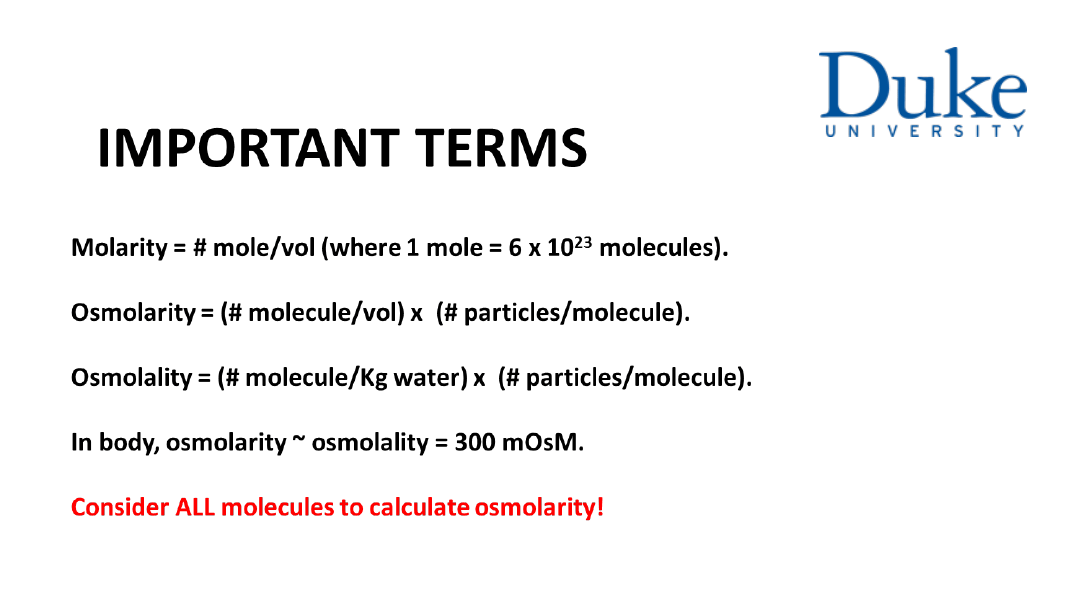
EFFECTIVE SOLUTES
& WATER TRANSPORT
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
• Explain osmosis
• Contrast osmolarity and tonicity
• Explain how effective solutes regulate
fluid compartments of the body.
GENERAL CONCEPTS
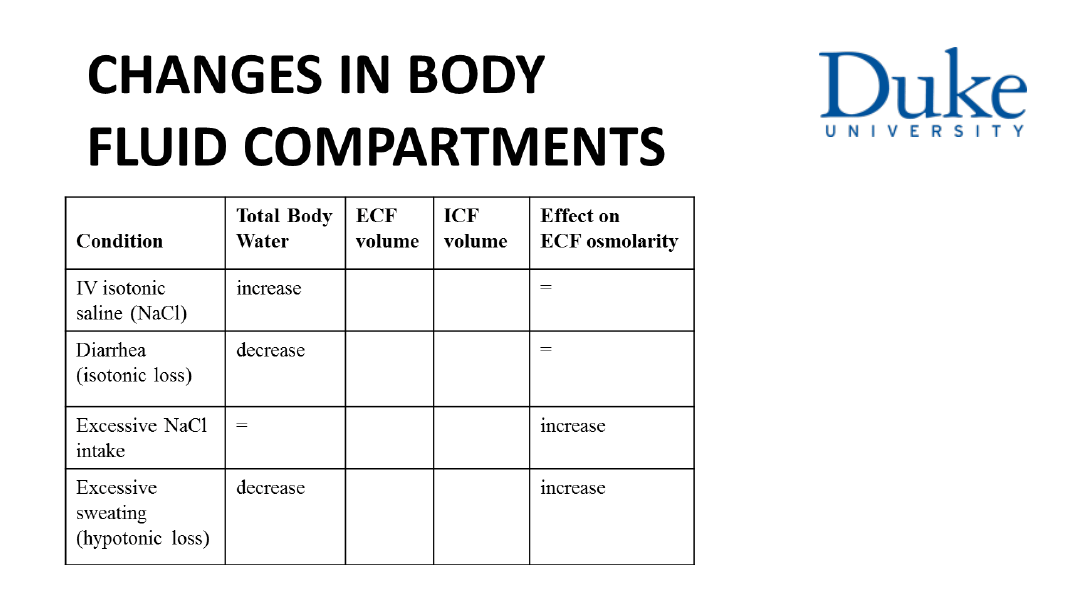
1. The two fluid compartments of the body, intracellular
fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF), are in osmotic
balance.
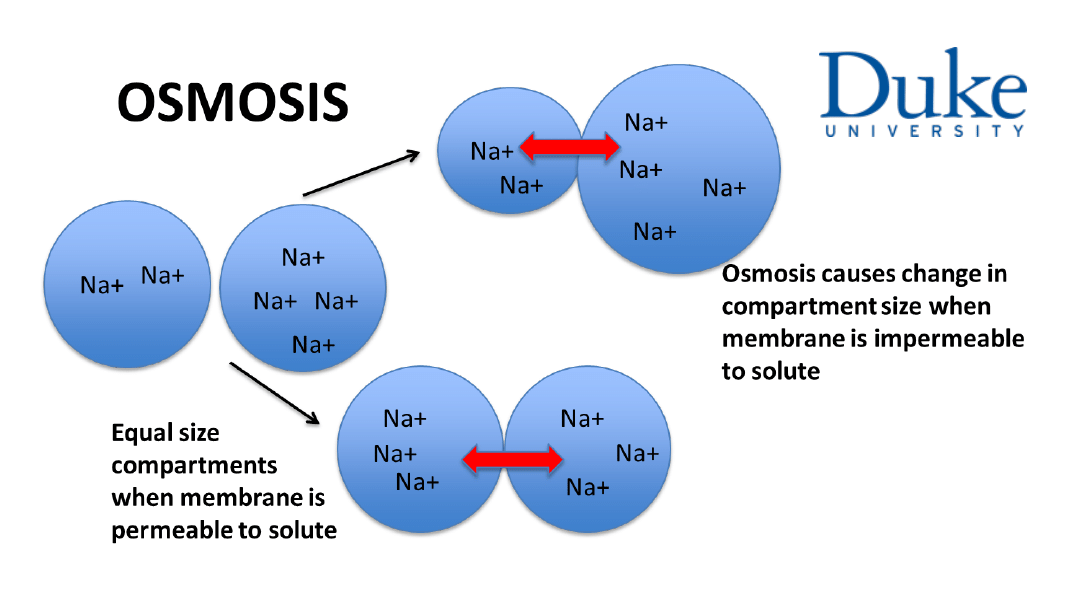
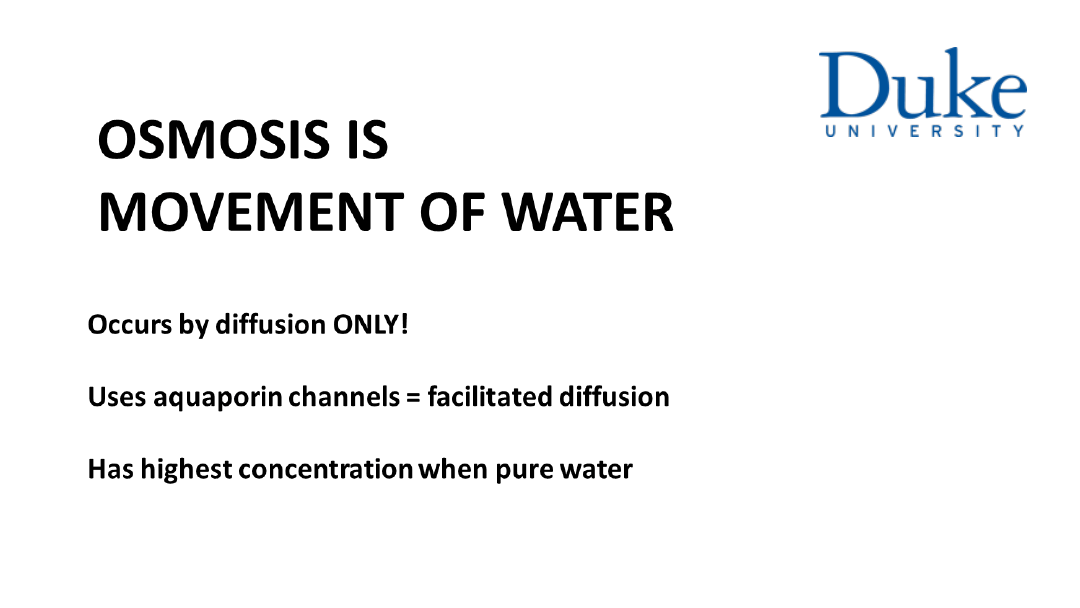
2. Water moves by facilitated diffusion through
aquaporin channels across most cell membranes. This
process is called osmosis.
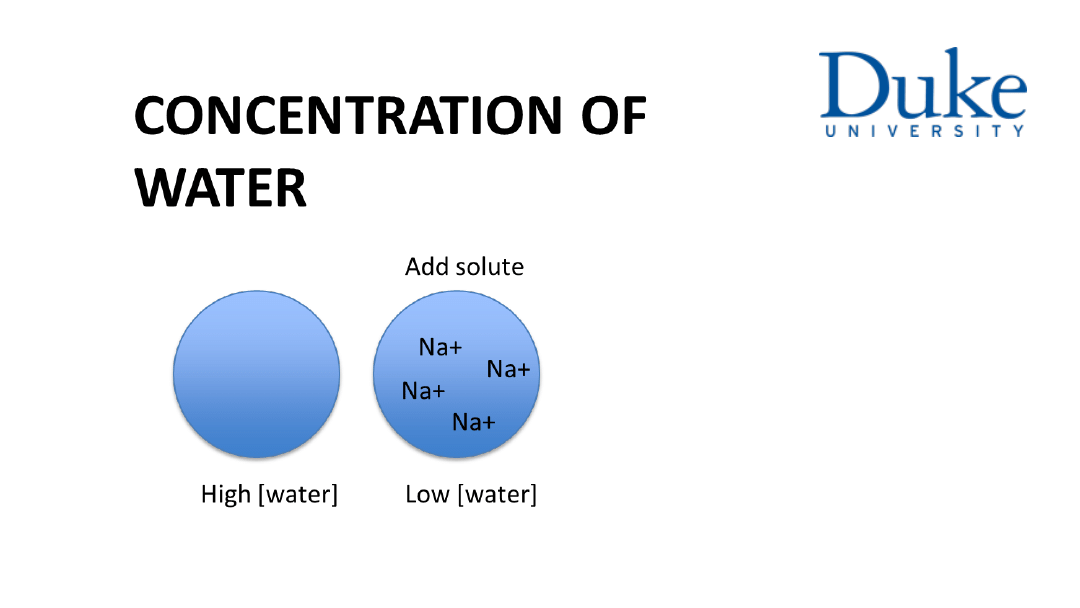
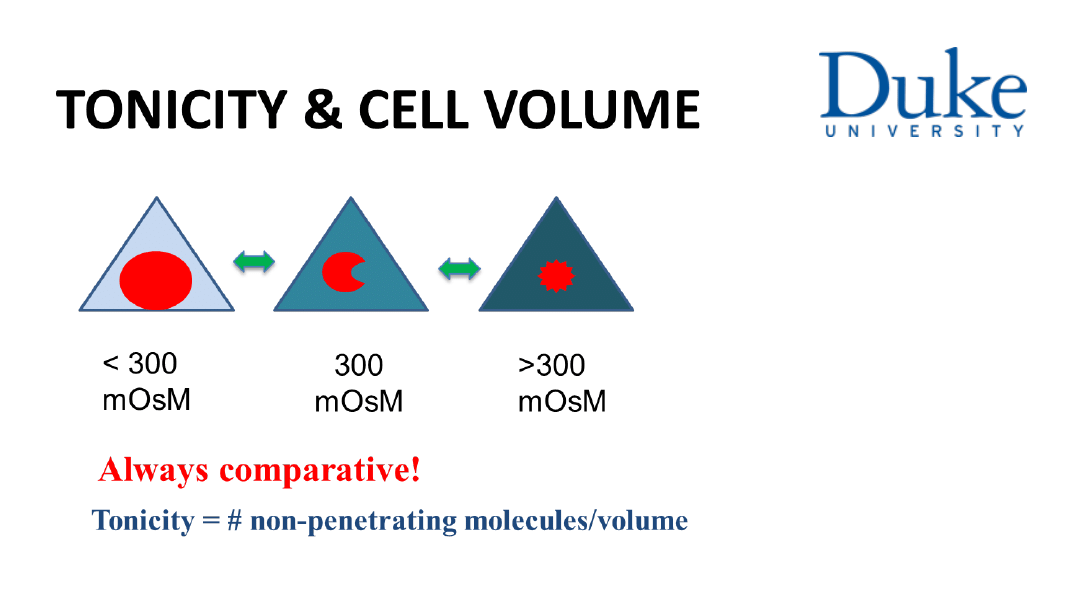
3. Non-permeable solutes are called effective solutes.
Cellular volume is critically dependent on the steady state
of effective solutes and water across the cell membrane
in exchange with the extracellular fluid compartment (ECF).
4. Cells shrink in hypertonic ECF conditions. Cells swell in
Hypotonic ECF conditions.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
lecture slides Powerpoint Slides Week1 1 1 Homeostasis revised
lecture slides Powerpoint Slides Week1 1 2 Homeostatic Regulation revised
lecture slides Powerpoint Slides Week1 1 3 Transporters, Pumps & Channels revised
lecture slides Powerpoint Slides Week1 1 6 Endocrine Assessment & Pathology revised v2
lecture slides Powerpoint Slides Week1 1 5 Endocrine General Concepts revised
lecture slides Powerpoint Slides Week1 1 0 Course Introduction revised
lecture slides 05
lecture slides
lecture slides 04
lecture slides 0105 EndoConcepts 2013 copyright
the effect of water deficit stress on the growth yield and composition of essential oils of parsley
Effect of Water Deficit Stress on Germination and Early Seedling Growth in Sugar
Positron emission tomography slides
jj slides tex
credit slides 1
slides01
więcej podobnych podstron