1
Antiviral Drugs
EWA GRABOWSKA
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF LODZ
Viruses
Obligate intracellular parasites
– protein + nucleic acid (DNA/RNA)
– no metabolic processes of their own
Difficulties in designing antiviral drugs:
– difficult to descriminate between viral
reactions and host cell reactions
– few virus groups respond to treatment
2
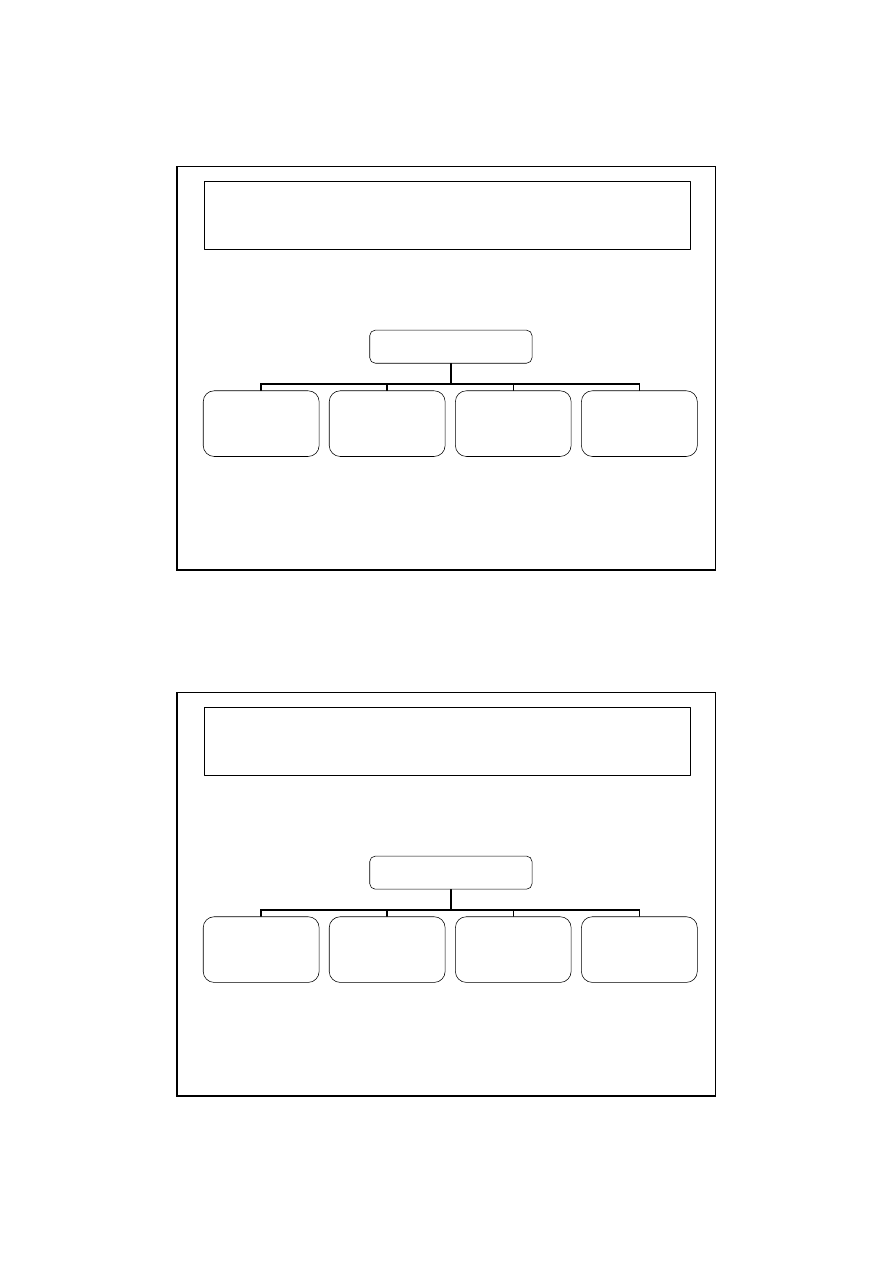
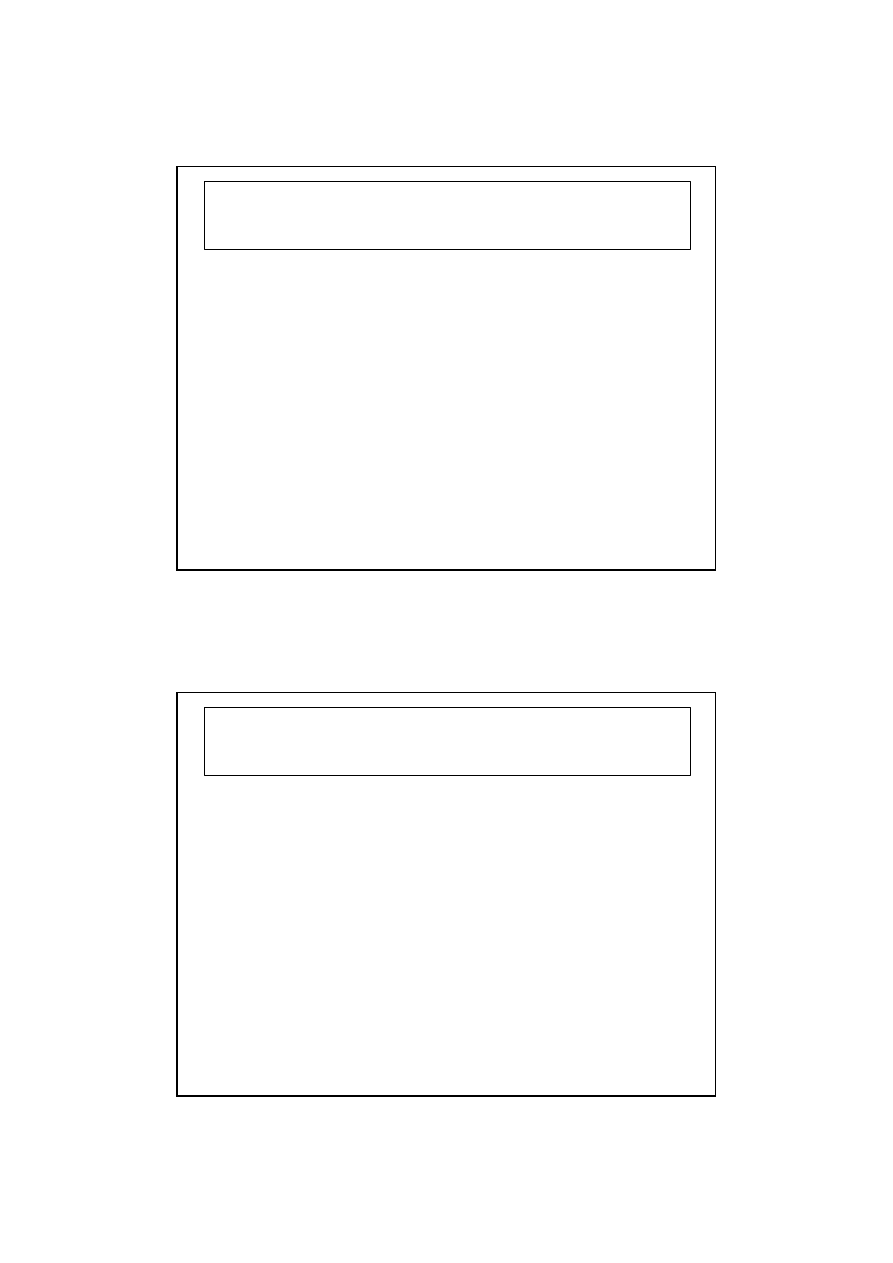
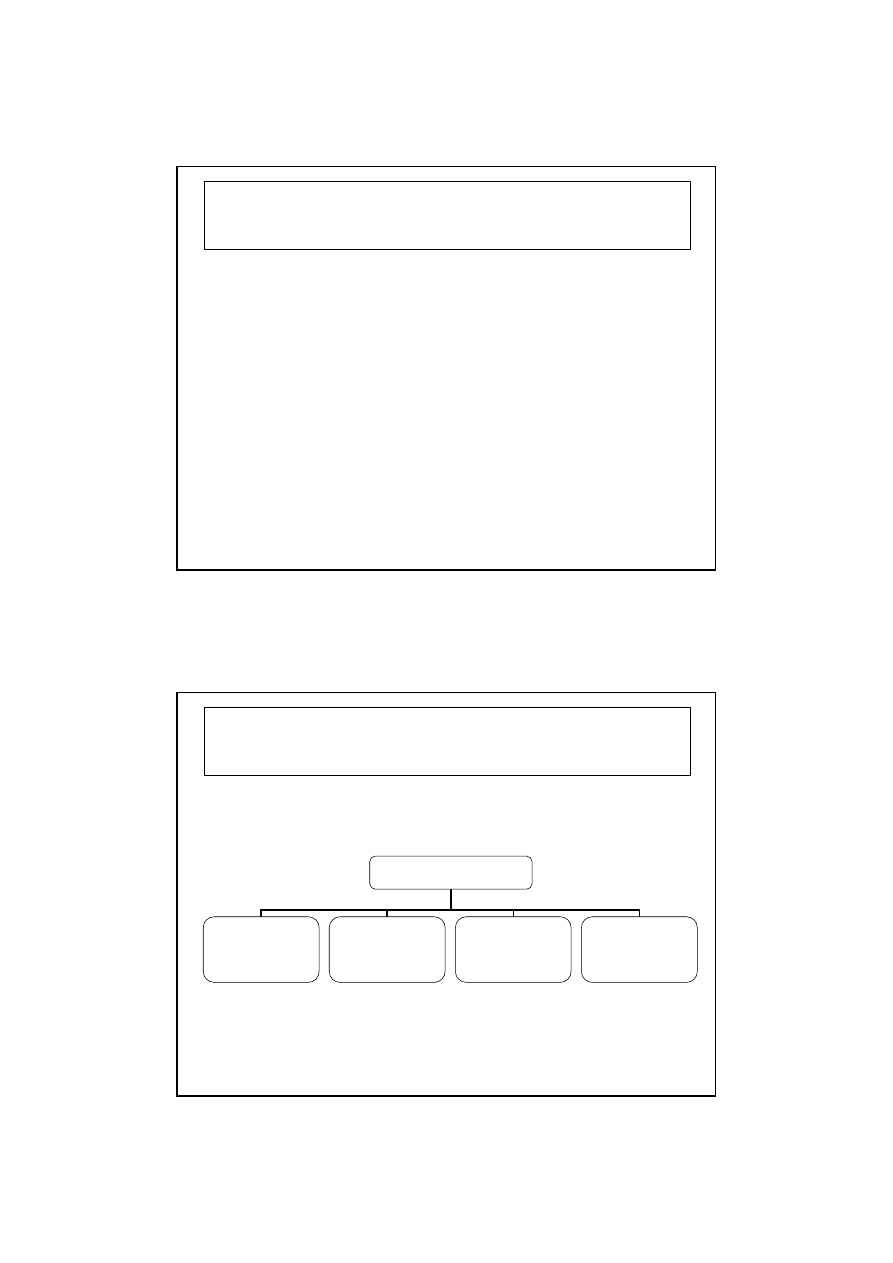
Types of Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral drugs
Drugs for
respiratory
virus infections
Drugs for herpes
and megalovirus
infections
Drugs for HIV
infections
Drugs for hepatitis
leukemia and
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Types of Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral drugs
Drugs for
respiratory
virus infections
Drugs for herpes
and megalovirus
infections
Drugs for HIV
infections
Drugs for hepatitis
leukemia and
Kaposi’s sarcoma
3
TMT of Viral Respiratory Infections
Influenza A virus
Influenza B virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
TMT of Viral Respiratory Infections
Immunization against influenza
– prevention is better than cure:
elderly people
children
chronically ill
– (-) strain not covered by the vaccine (quick
mutations of the virus)
– ADE: rarely – allergic reactions
4
Amantadine and Rimantadine
Amantadine, Rimantadine:
– MoA: (?) blockade of M
2
matrix protein
blockade of endocytosis
– TA: prevention of influenza infections
in risk groups or in case of epidemics
modest therapeutic efficacy if infection already present
must be started within first 48h of infection
– TA: Amantadine – also in the tmt of Parkinson’s
– RES: some strains resistant (modification of M
2
protein)
– SP: influenza A virus
Amantadine and Rimantadine
Amantadine:
– PK: good PO absorption
– PK: good distribution (crosses BBB)
– PK: little metabolism
excretion in urine
(!) in renal failure patients
– ADE: CNS
insomnia, dizziness, ataxia (hallucinations,
seizures)
(!) in patients with psychiatric problems, cerebral atherosclerosis,
epilepsy
Rimantadine:
– PK: good PO absorption
– PK: doesn’t cross BBB
– PK: extensive metabolism
excretion in urine
– (+): fewer CNS effects than amantadine
Both:
– CI: pregnancy, nursing mothers (teratogenic, embryotoxic)
5
Ribavirin
Ribavirin
– MoA: guanosine analog
converted into RTP
(ribavirin triphosphate)
Ø mRNA synthesis
(-) ineffective against RNA viruses
– SP: RSV, influenza A, B, hepatitis A, (?) Lassa virus,
hantavirus (hemorragic fever renal syndrome)
– TA: RSV infections in children
– PK: PO, IV, aerosol
– PK: retention in tissues, no retention in CNS
– PK: elimination in urine (drug + metabolites)
– ADE: transient anemia in Lassa fever,
bilirubin (for
PO, IV)
– ADE: respiratory problems in children (for aerosol)
– CI: pregnancy (teratogenic)
Types of Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral drugs
Drugs for
respiratory
virus infections
Drugs for herpes
and megalovirus
infections
Drugs for HIV
infections
Drugs for hepatitis
leukemia and
Kaposi’s sarcoma
6
TMT of Herpes and Megalovirus
Infections
Herpesviruses:
– cold sores (HSV)
– chickenpox, shingles
varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
– viral encephalitis
– genital infections
transmitted on newborn during parturition
Drugs against herpesviruses:
– effective during acute phase
– ineffective during latent phase
– MoA: purine/pyrimidine analogs
Ø of viral DNA
synthesis (exception foscarnet)
Nucleoside Analogs
Acyclovir
– MoA: guanosine analog
phosphorylated by viral
thymidine kinase
further phosphorylation by host
cell enzymes
acyclovir triphosphate
competes
with dGTP
incorporation into viral DNA
premature DNA termination, Ø of viral DNA
polymerase
– RES: altered/deficient thymidine kinase (enzyme
absent in CMV – natural resistance)
– SP: HSV-1, HSV-2, varicella-zoster virus, Epstein-
BArr virus
– TA: HSV encephalitis (more efficacious than
vidarabine)
– TA: genital herpes infections
– TA: prophylaxis
before bone marrow transplant
and after heart transplant (immunosuppressive drugs)
7
Nucleoside Analogs
Acyclovir
– PK: PO, IV,
– PK: topical
??? efficacy
– PK: good distribution
– PK: partial metabolism
inactive
– PK: excretion – urine (filtration, tubular secretion)
(!) in renal failure patients
– ADE: topical
irritation
– ADE: PO
headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
– ADE: IV
transient renal dysfunction (in dehydrated
patients or at high doses)
Nucleoside Analogs
Ganciclovir
– MoA: as in acyclovir; CMV
another route
– RES: some strains of CMV (? mechanism)
– TA: as in acyclovir + CMV retinitis
– PK: IV, good distribution, renal elimination
– ADE: severe neutropenia
– ADE: carcinogenic
– ADE: embryotoxic,
teratogenic
CI: pregnancy
8
Nucleoside Analogs
Famciclovir
– MoA: analog of deoxyguanosine (converted
into active metabolite penciclovir)
– SP: as in ganciclovir
– TA: approved only for acute herpes zoster
infection (shingles)
– PK: PO
– ADE: headaches, nausea
Nucleoside Analogs
Penciclovir
– MoA: analog of deoxyguanosine
– SP: HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV
– TA: cold sores
– PK: topical adm
no absorption
experimental
IV
– PK: long half-life
9
Nucleoside Analogs
Cidofovir
– MoA: analog of cytosine nucleotide
independent on viral enzymes
– TA: CMV-induced retinitis
– PK: PO, slow elimination
– ADE: nephrotoxicity
esp. in preexisting renal impairment/patients taking
nephrotoxic drugs (NSAIDs)
antidote
probenecid (ADE: rash, headache,
fever, nausea)
– ADE: neutropenia, metabolic acidosis, ocular
hypotony
Nucleoside Analogs
Vidarabine (ara-A)
– MoA: nucleoside analog (arabinofuranosyl adenine)
converted to ara-ATP
– SP: HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV
– TA: HSV keratitis or encephalitis , VZV infections
immunocompromised patients
(-) less effective than acyclovir
– RES: modified DNA polymerase
– PK: IV infusion (poorly soluble)
12 hours
good BBB penetration
– PK: topical
keratitis/keratoconjunctivitis
– PK: excretion
urine (native/metabolites)
– ADE: mild
in renal/hepatic failure
CNS disturbances, fluid overload
10
Nucleoside Analogs
Trifluridine:
– MoA: pyrimidine
– TA: HSV keratoconjunctivitis
– PK: topical adm.
Foscarnet
Foscarnet
– MoA: pyrophosphate analog
reversible Ø
of RNA and DNA polymerases
– SP: CMV, HSV (acyclovir-resistant), VZV
(acyclovir-resistant)
– TA: cytomegalic retinitis in
immunocompromised (HIV infected) patients
– RES: mutation of polymerase structure
cross-resistance with gancyclovir
11
Foscarnet
Foscarnet
– PK: IV, frequent administration
– PK: distribution into bone matrix
– PK: elimination
native form in urine
(filtration, secretion)
– ADE: nephrotoxicity, anemia, nausea, fever
– ADE: chelation with bivalent cations
hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia
seizures,
arrhytmias
Types of Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral drugs
Drugs for
respiratory
virus infections
Drugs for herpes
and megalovirus
infections
Drugs for HIV
infections
Drugs for hepatitis
leukemia and
Kaposi’s sarcoma
12
Nucleoside Analogs
Zidovudine (AZT)
– MoA: 3’-azido-3’deoxythymidine
conversion into triphosphate (mammalian
thymidine kinase)
blocks DNA synthesis by
reverse transriptase
doesn’t block host’s DNA polymerase
– MoA: Ø of dTMP
dTDP conversion
– RES: mutation of reverse transcriptase
– TA: HIV infections
slows progression
protects fetuses in infected mothers
Nucleoside Analogs
Zidovudine (AZT)
– PK: PO
good absorption
– PK: wide distribution (crosses BBB), half-life ~1 hr
– PK: glucuronidation in liver, excretion in urine
– ADE: bone marrow toxicity
anemia, leukopenia
– ADE: headaches
– ADE: seizures (in patients with advanced AIDS)
– INT: glucuronidation inhibitors: probenecid,
acetaminophen, lorazepam, indomethacin, cimetidine
13
Nucleoside Analogs
Didanosine (ddI)
– MoA: dideoxyinosine
converted into ddATP
termination of chain elongation
– TA: AZT-resistant HIV infections
– RES: mutation of reverse transcriptase
(+) no cross-resistance with other nucleoside
analogs
Nucleoside Analogs
Didanosine (ddI)
– PK: PO
chewable buffered tablets or
buffered solution
– PK: good abs. in the fasting state (food
abs)
– PK: crosses BBB (less than AZT)
– PK: excretion – urine (55% unchanged)
– ADE: pancreatitis (! may be fatal)
monitoring of serum amylase
– ADE: peripheral neuropathy
– INT: buffer may
absorption of other drugs
(ketoconazole)
14
Nucleoside Analogs
Zalcitabine (ddC)
– MoA: dideoxycytidine
converted into ddCTP
– TA: HIV
in conj. with AZT or instead of AZT
– RES: mutations of reverse transcriptase
– PK: PO
good abs,
by food/gastric acid
neutralizers
– PK: good distr
lower BBB penetration than AZT
– PK: metabolism (ddU), excretion
urine, some with
feces
– ADE: peripheral neuropathy (Ø mitochondrial DNA
polymerase)
– ADE: rash, stomatitis (resolve with tmt)
– ADE: pancreatitis (esp with pentamidine)
Nucleside Analogs
Stavudine (d4T)
– MoA: conversion into d4TTP
Ø RT
– PK: PO
good abs., not affected by food
– PK: BBB penetration
– PK: excretion
urine
– ADE: peripheral neuropathy (Ø mitochondrial
DNA polymerase)
15
Nucleoside Analogs
Lamivudine (3TC)
– MoA: nucleoside analog
– SP: HIV, HBV (hepatitis B)
– (+): does not affect mithochondrial DNA polymerase,
does not affect bone marrow
– TA: HIV + AZT (slower development of resistance to
AZT)
– PK: PO
good abs
– PK: renal elimination
– ADE: children
pancreatitis
– INT: co-trimoxazole
bioavailability of 3TC
Nucleoside Analogs
Abacavir:
– TA: for patients who canot tolerate or do not respond
to other drugs and combinations
– RES: some cross-resistance with AZT and 3TC
– ADE: drug fever, GI symptoms, malaise, rash
in sensitized subjects
hypotension, respiratory problems
Adefovir:
– TA: as in abacavir
– SP: in vitro
HIV, herpes, HBV
– ADE: nephrotoxicity (30%)
– ADE: nausea, diarrhea, asthenia,
hepatic enzymes
16
HIV Protease Inhibitors
MoA: Ø HIV protease
– viral protein
autocatalytic cleavage
generation of
viral proteins from precursor
TA: HIV infection
– in combination with AZT or 3TC
INT: Ø CYP-450
– antiarrhythmic drugs: amiodarone, quinidine
– antihistaminic drugs: astemizole, terfenadine
– antimigraine drugs: ergot derivatives
– antimycobacterial drugs: rifampin
– BZDs: midazolam, triazolam
– GI prokinetic drugs: cisapride
HIV Protease Inhibitors
ADE: lipodystrophy, hyperglycemia
– more with indinavir, ritonavir, less with
nelfinavir, saquinavir
– lipodystrophy
skinny legs, fat relocated to
abdomen and upper back
– hyperglycemia (rarely)
exacerbation or
initiation of DM
ADE:
TG,
cholesterol
17
HIV Protease Inhibitors
Saquinavir
– PK: PO, low bioavailability (12%)
better with high-fat meals
– PK: good distribution
– PK: metabolism
liver; elimination
bile
lower when combined with delavirdine
– ADE: headache, fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, GI
disturbances
HIV Protease Inhibitors
Ritonavir:
– PK: PO good BA (60%), unaffected by food
taken with nutritional supplements to improve taste
– PK: metabolism
liver; excretion
bile
– ADE: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, asthenia
– ADE: circumoral paresthesia, headache
– ADE:
aminotransferase
– ADE:
TG
18
HIV Protease Inhibitors
Indinavir
– PK: good PO abs.
better in acidic gastric conditions
lower with meals
– PK: low protein binding
– PK: short half-life (1.8 hrs)
– PK: metabolism
liver
– ADE: GI disturbances, headache
– ADE: risk of nephrolithiasis
prevention by adequate hydration
– ADE: risk of reversible hyperbilirubinemia
HIV Protease Inhibitors
Nelfinavir
– PK: good PO abs.
– PK: active hydroxylated metabolite
– PK: half-life 5 hrs
– ADE: diarrhea
antidote
loperamide
Amprenavir
– PK: long half-life
– ADE: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, oral and
perioral paresthesia, rash
19
Non-nucleoside RT inhibitors
MoA: highly selective, noncompetitive
ihibitors of RT
– (+) no effect on human DNA polymerases
no effect on bone marrow
– (+) no cross-resistance with nucleoside
analogs
– (-) quick development of resistance in
monotherapy
most often used in combination with other drugs
(nucleoside RT inhibitors)
Non-nucleoside RT inhibitors
Nevirapine:
– PK: good PO absorption
– PK: good distribution (crosses BBB)
– PK: metabolism
liver; excretion
urine
– ADE: rash, fever, headache,
serum transaminases
– ADE: sever dermatologic diseases
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis
14 day titration period with ½ dose (
of risk)
– ADE: hepatotoxicity (may be fatal)
– INT: inducer of CYP3A4
metabolism of protease inhibitors
dose adjustment (
dose of indinavir and nelfinavir, do not use with saquinavir)
metabolism of other drugs: oral contraceptives,
ketoconazole, methadone, metronidazole, quinidine,
theophylline, warfarin
20
Non-nucleoside RT inhibitors
Delavirdine
– PK: good PO abs. (unaffected by food)
– PK: high protein binding (98%)
– PK: extensive metabolism; elimination by feces, urine
– ADE: rash (44% of patients), nausea, dizziness,
headache
– INT: inhibitor of protease inhibitor metabolism (
plasma levels of saquinavir, indinavir)
– INT: fluoxetine, ketoconazole
plasma delavirdine
– INT: phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine
plasma delavirdine
Non-nucleoside RT inhibitors
Efavirenz
– PK: good PO abs.
– PK: high protein binding (99%)
– PK: crosses BBB
– PK: half-life 40 hrs
once-daily dosing
– ADE: CNS (50%): dizziness, headache, vivid
dreams, loss of concentration
– ADE: rash
– INT: modest CYP-450 inducer (
dosage of
indinavir)
21
Types of Antiviral Drugs
Antiviral drugs
Drugs for
respiratory
virus infections
Drugs for herpes
and megalovirus
infections
Drugs for HIV
infections
Drugs for hepatitis
leukemia and
Kaposi’s sarcoma
Interferon
TA: hepatitis B and C
TA: cancer
hairy cell leukemia, Kaposi’s
sarcoma
MoA: (?) induction of host enzymes
RNA
translation
degradation of viral RNA
PK: IV, crosses BBB
ADE: fever, lehtargy, bone marrow suppression,
CV problems (CHF), hypersensitivity
ADE: hepatic failure, pulmonary infiltrates
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Antiviral Drugs
Neuroleptic drugs
VA 004 Drugs, STW
drugs for youth via internet and the example of mephedrone tox lett 2011 j toxlet 2010 12 014
History of the United States' War on Drugs
Enzyme Systems that Metabolise Drugs and Other Xenobiotics Current Toxicology
math&drugs egz 08 i 09 rozwiązania
Narkot Data Rape Drugs FINALppt
D7 Antivirals
Antibacterial Drugs id 65683 Nieznany
Hallucinogenic Drugs And Plants In Psychotherapy And Shamanism
Antifungal drugs
więcej podobnych podstron