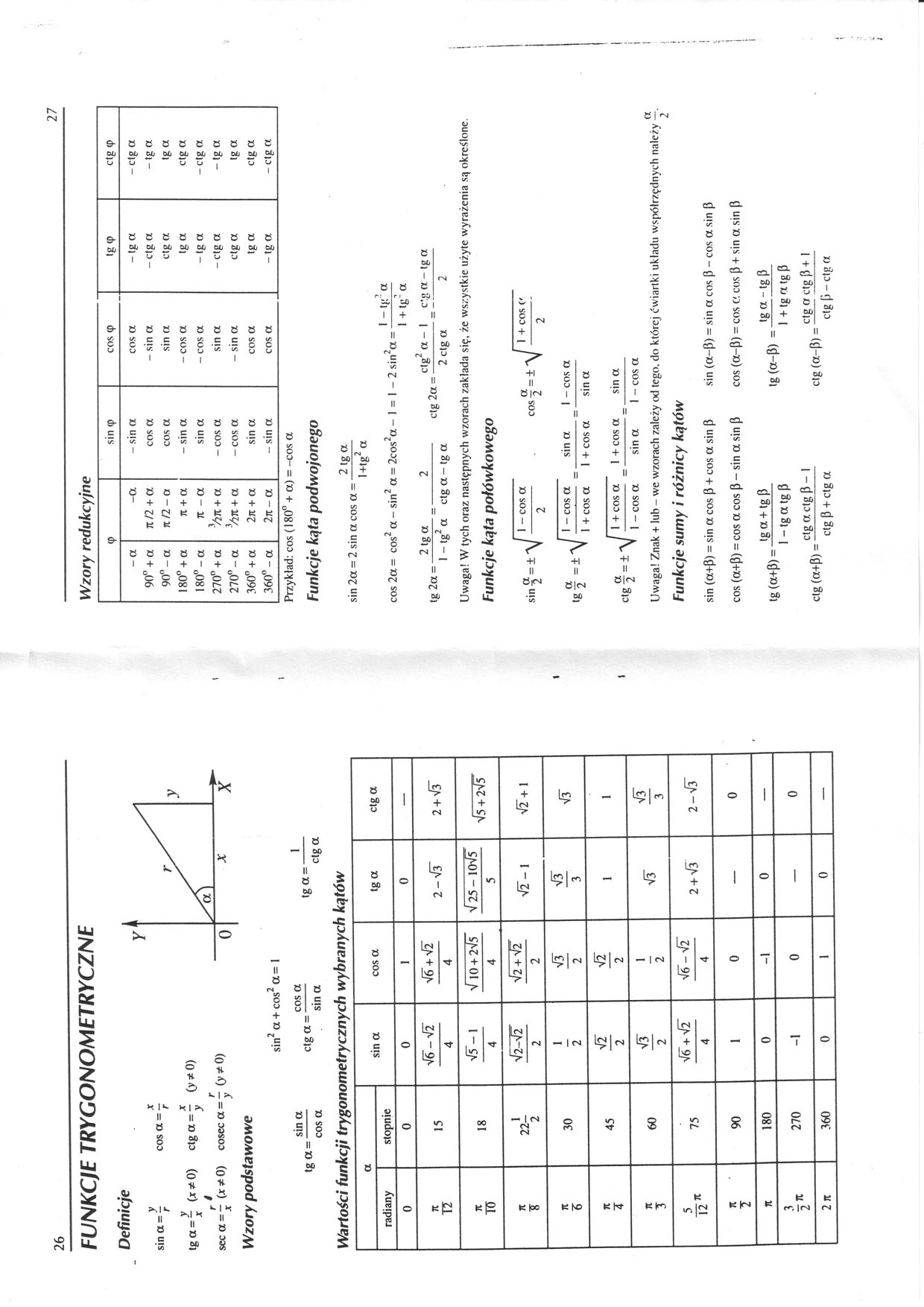
Definicje
y
sin a = -
X
cos o. — — tga = 7 (**0) ctg a = “ (y*0)
/ y
r 9 r
sec a = - (jr*0) cosec a = - (y*0)
■* y
Wzory podstawowe
tga = -
sin2 a + cos2 a = 1 cos a
ctga =
sin a
tg a =
ctga
Wartości funkcji trygonometrycznych wybranych kątów
|
a |
sin a |
cos a |
tg a |
ctga | |
|
radiany |
stopnie | ||||
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
i |
0 |
— |
|
71 Tl |
15 |
V6-<2 4 |
<6+Ś2 4 |
2-VT |
2 + VF |
|
n JO |
18 |
Ś5-1 4 |
V 10 + 2^5 4 |
V 25 - ltWif 5 |
'15 + 2'ts |
|
n S |
22- 2 |
■fen 2 |
V2 + V2 2 |
V2-l |
V2 + 1 |
|
TC 5 |
30 |
1 2 |
V3 2 |
V3 3 |
V3 |
|
TC ? |
45 |
V2 2 |
<2 2 |
1 |
1 |
|
TC I |
60 |
V3 2 |
1 2 |
V3 |
V3 3 |
|
5 72* |
75 |
Vó+y/2 4 |
<6-<2 4 |
2 + V3 |
2-vr |
|
TC * |
90 |
1 |
0 |
— |
0 |
|
TC |
180 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
— |
|
3 2* |
270 |
-1 |
0 |
— |
0 |
|
2 TC |
360 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
— |
Wzory redukcyjne
|
<p |
sin <p |
cos (p |
tgtp |
ctg tp | |
|
-a |
-a |
- sin a |
cos a |
-tg a |
-ctga |
|
90° +a |
n/2 + a |
cos a |
- sin a |
-ctga |
- tg a |
|
90°-a |
tt/2-a |
cos a |
sin a |
ctg a |
tga |
|
180° +a |
Ti + a |
- sin a |
- cos a |
tg a |
ctg a |
|
0 1 c oc |
Ti -a |
sin a |
-cos a |
-tg a |
-ctga |
|
270° + a |
lótt + a |
- cos a |
sin a |
- ctg a |
- tg a |
|
270°-a |
’/ó7t + a |
- cos a |
- sin a |
ctg a |
tg a |
|
360° +a |
2tt + a |
sin a |
cos a |
tg a |
ctga |
|
360° -a |
2tt-a |
- sin a |
cos a |
- tg a |
- clg ot |
Przykład: cos (180° + a) = -cos a
Funkcje kąta podwojonego
sin 2a = 2 sin a cos a =
tg 2a =
2 tg a
ctg 2a =
I + tg- a ctg2 n - I ctg a - tg a
I - tg a ctg a - tg a 2 ctg a 2
Uwaga! W tych oraz następnych wzorach zakłada się, żc wszystkie użyte wyrażenia są określone. Funkcje kąta połówkowego
|
sin^ |
— + A |
/ 1 - cos a |
cos“ = ±-\^ |
1 1 + COS (' |
|
* \ |
/ 2 |
2 | ||
|
<■! |
/ 1 - cos a |
sin a 1 - cos a | ||
|
* \ |
1 1+ cos a |
1 + cos a sin a | ||
|
. a ctg y |
- + A |
1 1+ cos a |
1 + cos a sin a | |
|
1 > |
V 1 - cos a |
sin a 1 - cos a |
Uwaga! Znak + lub - we wzorach zależy od tego. do której ćwiartki układu współrzędnych należy —.
Funkcje sumy i różnicy kątów
sin (a+(5) = sin a cos p + cos a sin p cos (a+P) = cos n cos p - sin a sin p sin (a-P) = sin a cos p - cos a sin P cos (a-P) = cos et cos p + sin a sin P
tg (a+p) = -ctg (a+P) =
tg (a-P) = ctg (a-P) =
tg a + tg P I - tg a tg p ctg a ctg p - I ctg p + ctg a
tg a - tg P
+ tg a tg p
ctg a ctg P + I ctg p - ctg a
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
img169 (18) 12. Trygonometria • Definicje funkcji trygonometrycznych y sin a = — r x cos a = — r tg«
14870 img169 (18) 12. Trygonometria • Definicje funkcji trygonometrycznych y sin a = — r x cos a = —
tabela wartości funkcji trygonometrycznych Tabela wartości funkcji trygonometrycznych a sin a cos
14870 img169 (18) 12. Trygonometria • Definicje funkcji trygonometrycznych y sin a = — r x cos a = —
Slajd36 Trygonometria płaska Wzory redukcyjne funkcji trygonometrycznych (i sin
18. TABLICA WARTOŚCI FUNKCJI TRYGONOMETRYCZNYCH «[•] sin a cos [i tg
img169 (18) 12. Trygonometria • Definicje funkcji trygonometrycznych y sin a = — r x cos a = — r tg«
img218 Wykresy funkcji trygonometrycznych Wartości f sin .r cos.t tg* Ctg.TWartości fun l/(7t±JT)
Funkcje trygonometryczne w trójkącie sin cos tg ctg Funkcje trygonometryczne w trójkącie prostokątny
skanuj0033 (11) TAB^ieA^FWKOJł-TRYGONOMETRYCZNYGłtr^ tf[°J sin <2 cos p tgor ctg/? pn 0 0,0000
M 2 272 Andrzej Zero — Mathcad 7.0 Funkcje trygonometryczne • sin(x) - sinus; •
6.10. Związki między funkcjami trygonomotrycznymi sino = 2, cos o = tg ot =
więcej podobnych podstron