Name:………………………………………….Group 1
18.04.2008.
1. A chronic infection of hepatitis B is defined as having demonstrated the presence of
a) HBsAg for more than 1 month
b) HBsAg for more than 3 months
c) Antibody against HBsAg for more than 6 months
d) HBcAg for 3 months
2. Coronaviruses are recognized by club-shaped surface glycoproteins that are 20 nm long and resemble solar coronas. Which one of the following is a characteristic ability of these viruses?
a) Agglutinate human red blood cells
b) Cause the common cold
c) Grow well in the usual cultured cell lines
d) Infect infants more frequently than adults
3. The most common natural mode of transmission of infection with hepatitis B virus is via:
a) contaminated water supply
b) body fluids, such as blood
c) direct contact
d) respiratory droplets
4. What virus is noted for genetic reassortment, which leads to major pandemics about once every 10 to 11 years?
a) Adenovirus
b) Herpes virus
c) HIV
d) Influenza virus
5. A patient who worked in an industrial setting presented to his ophthalmologist with acute conjunctivitis, enlarged and tender preauricular nodes and early stages of keratitis. The differential diagnosis should include infection with which of the following viruses?
a) Adenovirus
b) Epstein-Barr virus
c) Respiratory syncytial virus
d) Varicella-zoster virus
6. Two siblings, ages 2 and 4, experienced fever, rhinitis and pharyngitis that resulted in laryngotracheo bronchitis. Both had harsh cough and hoarseness. Which virus is the leading cause of the croup syndrome and when infecting mammalian cells in culture, will hemabsorb red blood cells?
a) Adenovirus
b) Group B coxsackievirus
c) Parainfluenzae virus
d) Rhinovirus
7. Within the first years of life, an infant exhibited sever hearing loss, ocular abnormalities, and apparent mental retardation. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection was detected by viral isolation and PCR. Which of the following statements best characterizes CMV?
a) it can be transmitted across the placental barrier
b) while a common infection, CMV is almost always symptomatic
c) the CMV culture can be cultured from red blood cells of infected patients
d) There is no specific therapy for CMV
8. The diagnosis of a rotavirus infection:
a) can, in most cases, be made on the basis of the clinical presentation
b) can be made on epidemiologic grounds (for example, if there is an epidemic)
c) can be made (test by which rotavirus antigens) Slidex Rota Kit
d) is routinely made by electron microscopy of suitably treated stool samples
9. Which specimen is best for cytomegalovirus?
a) blood
b) cerebrospinal fluid
c) cervical tissue
d) skin
10. Which one of the following viruses may be a definitive human tumor virus?
a) Herpes simplex virus, type 2
b) HIV
c) Papillomavirus
d) Varicella-zoster virus
Name:……………………………………Group 2
18.04.2008.
1. Patients in an outbreak of Flavoviridae disease on a Caribbean island presented with a variety of symptoms, including encephalitis, hemorrhagic fever, or fever with myalgia. Which one of the following is a characteristic of Flavoviridae?
a) Are transmitted by insect vectors
b) Are treatable with antiviral chemotherapy
c) Are usually resistant to other
d) Usually cause symptomatic infection in humans
2. Serological test results from a hepatitis patient reveal: anti-HBcIgM positive, HBsAg positive, HBeAg positive. The correct interpretation of patient's status is:
a) Immune to hepatitis B virus
b) Evidence of receiving hepatitis B vaccine
c) Hepatitis B virus chronic carrier state
d) Acute hepatitis B
3. A 30-year-old man develops fever and jaundice. He consults a physician, who finds that blood tests for HBs antigen and anti-HBs antibody are negative. Which one of the following additional tests is most useful to establish that the hepatitis was indeed due to hepatitis B virus?
a) HBe antigen
b) Anti-HBc antibody
c) Anti-HBe antibody
d) Delta antigen
4. First serological marker indicative of HIV infection is:
a) p24
b) gp 160
c) anti p24
d) all of above
5. An obstetrician sees a pregnant patient who was exposed to rubella virus in the eighteenth week of pregnancy. She does not remember getting a rubella vaccination. Which of the following represents the best immediate course of action?
a) administer rubella immune globulin
b) administer rubella vaccine
c) order a rubella antibody titer to determine immune status
d) terminate the pregnancy
6. A nurse develops clinical symptoms consistent with hepatitis. She recall sticking herself with a needle approximately four months before, after drawing blood from a patient. Serologic tests for HBsAg , antibodies to HBsAg, and hepatitis A virus (HAV) are all negative, however, she is positive for IgM core antibody. Which of the following characterizes the current health state of the nurse?
a) does not have hepatitis B
b) has hepatitis A
c) has hepatitis C
d) is in the “window” (after the disappearance of HBsAg and before the appearance of anti-HBsAg)
7. The “asymptomatic period” following the initial acute disease due to HIV infection is characterized by:
a) high levels of HIV replication in lymphoid tissue
b) high levels of HIV replication in circulating T lymphocytes
c) inability of the immune system to respond to antigenic stimuli
d) high titers of free virus in the blood
8. Atypical lymphocytosis is most likely to be found in which one of the following disease?
a) Encephalitis caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV)
b) Chronic hepatitis C
c) Mononucleosis induced by Epstein -Barr virus
d) Rotavirus gastroenteritis
9. Which one of the following groups of people may be at increased risk for HIV infection?
a) factory workers whose coworkers are HIV- positive
b) foreign service employees who are hospitalized in Zair for bleeding ulcers
c) homosexual females
d) receptionists at a hospital
10. The virus shown in the accompanying electron micrograph contains double-stranded RNA within a double-walled capsid. Which one of the following statements best describes this agent?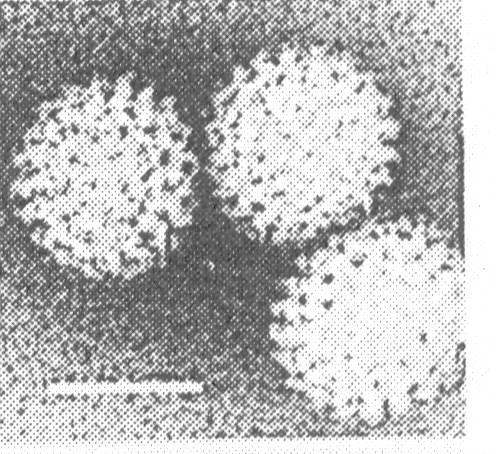
a) Early breast-feeding offers no protection to neonates against it
b) It is a major cause of neonatal diarrhea
c) It is readily cultured from the stool of infected persons
d) Maternal antibody does not appear to be protective
Name:……………………….…………Group 3
18.04.2008.
1. A newborn infant presented with disseminated vesicular lesions and seemed not to thrive. Herpes simplex virus was suspected, and laboratory confirmation was desired to justify antiviral chemotherapy. The most sensitive test for the diagnosis of HSV meningitis in a newborn infant is which of the following?
a) Cerebrospinal fluid protein analysis
b) HSV culture
c) HSV IgG antibody
d) HSV polymerase chain reaction
2. A 10-year-old boy was taken to his pediatrician after experiencing fever, malaise and anorexia, followed by tender swelling of his parotid glands. Mumps was diagnosed on the clinical presentation. Mumps virus accounts for 10 to 15% of all cases of aseptic meningitis in the US. Which of the following characterizes infection by this virus?
a) Is apt to recur periodically in many affected persons
b) Is maintained in a large canine reservoir
c) Is preventable by immunization
d) Usually produces severe systemic manifestations
3. Rotavirus can be ethiological factor of:
a) nonbacterial meningitis
b) diarrhea
c) conjuctivitis
d) all of above
4. A 5-month-old infant, seen in the ER, presents with a fever and persistent cough. Physical examination and a chest x-ray suggest pneumonia. Which of the following is most likely the cause of this infection?
a) Adenovirus
b) Coxsackievirus
c) Respiratory syncytial virus
d) Rhinovirus
5. A husband and wife performed the yearly spring cleaning of their mountain cabin. The wife presented to her physician two weeks later with fever, myalgia, headache and nausea, followed by progressive pulmonary edema. Which of the following statements best desribes the pathogen or disease progression in this patient?
a) Influenza-like symptoms are followed rapidly by acute respiratory failure
b) It is acquired by inhalation of aerosols of the urine and feces of deer
c) Transmission from human to human is common
d) There is effective antiviral therapy available
6. From 1918 until 1956 the only subtype of influenza that was seen in humans was H1N1 was replaced by H2N2. This is an example of:
a) viral interference
b) phenotypic mixing
c) antigenic shift
d) antigenic drift
7. The typical clinical syndrome associated with rotavirus infection is
a) acute gastroenteritis of the young adults
b) acute bronchiolitis of infants
c) acute hepatitis
d) nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea in infants and very young children
8. A hospital worker is found to have hepatitis B surface antigen. Subsequent tests reveal the presence of e antigen as well. Which of the following best describes the worker?
a) is infective and has active hepatitis
b) is infective but does not have active hepatitis
c) is not infective
d) has both hepatitis B and hepatitis C
9. Which of the following markers is usually the first viral marker detected after hepatitis B infection?
a) HBcAg
b) HBeAg
c) HBsAg
d) anti-HBs
10. In a latent viral infection
a) cytopathic effects are commonly seen
b) many viral particles are shed from infected cells
c) the virus is not replicating in the cell
d) the virus is replicating actively but few viral particles are being released
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Mikro testy wyjscie
Mikro testy, spr7, ______________________________________________
Mikro testy, spr7, ______________________________________________
Mikro testy, testy na ost test..., 5
Mikro testy, spr2, Zakażenia wywołane przez szczepy MRSA leczy się :
Mikro testy, spr1, 10
Mikro testy, pytania testowe stomka, 1
Mikro testy, pyt mikrob egz, 1
mikro testy, test na mgr ekonomia, 1
Mikro testy, mikroby
TEST mikro, testy
Mikro testy, pytania egz, 1
więcej podobnych podstron