
Felicitas Fahrenkrog-Petersen, Marta Kędzierska,
Janani Pratap, Evelyn Kamau, Thomas Koch, Bastian Lorenz
The Low Cost Airline
24.05.2012
Strategic Management Case Study
Agenda
History /
Facts
Generic
strategies
model
Bowman‘s
clock
Core
competen
cies
Competito
rs
Alliance
option
Conclusio
n
2

History / Facts
History /
Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
198
7 -
89
199
1
198
5
200
0
199
7
•Website launch
•First routes to continental Europe
•Public limited company
•New CEO (Michael O‘Leary)
•Rapid expand
•Need for restructuring
•Foundation (Tony Ryan)
3

History / Facts
History /
Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
• Europe’s largest low fares carrier
• Headquarter in Dublin, biggest
operational base in London
• RyanAir’s numbers:
- 1 special type of boeing (737 -800)
- 14 further bases
- 250 destinations in all of Europe
- 2700 employees
4
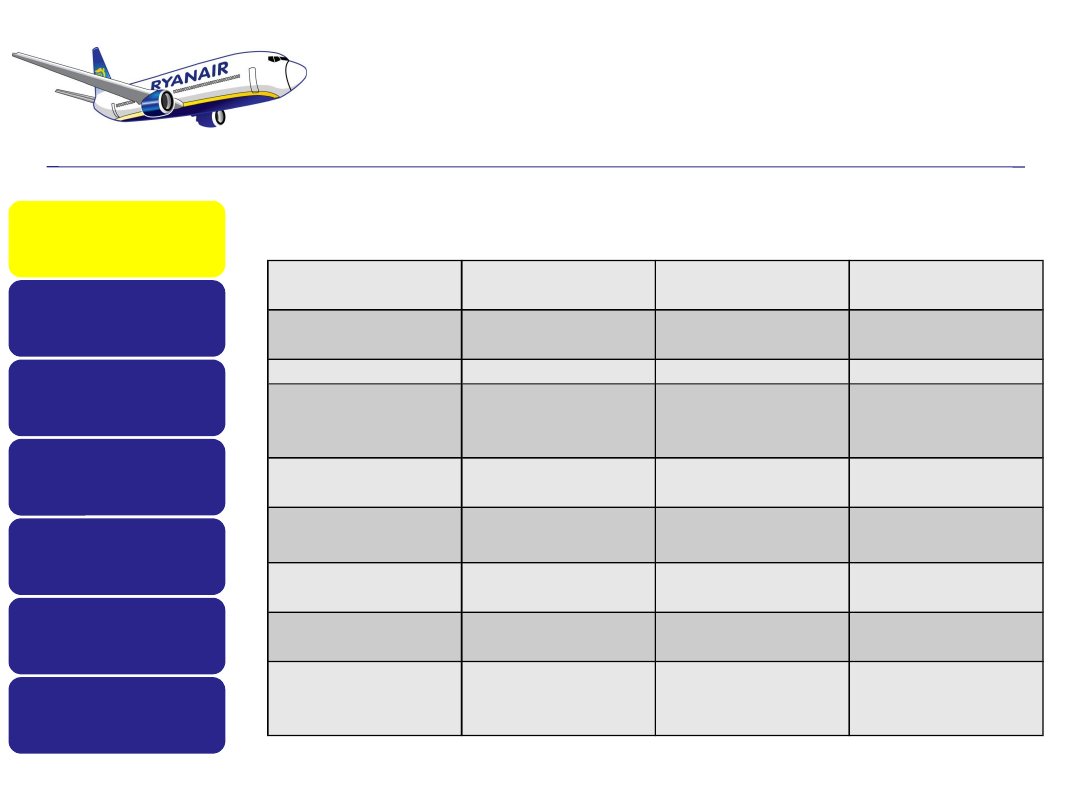
History / Facts
Measurement
Factor
Ryanair
EasyJet
Lufthansa
Total number of
passengers
27.6 million
29.6 million
50.9 million
Average fare
€ 41
€ 62
NA
Average
revenue per
passenger
€48.4
€72
€333
Average Cost
per passenger
€38.7
€69.4
€328
Operating
Margin
25%
3.8%
1.6%
Total number of
planes
119
109
377
Plane Load
Factor
86.4%
85.2%
74%
Ground handling
+ airport
charges (000)
€178.4
€540.9
NA
History /
Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Comparative Operating Figures for Ryanair and selected
competitors (2005)
Source: Neil Thomson and Charles Baden-Fuller, Basic Strategy in Context (Wiley, 2010)
Ryanair Case Study
5

History / Facts
Generic
strategies
model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
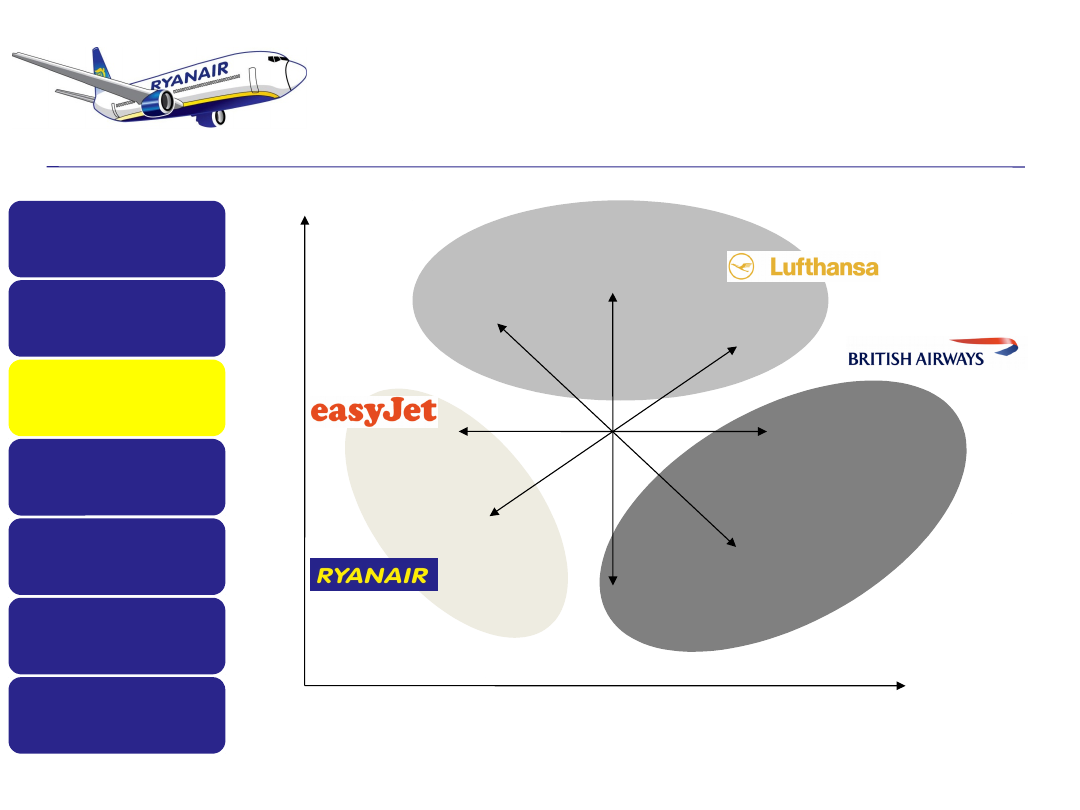
Where is RyanAir on the Generic Strategies
Model and Bowman’s clock? Should they
move and if so where do you feel they
should move to?
Overall Cost Leadership
Cost Focus
Differentiation Focus
Differentiation
B
ro
a
d
N
a
rr
o
w
Low cost
Higher cost
Source: Neil Thomson and Charles Baden-Fuller, Basic Strategy in Context
(Wiley, 2010), 180.
Competitive advantage
C
o
m
p
e
ti
ti
v
e
s
c
o
p
e
6
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s
clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Where is RyanAir on the Generic Strategies
Model and Bowman’s clock? Should they
move and if so where do you feel they
should move to?
Source: Neil Thomson and Charles Baden-Fuller, Basic Strategy in Context
(Wiley, 2010), 184.
Pric
e
Low
Lo
w
High
H
ig
h
Hybrid
Differentiatio
n
Low
Price
Focused
Differentiation
No
Frills
Differentiation
Strategies
Low Price
Strategies
Risk
Strategies
Increased
Price/ Standard
Value
Increased
Price/ Low
Value
Standard Price/
Low Value
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
P
e
rc
e
iv
e
d
A
d
d
e
d
V
a
lu
e
7
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s
clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
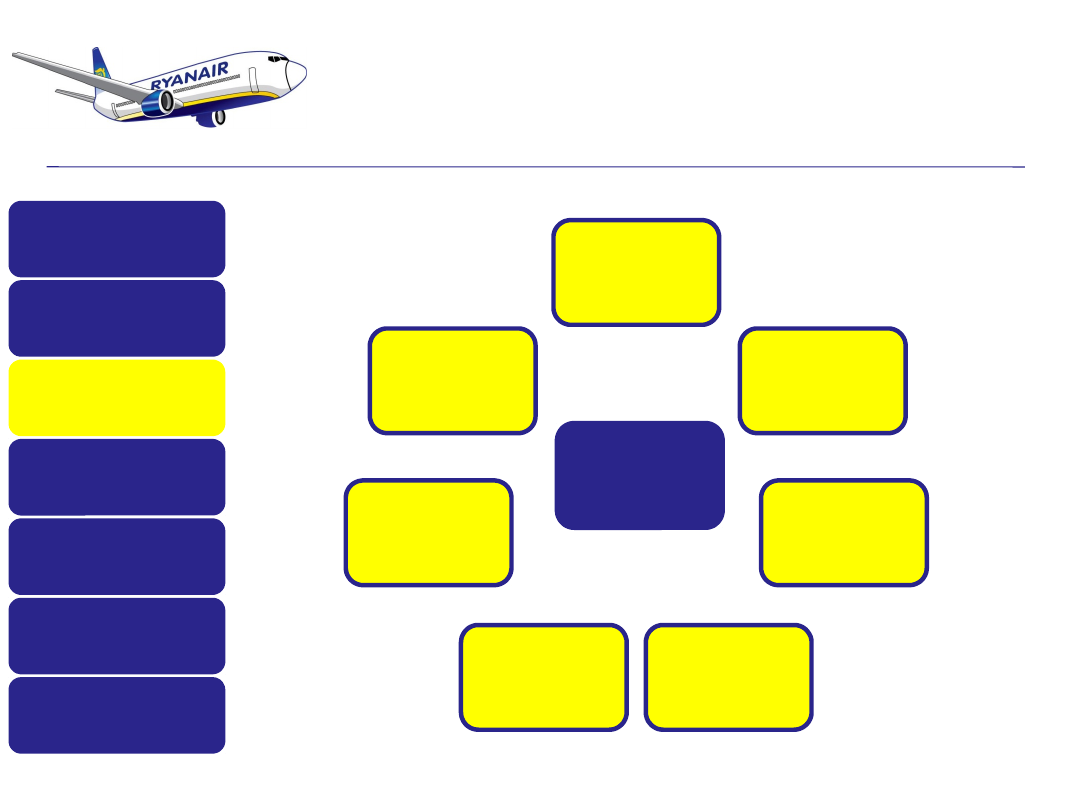
Where is RyanAir on the Generic Strategies
Model and Bowman’s clock? Should they
move and if so where do you feel they
should move to?
Short-haul
flights
(Point-to-
point)
Low costs
Single
aircraft type
Internet
booking
Secondary
airport
Basic
service on
board
Fast and
easy Check-
In
NO FRILLS
8

History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencie
s
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
What are RyanAir’s core competencies?
(max. 2) Why? Pick number one, why?
Core Competencies - A combination of
pooled knowledge, resources and
capabilities that enable a company to gain
competitive advantages
9
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencie
s
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
What are RyanAir’s core competencies?
(max. 2) Why? Pick number one, why?
TEST 1
Desirable to
customer?
Change over
time?
Defendable?
Cost
Leadership
Yes
Yes
Yes
10
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencie
s
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
What are RyanAir’s core competencies?
(max. 2) Why? Pick number one, why?
TEST 2
Valuabl
e?
Rare?
Hard to
imitate?
Organiz
ed
Properl
y ?
Competiti
ve
Implicatio
ns
Cost
Leadersh
ip
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Sustainabl
e
Advantag
e
11

Major competitors
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Imagine you are RyanAir’s major competitor.
How would you exploit RyanAir’s strategy to
your benefit?
12

• The Critical Success Factors (CSFs):
– lowest
prices
,
reliability
,
comfort
,
service
,
frequency
and
safety
• Cost reduction strategy:
– fleet commonality
– 3
rd
party service contractors
– low airport charges (secondary
airports)
– managed staff costs and productivity
– managed marketing costs (only
Ryanair.com)
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Imagine you are RyanAir’s major competitor.
How would you exploit RyanAir’s strategy to
your benefit?
13
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Imagine you are RyanAir’s major competitor.
How would you exploit RyanAir’s strategy to
your benefit?
DIFFERENTIATION
Result of efforts to make
a product or brand stand out as
a provider of
unique value to customers in
comparison with its competitors.
ADAPTATION
Modification of a concept or object to
make it applicable in situations different
from originally anticipated.
14
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Imagine you are RyanAir’s major competitor.
How would you exploit RyanAir’s strategy to
your benefit?
RyanAir
Competitor
ROUTES
Direct / short
distance /
Europe
Full range / worldwide
AIRPORTS
Secondary
airports
Primary airports /
infrastructure
AIRCRAFT
S
One type
One type
COSTS
Cooperations /
third
contractors
Cooperations / third
contractors
BOOKING
Mainly online
Exclusively online /
Permanent availability
SERVICE
Low service
Excellent Service
EXTRAS
Fee for extra
service
e.g. Frequent traveler
program
DIFFERENTIA
TION
ADAPTATION
15

Should RyanAir stay independent?
• Company philosophy clashes
• Security and quality differences
• Image destruction
• Higher failure rate
• More management required
• Long hall flight issues (higher cost)
• Current state of success
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance
option
Conclusion
Should RyanAir stay independent?
Or should it join an alliance?
16

Should RyanAir join an alliance?
• increase passenger demand
• loyal customers
• more destinations, new market
• lesser competition
• benefits:
– faster and smoother transfer
– frequent flyer program
– easier booking
•if opponent airlines join an alliance
(“first- mover”)
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance
option
Conclusion
Should RyanAir stay independent?
Or should it join an alliance?
17
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance
option
Conclusion
Should RyanAir stay independent?
Or should it join an alliance?
Stay
Independent
18
Conclusion
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Pick and stick!
Adapt and
differentiate!
Stay
independent!
For now…
19
Outlook
History / Facts
Generic
strategies model
Bowman‘s clock
Core
competencies
Competitors
Alliance option
Conclusion
Present
• Profits rose 25 % to € 503 Mio.
• Passengers rose 5 % to 76 Mio.
• Average fares rose 16 %
Future
• Profits will sink 10 – 15 %
• Traffic will grow 5 %
• Average fares will continue to rise
Source: http://www.ftd.de/unternehmen/handel-dienstleister/:nach-
gewinnsprung-ryanair-kapituliert-vor-kerosinkosten/70039893.html
20
Document Outline
- Slide 1
- Agenda
- History / Facts
- History / Facts
- History / Facts
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Conclusion
- Outlook
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
investor day presentation 24 09 08 final
Sabu Chats m45t3rs4d0w8 Mar 30 May 24, 2012
Wniosek 24, Łódź, Budżet 2012 (wnioski)
Bilet EURO NYSA od 2012 09 24
Informatyka 24 04 2012
2012 24
FOR popiera 7 Dobre propozycje zmian w zamowieniach publicznych 24 02 2012 pdf
Niesteroidoew leki przeciwzapalne 24,10,2012
AM zaliczenie 24 styczeń 2012 i odpowiedzi
Informatyka 24.04.2012
3) 24 03 2012
Wykład 24.11.2012 prawo międzynarodowe, Administracja-notatki WSPol, prawo międzynarodowe publiczne
(TPL PRAC 2012-09-24 Woda koprowa)
(TPL WYK 2012-09-24 Preparaty galenowe)
24.03.2012 Techniczne bezpieczeństwo pracy
Wykład 24.03.2012 r, WSTiH, Żywienie
Duża Aglomeracja Wrocławska od 2012 09 24
więcej podobnych podstron