- 8 -
N° 43 - October 2003 - CEDRAT - CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES - MAGSOFT Corp.
SOFTWARE
>>
E
lectrical distributed
generation produced with
renewable energy (wind,
solar, biomass, fuel-cells,etc.)
takes more and more importance
in the global electrical production.
The power which can be produced
with a windmill (2.5 MVA), as well
as the committed sums (1000€ for
1 KW installed) imply to carry out
simulations in order to make the
good technological choices and
analyze the network connection
consequences as well as study
economic profi tability.
PSCAD integrates all tools
necessary to simulate a windmill
and its connection to the network.
Such a study has been performed
in CEDRAT and is presented in the
technical paper «Wind Turbine
and Grid Connection Modelling
with PSCAD».
The tools
These 3 components (fi g.1),
designed according to IEEE
models, are available in the PSCAD
Master library and make it possible
to simulate all the parameters
involved in a wind mill study :
●
Wind sources: possibility
to simulate different wind
distributions (gusts, random,etc.),
● Pitch regulation : the «passive
pitch control» and the «dynamic
pitch control» which play on
incidence angle of the blades
(Beta),
● The choice of the number of
blades from which depends the
power coeffi cient characteristics of
the turbine (Cp),
● The blade length (R) and the
air density (
ρ) which make it
possible to calculate the output
power of the turbine (P = ½ Cp
ρ
π R
2
Vvent
3
) and the corresponding
torque,
● The step-up ratio and the ef-
fi ciency of the gear box located
between the turbine
hub and the genera-
tor hub.
The model
Many recent wind
mills use synchro-
nous brushless ma-
chines like annular
or discoidal multipo-
lar generators with
permanent magnets.
They are weaker
than traditional ge-
nerators at identical
torque and speed
(the mass reduction
according to techno-
logy can reach from
20 to 40%). Another
advantage is that
these machines can
have a great num-
ber of poles (200)
and thus rotate at
low speed without
mechanical multi-
plier. A conversion
stage AC/DC/AC is
necessary in order to
be connected to the
network at the con-
venient frequency.
The PSCAD models
make it possible to
simulate this type of
generator with all the
required power elec-
tronic devices.
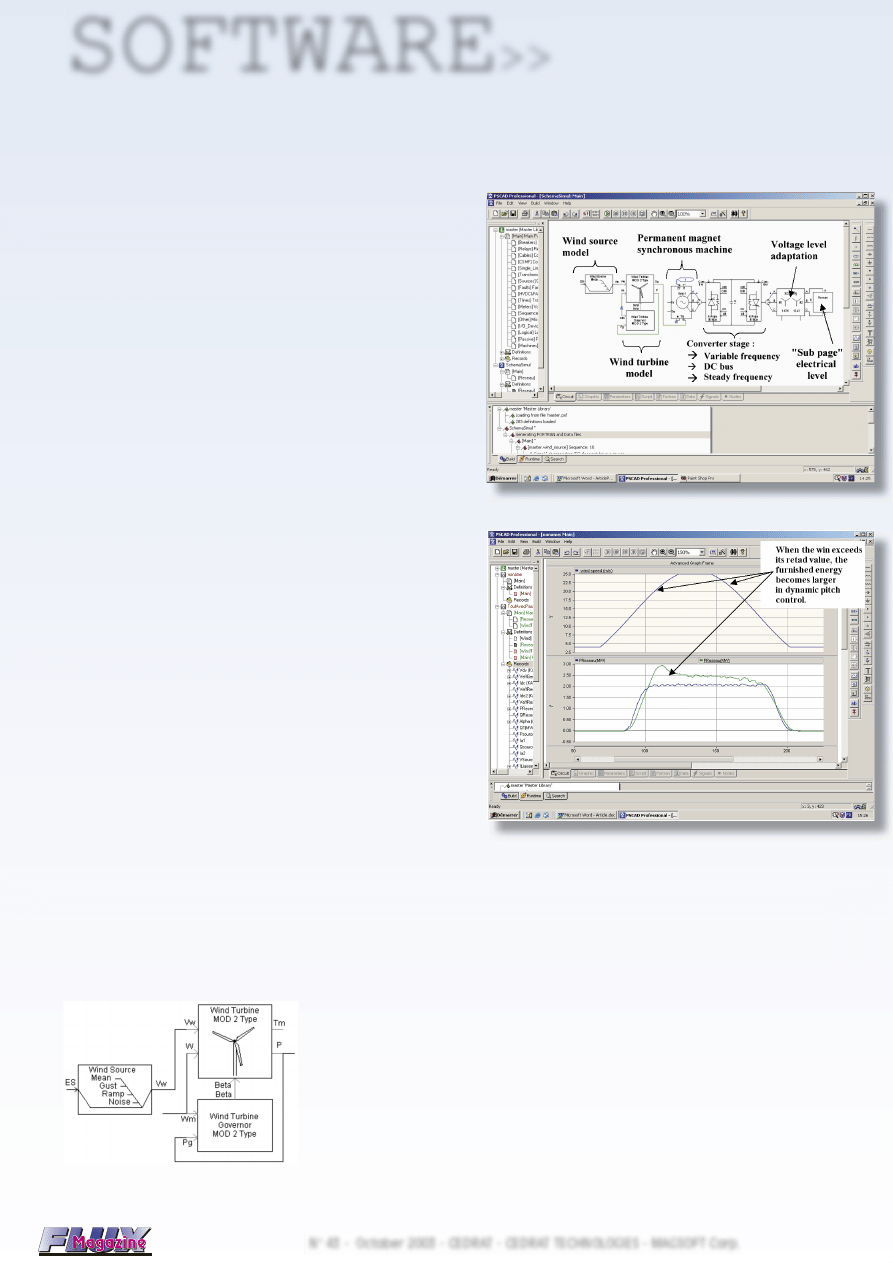
The complete simu-
lation scheme is pro-
posed on fi g. 2.
Simulations
The simulations performed with
PSCAD allowed us to study
the dimensionning of the wind
turbine and the generator, the
DC bus voltage regulation and
the connection to the distribution
network.
In fi gure 3, you can observe the
difference in the power produced
by a wind generator in static pitch
control (blue curve) or dynamic
pitch control (green curve) with a
variable wind speed.
Faults analysis have been made
with PSCAD allowing to know the
infl uence of the wind mill on the
network in such confi gurations
and to defi ne the protections to
choose.
Finally, an entire wind farm
(300 MVA) has been modelled in
PSCAD. Voltage and frequency
stability investigations at the
connection point have been
performed, de to the high power
level of the windfarm compared
with the connected grid.
Conclusion
PSCAD tools and capabilities
allowed to see a large part of the
technical aspects of a wind-mill
dimensionning and its connection
to the network. You will fi nd all
the details of this study in the
technical paper: «Wind Turbine
and Grid Connection Modelling
with PSCAD», available on
software@cedrat.com.
Wind Turbine and Grid Connection Modelling with
PSCAD.
Eric Flammier - EDF; Augstin M'Panda - ESIEE; Fabrice Foucher - CEDRAT.
Figure1: PSCAD model
deicated at wind turbine.
Figure 2: PSCAD model.
Figure 3: Power received on the network
in static and pitch control.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Blade sections for wind turbine and tidal current turbine applications—current status and future cha
[US 2006] D517986 Wind turbine and rotor blade of a wind turbine
[US 2006] D517986 Wind turbine and rotor blade of a wind turbine
Tesla Wind Turbine Grid Connection And Interaction
Modeling Of The Wind Turbine With A Doubly Fed Induction Generator For Grid Integration Studies
DIN 61400 21 (2002) [Wind turbine generator systems] [Part 21 Measurement and assessment of power qu
Darrieus Wind Turbine Design, Construction And Testing
(WinD Power) Dynamic Modeling of Ge 1 5 And 3 6 Wind Turbine Generator {}[2003}
MODELLING GRID CONNECTED VOLTAGE SOURCE INVERTER OPERATION
Grid Impact Of A 20 Kw Variable Speed Wind Turbine
Synchronous Generator And Frequency Converter In Wind Turbine Applications System Design And Efficie
Variable Speed Control Of Wind Turbines Using Nonlinear And Adaptive Algorithms
Design of the Zephyros Z72 wind turbine with emphasis onthe direct drive PM generator
Computer Modelling with CATT Acoustic Theory and Practice of Diffusion Reflection and Array Modelin
więcej podobnych podstron