1. Vowels - (pure vowels, monophthongs) a vowel made without the glide; vowel sound, one whose articulation at both begginning and end is relatively fixed and which does not glideup and down towards a new position.
2. Description & classification of vowels:
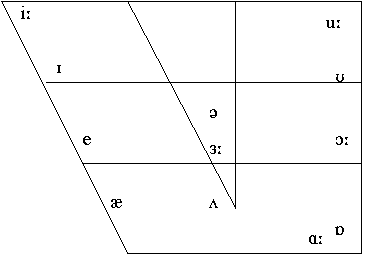
/i:/ - high front long spread vowel
/I/ - mid - high front vowel
/æ/ (ash) - low front vowel
/e/ - mid - low front vowel
/3:/ - mid - central long vowel
/υ/ - mid - high back rounded vowel
/u:/ - high back long rounded vowel
/Λ/ (wedge) - mid - low central vowel
/a:/ - low back long vowel
/כ:/ - mid - low back rounded vowel
/o/ - low back rounded vowel
/ə/ (schwa) - mid - central vowel
3. Factors important while describing vowels:
the shape of lips (rounded, spreaded)
the position of the tongue (high/low; front/back)
rhotacization
the lenght of vowel (short/long)
ALL VOWELS ARE VOICED!
4. Vowel Chart
5. The system of Cardinal Vowels:
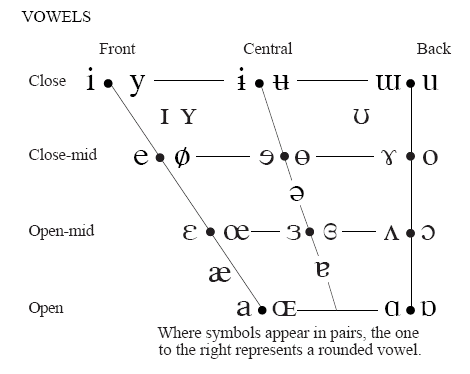
The 8 Cardinal Vowels are not real vowels. They are idealised, extreme points in the physiologically possible range of tongue movement so they can aslo be interpreted as representing a variety of real vowels, produced in the area close to their position. It is not possible to pronounce a Cardinal Vowel. They are useful for reffering to and classifying real vowels.
The difference between Cardinal Vowels and Second Cardinal Vowels is the shape of lips.
6. Diphthongs - (gliding vowel); is a contour vowel, that is a unitary vowel that changes quality during its pronounciation or „glides” with a smooth movement of the tongue from one articulation to another.
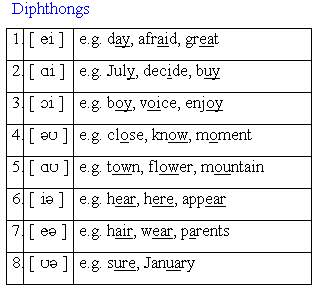
7. Falling diphtong - a diphthong composed of a vowel followed by a less sonorous glide (/oi/ - noise).
8. Rising diphthong - a diphthong in which the second element is more sonorous than the first (/wi/ - quit).
9. Centring diphthong - a diphthong that moves towards a central vowel position for its second element.
10. Closing diphthong - a diphthong which glides towards a closer sound.
11. Triphthong - is a monosyllabic vowel combination involving a quick but smooth movement of the articulator or from one vowel to another that passes over a third. (e.g. [auə] - hour)
12. Nasal vowel - a vowel that is produced with a lowering of the soft palate (velum) so that the air escapes both through nose as well as the mouth.
13. Vowel height - is named for the vertical position of the tongue relative to either the roof of the mouth or the aperture of jaw; tongue is positioned high in the mouth.
14. Vowel lenght - is the percieved duration of a vowel sound.
15. Vowel frontness - describes the position of the tongue where it is as far forward as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction.
16. Vowel backness - describes the position of the tongue where it is positioned as far back as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction.
17. Lip rounding - the shape of your lips while pronouncing rounded vowels; lips form kind of circle like the letter „o”. (horse)
18. Lip spreading - the shape of your lips while pronouncing spreaded vowels; your lips are spread widely. (seed)
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
vowels and cardinal vowels diagram
vowels diphtongs syllable exercises
Krynicki cardinal vowels Polish and English
High back and central vowels handout
diphtongs, vowels exercises
Postmodernity and Postmodernism ppt May 2014(3)
Scoliosis and Kyphosis
L 3 Complex functions and Polynomials
4 Plant Structure, Growth and Development, before ppt
Osteoporosis ľ diagnosis and treatment
05 DFC 4 1 Sequence and Interation of Key QMS Processes Rev 3 1 03
Literature and Religion
lec6a Geometric and Brightness Image Interpolation 17
Historia gry Heroes of Might and Magic
Content Based, Task based, and Participatory Approaches
Lecture10 Medieval women and private sphere
A Behavioral Genetic Study of the Overlap Between Personality and Parenting
Hine P Knack and Back Chaos
więcej podobnych podstron