
Database Modeling and
Basic SQL Syntax
CS 492 Presentation
By: David Zazeski

Goals for this Presentation
1) Learn how to create data models
(specifically E-R diagrams)
2) Understand important SQL syntax

Questions about Data Modeling
What is Data Modeling?
Why do I need it?
How to make a data model?

What is an Entity?
Definition: A noun which describes
a repeatable event, person, place, or
concept which will be stored and
retrieved.
1
1 Source: Modern Database Management by
Hoffer, Prescott, and McFadden

Examples of Entities
Examples:
●
Student
●
Teacher
●
Purchase Order
●
Book

Question
Which of the following should NOT
be considered an entity?
a.)CEO of a company
b.)Student at a University
c.)Printers for sale at Wal-Mart

Attribute
Definition: Property of an entity
Examples:
●
Age of student
●
Hometown of student
●
Length of book
●
ISBN for book

Question
Which of the following should NOT
be an attribute for a printer entity?
a.)Speed of the printer
b.)Quantity of HP model 4338 printer
remaining in the warehouse
c.)Pages Per Minute (PPM)

Relationship
Definition: A connection between
more than one entity
Examples:
●
Student enrolls in class
●
Instructor teaches a class
●
Customer buys a book

Cardinality
Quantifies the size of a relationship.
Examples:
●
More than one student in a class.
●
Only one instructor per class.
●
Book sold to many customers.

Cardinality
List of all possible relationships:
●
Zero to one
●
One to one (ex: Bob marries Susie)
●
One to many (ex: Professor teaches
many students)
●
Zero to many (ex: Product at a store)
●
Many to many (ex: Student enrolls in
course)

Symbols to Represent Cardinality
Can you identify these symbols?

Symbols to Represent Cardinality
Can you identify these symbols?
One to Many
Zero to Many
One to One

Pictorial Example
Draw the ER Diagram for this problem:
Each student has one academic
advisor and each advisor has only
one student. Create an ER diagram
to represent this problem.
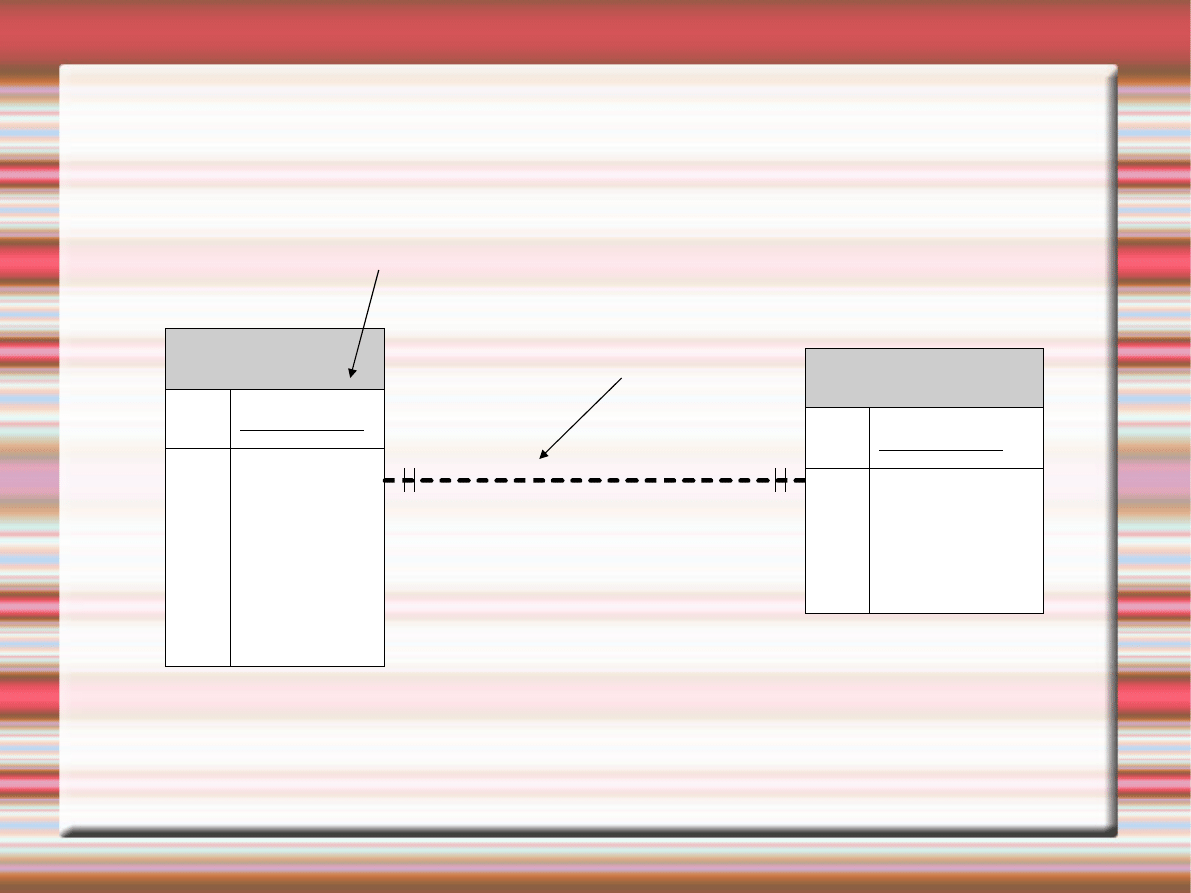
Pictorial Version
Entity:
Student
PK StudentID
Name
Year
Hometown
Major
GPA
has a
Academic Advisor
PK AdvisorID
Name
Department
Available
One to one
Relationship:

Implementation Details
Major SQL statements:
●
Create Table
●
Select
●
Update
●
Delete
●
Drop Table

Popular SQL Queries
Create Table: Used once to setup a table
Syntax: Create Table tablename
(variableName Type, ....);
Example: Create Table Advisors (AdvisorID
Integer, Name String, Department String,
Available Boolean);

Select Statement
Select: Used to retrieve data from a table
Syntax: Select fields from tablename where
Identifier = Value;
Example: Select AdvisorID, Name from
Advisors where Available = true;

Selecting from Multiple Tables
Join: Selects data stored in multiple tables
Two different Types:
Inner Join - Used when two tables share a
common row.
Outer Join - Returns results even when there
is no matching row between tables.

Inner Join Example
Syntax: Select fields from firstTable INNER
JOIN secondTable On firstTable.attribute =
secondTable.attribute where Identifier =
Value;
Example: Select * from Students INNER
JOIN Advisors ON Students.Major =
Advisors.Department where
Advisors.Available = true and
Students.Major = Advisors.Department;

Outer Join Example
Syntax: Select fields from firstTable Left/Right
Join secondTable On firstTable.attribute =
secondTable.attribute where Identifier =
Value;
Example: Select * from Students LEFT JOIN
Advisors ON Students.Major =
Advisors.Department where
Advisors.Available = true and
Students.Major = Advisors.Department;

Update Statement
Update: Change the value stored in a row
Syntax: Update table Set field where
Identifier = Value;
Example: Update Students Set year="senior"
where year="junior";

Delete Statement
Delete: Remove all values meeting certain
criteria
Syntax: Delete fields from tablename where
Identifier = Value;
Example: Delete * from Students where Year
= “Senior”;

Drop Table Command
Drop Table: Remove a table and all of its
contents
Syntax: Drop table tablename;
Example: Drop table Advisors;

Review
1) E-R diagrams help visualize table
structure to aid in design
2) SQL statements implement the
database specified by the Entity-
Relationship diagrams

Additional Topics
1)Normalization – Optimizing
Database Structure between
multiple tables
2)Primary/Foreign Key – Providing a
unique identifier for a table
3)Indexes – Used to optimize tables
4)Views – Aliases to identify frequent
database requests

Sources Cited
1) Modern Database Management by Hoffer,
Prescott, and McFadden (7
th
edition)
2) PHP and MySQL for dynamic web sites by
Larry Ulhman (2003 edition)
3) MySQL website
4) Microsoft Access 2003 Online Help
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Security and Azure SQL Database White paper
Oakeley, H D Epistemology And The Logical Syntax Of Language
02 Modeling and Design of a Micromechanical Phase Shifting Gate Optical ModulatorW42 03
Barite Sag Measurement, Modeling, and Management
Modeling and minimizing process time of combined convective and vacuum drying of mushrooms and parsl
part 2 7 Information Structure and Non canonical Syntax
PROPAGATION MODELING AND ANALYSIS OF VIRUSES IN P2P NETWORKS
Modeling And Simulation Of ATM Networks
Kitayama Culture and Basic Psychological Processes
Code Red Worm Propagation Modeling and Analysis
Multiscale Modeling and Simulation of Worm Effects on the Internet Routing Infrastructure
(Ebook Pdf) Informix 4Gl And Informix Sql
Modeling and tool wear in drilling of CFRP
Bat House Plan and Basic Bat info
AES Information Document For Room Acoustics And Sound Reinforcement Systems Loudspeaker Modeling An
Worm Propagation Modeling and Analysis under Dynamic Quarantine Defense
Modeling and Control of an Electric Arc Furnace
więcej podobnych podstron