F00574 003 f002
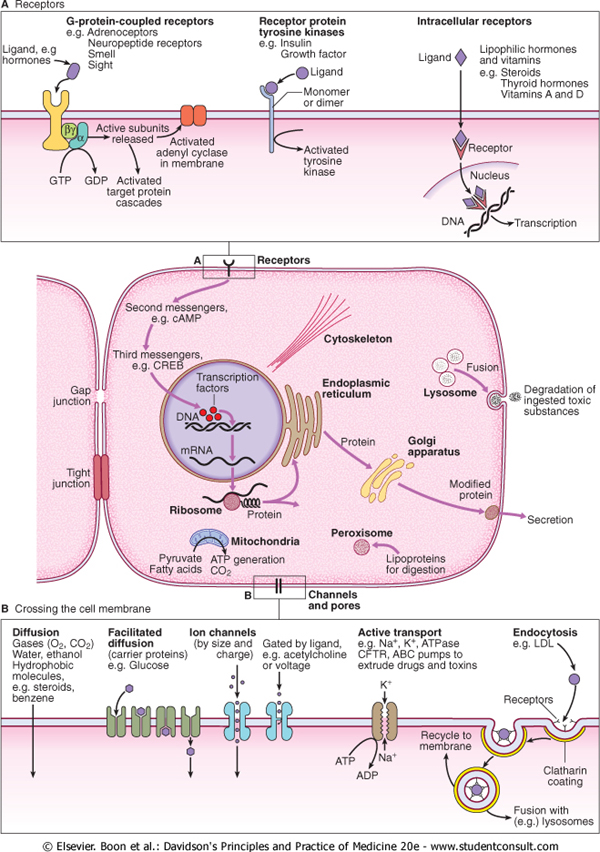
A Receptors
Ugand, e.g hormones•
G-protoin-couplod receptors
e.g. Adrenoceptors
Neuropeptide receptors Smell Sight
Roccptor protein tyrosine kinases
e.g. Insulin
Growth factor
Intracollular rccoptors
a Lipophilic hormones Ligand ty and yitamins e.g. Steroids
Thyroid hormones Yitamins A and D
GTP
GDP Activated target protein cascades
*Activated
tyrosine
kinase
^Receptor
Nucieus
DNA
■P
Transcription
Receptors
Second messengers, e.g. cAMP
Cytoskoloton
Gap
junction
Transcriptii
factors
Fusion
Endoplasmic
reticulum
Lysosomc
Degradation ingested toxi substances
mRNA
rotein
Golgi
apparatus
Tight
junction
Modified
protein
Ribosomo
Protein
Secretion
Mitochondria
Pyruvate ATP generation Fatty adds CO2 ,_
Peroxisomo
Lipoproteins
for digestion
Channels
the celi membranę
and poroś
Diffusion
Gases (02. C02) Water. ethanol Hydrophobic mdecules. e.g. sterokfs. benzene
Facilitatcd
diffusion
(carrier proteins) e.g. Glucose
Active transport
e g Na*. K*. ATPase Cm R. ABC pumps to extrude drugs and toxins
Endocytosis
e.g. LDL
Receptors
qrs
Recycle membran®
Clatharin
coating
Fusion with (e.g.) lysosomes
© Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine 20e - www.studentconsult.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
F00574 001 f002 Propositional knowledgo Knowing what needs to be done Can be taught and leamed © Els
F00574 003 f003 Cłuiescent incomplete DNA repair © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson
F00574 003 f005 First mutationDDEOCttCrc First mutation Normal /_ epittielium — — Basal lamina -
F00574 003 f006 Aj Normal karyotype ^5/ [BjAbnormal karyotype e.gtrisomy21U)l • i_
F00574 003 f007 □ oo 0 d. 50 y Małe. female. unknown sex Clinically affected (specify condition in k
F00574 003 f008 Father Mother Autosomal inheritance (gene on chromosome 1-22) 00_sS Dominant inherit
F00574 003 f009 100% Contribution to phenotype Penetrance threshold (disease manifests) © Elsevier.
F00574 003 f010 Therapy Approaches Some problems Gene therapy Replacement of defective or therapeuti
F00574 006 f002 Scalp As for skin Nail folds/skin webs Topical fungal infections
F00574 009 f002 Routes of cxposurc to toxinsDirect eye contact Eye Eye irrigationMethods of preventi
F00574 011 f002 Cłuiescent Restriction point (regulated by growth factors) Antibiotics and alky
F00574 012 f002 Start here (can take NSAlDs) Start here (can t take NSAlDs) Pain Analgcsics Mild 1
F00574 017 f002 Renal pelvis Prostatę Ureteric orifice Detrusor muscle Urethra © Elsevier. Boon et a
F00574 027 f002 Basement membranę Epidermis Desmosome (desmoglein-1 desmoplakin) -1 and -3, Basal ke
F00574 003 f004 Normal seąuence DNA mRNA Amino acid Point mutations [a] Mis-sense DNA mRNA Amino aci
F00574 007 f002 Changes with ageing Clinical conseguences CNS • Neuronal loss •
003 (38) RECEPTORY: JONOTROPOWE METABOTROPOWE GPCR sprzężone z białkami G ZWIĄZANE Z KINAZĄ TYROZYNO
Serotonina- biologicznie czynna amina, hormon pełniący funkcję m.in. ważnego neuroprzekaźnika w
więcej podobnych podstron