F00574 024 g002
o ANAEMIA
The box shows the symptoms and signs that will help to indicate the dinicai $everity of anaemia.
ANAEMIA
Search for symptoms and signs łntfccating the cause of anaemia
Non-specific symptoms
• Tlredness
• Lightheadedness
• Breathlessness
• AnWe-swelling
• Worsening of any previous coewsting disease such as angina
Non-specific signs
• Mucous membranę palior
• Tachypnoea
• Raised jugular venous pressure
• Flowmurmurs
• Ankie oedema
• Posturai hypotension
• Tachycardia
Abnormalities in the blood are caused not only by primary diseases of the blood and lymphoreticular systems but also by diseases affecting other systems of the body. The dinicai assessment of patients with haematological abnormalities must include a generał history and examinahon as well as a search for symptoms and signs of abnormalities of red cells, white cells, piatelets, bleeding and clotting systems. lymph nodes and lymphoreticular tissues.
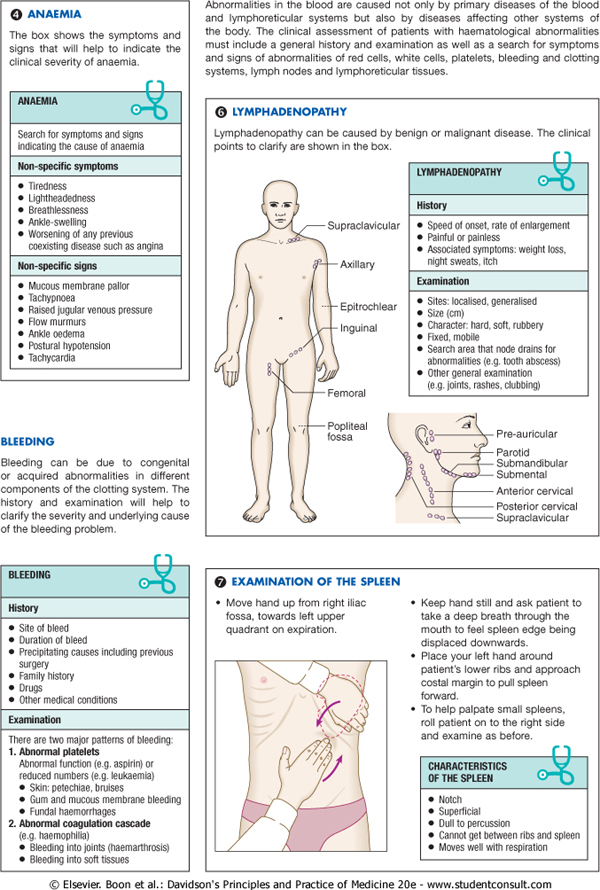
Lymphadenopathy can be caused by benign or malignant disease. The clinical points to ciarify are shown in the box.
LYMPHAOENOPATHY
BLEEDING
Bleeding can be due to congenital or acquired abnormahties in different components of the clotting system. The hlstory and exammation will help to ciarify the severity and underiymg cause of the Weeding problem.
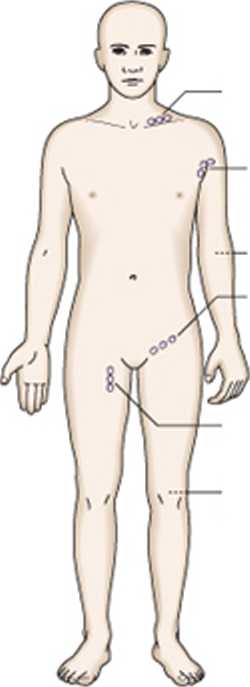
Supradavicular
Axiilary
Epitrochlear
Inguinal
Femoral
History
Speed of onset. ratę of eniargement Painful or painless Associated symptoms: weight lass. night sweats. itch
Examination
Sit es: locaiised. generaiised Size(cm)
Characler hard. soft. rubbery Fixed. mobile
Search area that node drains for abnormalities (e g. tooth abscess) Other generał examlnation (eg. joints. rashes. dubbing)
Popliteal
fossa
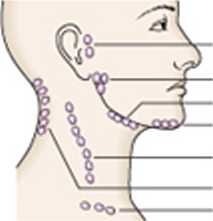
Pre-auricular
Parotid
Submandibular
Submentai
Antenor cervical Posterior cenńcal Supraciavicular
BLEEDING

History
• Site ol bieed
• Duration ot bieed
• Precipitating causes indtiding previous surgery
• Family history
• Drugs
• Other medical conditions
• Move hand up from right iliac fossa. towards left upper guadrant on expiration.
Examination
There are twe major patterns of bleeding
1. Abnormal piatelets
Abnormai function (eg. aspirin) or reduced numbers (eg. leiAaemia)
• Skin: petechiae. bruises
• Gum and mucous membranę bleeding
• Fundal haemorrhages
2. Abnormal coagulation cascade (e.g haemophliia)
• Bleeding Into joints (haemarthrosis)
• Bleeding into soft tissues
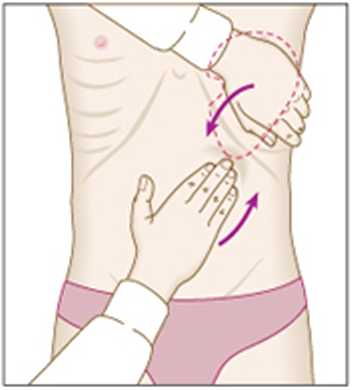
• Keep hand stiil and ask patient to take a deep breath through the mouth to feel spleen edge being dispiaced downwards.
• Race your left hand around patienfs lower nbs and approach costal margin to puli spleen forward.
• To help palpate smali spleens. roli patient on to the right side and examine as before.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SPLEEN

• Notch
• Supcrficial
• Oull to percussion
• Cannoł get between ribs and spleen
• Moves wel with respiration
© Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine 20e - www.studentconsult.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
i * i * signs. or complexes of symptoms and signs. The “diagnoses** of the screening method use
page# (5) Sally, the motel owner, comes to court and says that McQueen needs to fix the road he wrec
F00574 024 f032b © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medłcine 20e - www.s
HelpList2?se By matching four tiles or morę you recharge and upgrade the power-ups that will help yo
F00574 007 g002 © GET UP AND GO TEST Ask the patient to stand up from a sitting position, walk 10 m,
F00574 018 g002 o EXAMINATION OF THE ARTERIAL PULSE • The character of the pulse i
F00574 024 f022a [AjDirect antiglobulin test (DAT) (Coombs test) Detects the presence of antibody bo
koliber II (38) > SPEC1AL NOTĘ: The purple shaded area along the left side of this graph shows&nb
<Ethemet module and commumcation model> The following shows the software configuration of the
tmta 9 Platę 8 Back view of doublet This shows the characteristic V-back of the collar, sometimes ma
MZZ2010B0044 ROOM STRAIGHT-LINE DIMENSIONS (2) Shows position and shape ot the polnlsShows dctails o
dpp62 HOLDING AT ARM S LENGTH The illustration shows the Continental method of holding at arm’s leng
522 M. Daszykowski eł al. To illustrate this, Fig. la shows the original chromatogram of sample 12 (
20101121�7 gp Match the patients’ descriptions of thelr probloms włth tuHflbU technical terms from t
więcej podobnych podstron