netter89
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
Pulmonary Circulation
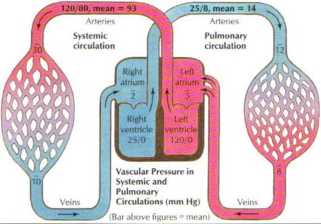
Distribution of Pulmonar>' Blood Flow VenouS
Arterial Alveolar pressure pressure
pressure (mm Hg) (mm Hg)
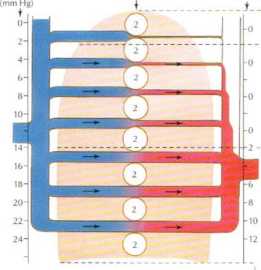
Zonę 1. Alveolar pressure ex ceeds arterial pressure and there is no blood flow to this area. Occurs only abnormally when alveolar pressure is in-creased or arterial pressure is reduced
Zonę 2. Arterial pressure exceed$ alveolar pressure, and alveolar pressure exceeds venous pressure. Blood flow varies with difterence between arterial and alveolar pressure and is greater at bottom of zonę than al top
Zonę 3. Both arterial and venous pressures excced akeolar pressure. Blood flow depends on arterial-venous pressure difterence, which is constant throughout the zonę. Because arterial pressure increases down zonę, transmural pressure becomes greater, capillaries distend, and resistance to flow falls

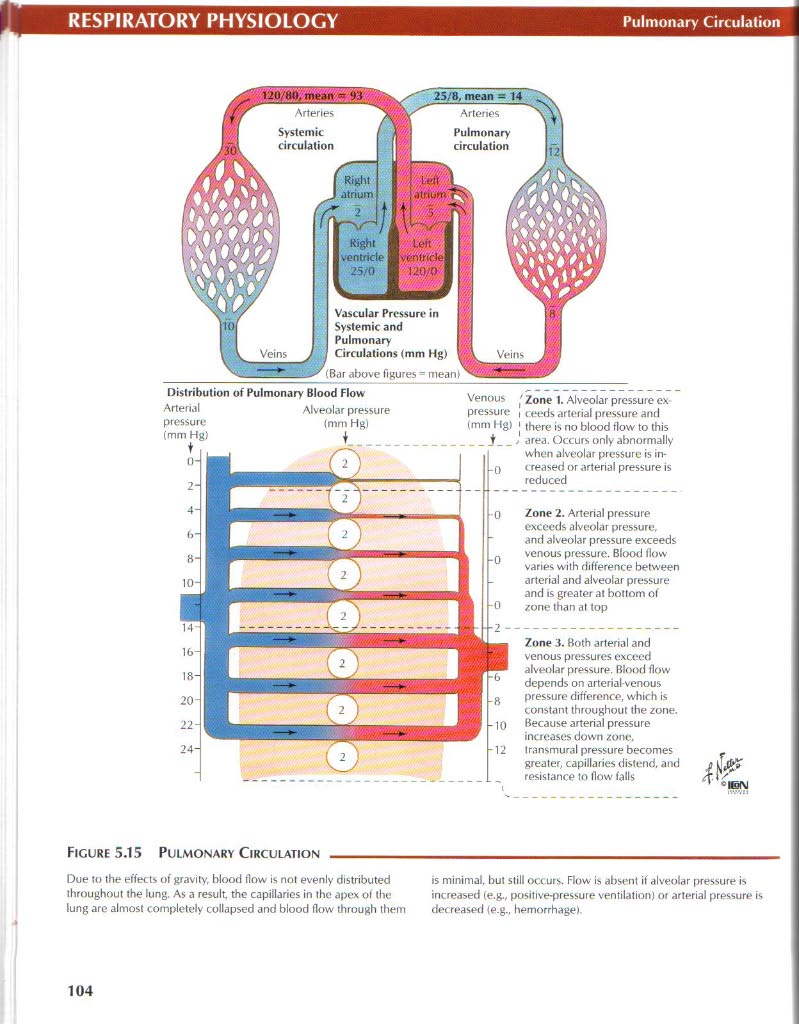
Figurę 5.15 Pulmonary Circulation
Due to the effects of gravitv. blood tlow is not evenly distributed throughout the lung. As a result. the capillaries in the apex o! the lung are almost completely collapsed and blood tlow through them
is minimal. but still occurs. Row is absent if alveolar pressure is increased te.g., positive-pressure ventilation) or arterial pressure is decreased łe.g., hemorrhage).
104
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter87 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYIntrapulmonary Circulatior Pulmonary voin Bfonchial artery (from left
netter85 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYMechanits of Respiration: Airway Flo» Laminar flow occurs mainly in s
45953 netter81 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYMechanics of Rcspiration: Forces during Quict Breathin pressure
82393 netter97 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYRole of the Lungs in Acid-Base BaLar A. Role ot Lungs and Kidne
netter77 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYAirway Struclure: Intrapulmonary Airways Segmental bronchus Largo sub
59840 netter71 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOCY Short-Term Regulation of Blood Pressure 2/3t „NE Ganglion-
netter103 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGYPulmonary Function Testing—cont d Mguimol «pBu!oc>
netter53 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Overview of thc Cardiovascular System Pulmonary
więcej podobnych podstron