netter103
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
Pulmonary Function Testing—cont'd
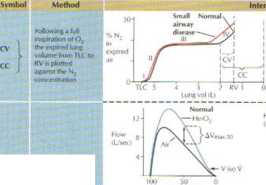
Mguimol «pBu!oc> Spitomeief ot
(WyoIuiih* cwvr pneumojachoyaph
breaMng 60% He to tecofd flow and
and 20% O, V iw V y-okone
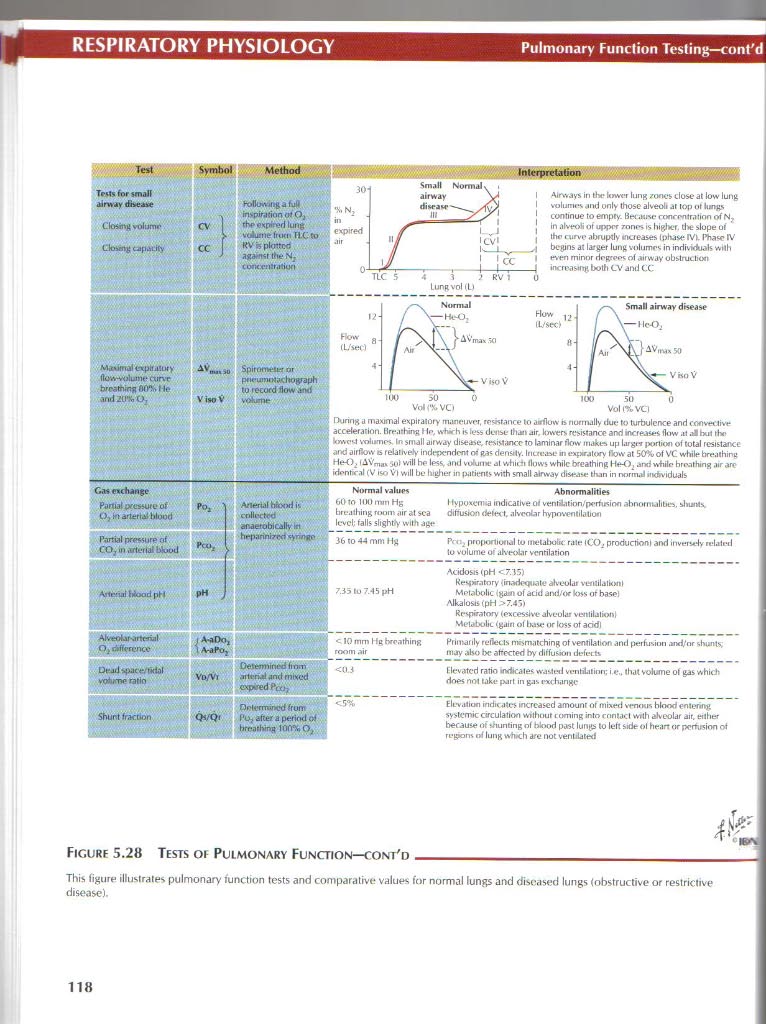
Closjng volumr Ctoung capacity
Airways iti the Iowcr lung zoncs closeat Iow lung yplumes and only those abeoli ar top ol lungs conlinue to empty. ffw.mie ronrnntratmn of N? In abeoli of upprr ronr*> is big) ter. tln- slope u! ihp mrvo abruptjy incteases (plute lVl. Pha^e IV' bcgins at larger lung yulumrs in indbiduaU willi men minor degrees of airway obslruclioo increasmg bolli CV and CC
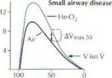
Vol<%VC) Voli%VC|
$ Dunng a maxunal esplratory maneuwr, resisrance to aeflow b nor maiły due to turtwlcnce and coflvettive $ accełeratinn. Hrr-.irhing I In, wh*rh is less deiise llian air. luwcrs resisłance and increases flow at .di bul thr S townJ yolumcs. In smali airway disease, resistancc to laniinar flow makt-s up largrr portion of total tesistancc £| and airflow s telatheły Independent of gasdenaly. Inueasc m exfxrj(ory fiówat 50% of VC wbili* bre.ithing f, He-Oj iJiVnia» sol will ho less, and yufome al whirfi flows whilc broalhlng Me-Oj andwłiile htoaihing airare « identiral (V iso Vi will be higher iii (Jiirients with smali airway disease tlun in norin.d mdwiduals
|
Ga* enchange Partia! pressute ot O, In arteria! blood |
ro. |
Arteria) bćood i*, collectcd ar-aetobioilb In |
Normal values 60 to 100 mm Hg brcalbing ronm air at sca k-vcl; falls slightfy with ag< |
Abnormalities 1 lyponcmia indicarlye Ol yentiLition/perfiision abnornulities. sliunK diffuSłon detect. abeoiar bypneentilalioo |
|
Partial pressure of CO, in arteria! Uuod |
hrparinired syn/łgo |
36 to 44 mm Hr |
P<«.. prnporliorul to ineiabołic rale tCO.. productioni and inveneły relalcil lo volume ot' aKeotir ventilation | |
|
Ai te? ml titoad pH |
pH |
7.35 lo 7.45 pH |
Acidosts (pH <7.35) Keswatory linadesjuale abeolar viMUilatk>nl Metabolic (gam of add and/Oe loss or basel Alkalosts (pH >7.43) Respiratory <excessive abeolar yentiblionl Metabolit. (gam of lwic or loss ot addl | |
|
AlveOłai-.irtPJVil Oj drffcrcncc- |
i A-aOa, t A^Po, |
c 10 mm Hg breathing |
Ptiiiuiily reileciN nK>m,itching oł ventilation and perfusinn amf/or shunts; may abo bc atrected by diffusioii defccts | |
|
Ui*ad space/tkiol y-oiiime talio |
Vo/Vt |
Derwmined finm .eterial and fnlKcd ©tpiredPco, |
<0.3 |
flcvated ratio inrikaleswasteli vent2.1tinn; i.*.*., tbat tolwne of gatwbieb dnes not lakę pait in gas t*xchanRc |
|
Shunt fraccio n |
Qt/Qr |
Oelermincd from Po, after a period of breathing 100% O, |
<5% |
Elev.ition indicalcs mtreasod amount ot mixed vm<Kis blood entering systemie ctrculatioo wilhnut i oming into cnntacl with aboolar ait. eitlier beeause ot sbunting of blood past lungs to left Side ol he.irt or perńrsion of repom of lung wh*h are not vent2at«l |
IW
Figurę 5.28 Tests oe Pulmonary Function—cont'd_
This figurę illusiraies pulmonary function tests and comparalivt? values for normal lungs and diseased lungs (obstructive or restriciive disease).
118
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter77 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYAirway Struclure: Intrapulmonary Airways Segmental bronchus Largo sub
netter85 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYMechanits of Respiration: Airway Flo» Laminar flow occurs mainly in s
netter87 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYIntrapulmonary Circulatior Pulmonary voin Bfonchial artery (from left
netter89 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pulmonary Circulation Distribution of Pulmonar> Blood Flow
45953 netter81 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYMechanics of Rcspiration: Forces during Quict Breathin pressure
82393 netter97 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYRole of the Lungs in Acid-Base BaLar A. Role ot Lungs and Kidne
więcej podobnych podstron