F00574 007 f002
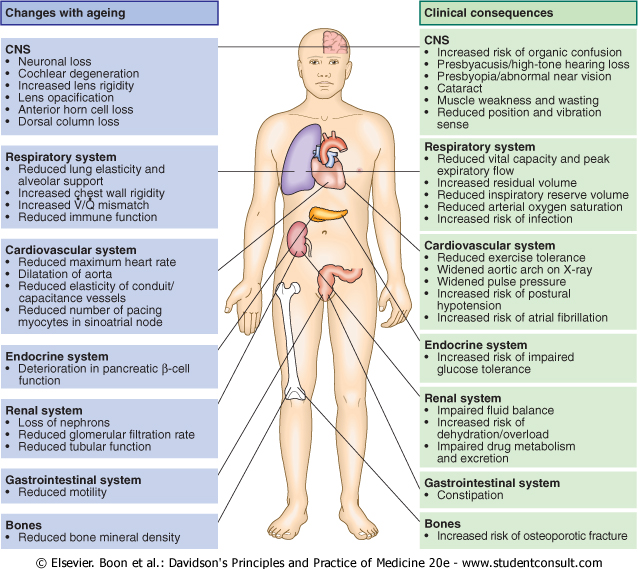
Changes with ageing
Clinical conseguences

CNS
• Neuronal loss
• Cochlear degeneration
• Increased lens rigidity
• Lens opacification
• Anterior hom celi loss
• Dorsal column loss
Respiratory system
• Reduced lung elasticity and alveolar support
• Increased ęhest wali rigidity
• Increased V/Q mismatch
• Reduced immune function
Cardiovascular system
• Reduced maximum heart ratę
• Dilatation of aorta
• Reduced elasticity of conduit/ capacitance vessels
• Reduced number of pacing myocytes in sinoatrial node
Endocrine system
• Deterioration in pancreatic £-cell function
Renal system
• Loss of nephrons
• Reduced glomerular filtration ratę
• Reduced tubular function
Gastrointestinal system
• Reduced motility
Bones
• Reduced bonę minerał density
CNS
• Increased risk of organie confusion
• Presbyacusis/high-tone hearing loss
• Presbyopia/abnormal near vision
• Cataract
• Muscle weakness and wasting
• Reduced position and vibration sense
Respiratory system
• Reduced vital capacity and peak expiratory flow
• Increased residual votume
• Reduced inspiratory reserve volume
• Reduced arterial oxygen saturation
• Increased risk of infection
Cardiovascular system
• Reduced exercise tolerance
• Widened aortic arch on X-ray
• Widened pulse pressure
• Increased risk of postural hypotension
• Increased risk of atrial fibrillation
Endocrine system
• Increased risk of impaired glucose tolerance
Renal system
• Impaired fluid balance
• Increased risk of dehydration/overload
• Impaired drug metabolism and excretion
Gastrointestinal system
• Constipation
Bones
• Increased risk of osteoporobc fracture
© Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine 20e - www.studentconsult.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
F00574 001 f002 Propositional knowledgo Knowing what needs to be done Can be taught and leamed © Els
F00574 003 f002 A Receptors Ugand, e.g hormones• G-protoin-couplod receptors e.g. Adrenoceptors Neur
F00574 006 f002 Scalp As for skin Nail folds/skin webs Topical fungal infections
F00574 007 g001 Vision Hearing Pulse Q Atrial fibrillation? a Cognitive function Abbreviated mental
F00574 007 g002 © GET UP AND GO TEST Ask the patient to stand up from a sitting position, walk 10 m,
F00574 009 f002 Routes of cxposurc to toxinsDirect eye contact Eye Eye irrigationMethods of preventi
F00574 011 f002 Cłuiescent Restriction point (regulated by growth factors) Antibiotics and alky
F00574 012 f002 Start here (can take NSAlDs) Start here (can t take NSAlDs) Pain Analgcsics Mild 1
F00574 017 f002 Renal pelvis Prostatę Ureteric orifice Detrusor muscle Urethra © Elsevier. Boon et a
F00574 027 f002 Basement membranę Epidermis Desmosome (desmoglein-1 desmoplakin) -1 and -3, Basal ke
968 A. Edorh et al. tumors were associated with advanced clinical and histological markers. The esti
It has to be noted that membranę temperaturę and gases partial pressures change with celi current: w
F00574 017 f009 1 1 PRE-RENAL Effects of pre-renal conditions Loss of renal function, e.g. from hypo
F00574 025 f018 Remodellmg of bonę contour Fibrillation and focal loss of hyaline cartilage Mar
Production Systems expectations evolved with changes in consciousness of clients and their awareness
28 1.3 Introduction With global changes comes a higher freąuency of unpredictable weather events (Ea
F00574 003 f007 □ oo 0 d. 50 y Małe. female. unknown sex Clinically affected (specify condition in k
F00574 005 f015 Total - 0 Total = 1 Total £ 2 Low risk Medium risk High risk • Routine clinica
więcej podobnych podstron