netter154
Bilirubin Excretion
Hemoglobin
IndirecHeacting bilirubin (unconjugated)
■■■i Direct-reacting bilirubin
(conjugated) and bile acids Urobilinogen
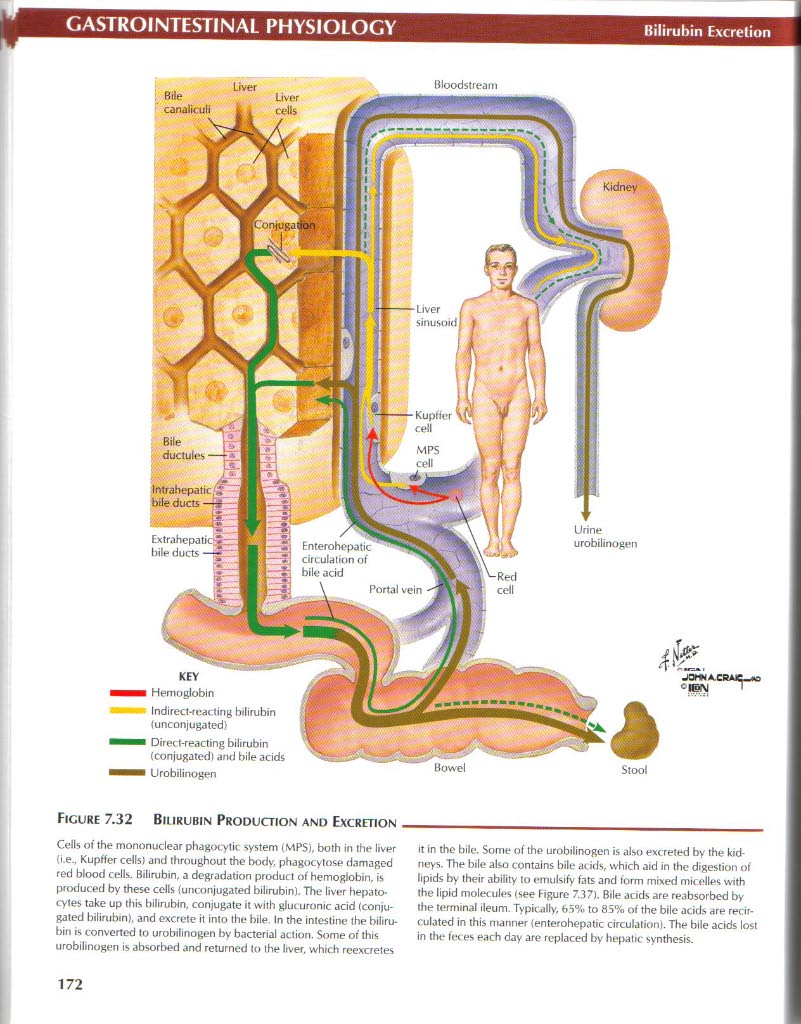
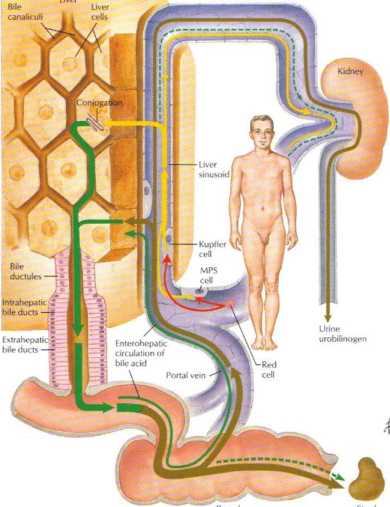
Ficure 7.32 Bil IRUBIN Production and Excretion
Cdls of the mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS), both in the liver (i.e.. Kupffer cells) and throughout tho body, phagocytose damaged red blood c.ells. Bilirubin, a degradation product of hemoglobin, is produced by these cells {unconjugated bilirubin). The liver hepato-cytes take up this bilirubin, conjugate it with glucuronic acid (conju-gated bilirubin), and excrete it into the bile In the intesline the bilirubin is convertcd to urobilinogen by bacterial aetion. Some of this urobilinogen is absorbed and returned to the lrver, which reexcretes it in the bile. Some of the urobilinogen is also excreted by the kid-neys. The bile also contains bile ac ids, which aid in the digestion of lipids by their ability to emulsify fats and form mixed micelles with the lipid molecules (see figurę 7.37). Bile acids are reabsorbed by the terminal ileum. Typically, 65% to 85% of the bile acids are recir-culated in this manner ienterohepatic circulation). The bile acids lost in the fot es each day are replaced by hepatic synthesis.
172
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter124 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Lowrr Esophageal Sphincter mm Mr Normal LES tonę is physiologi
netter132 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Appetite and Hunger Smell I Vcntomcdial hypothalami .offood 1
netter140 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Smali Intestinc Structure: III Mitochondria Tight junctions ■
netter156 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Overvievv of Cii Trać! Fluid and Electrolyte Transport Ingest
netter158 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Digestion of Carbohydrales Maftose Pancreatic amyiase
netter130 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Major Cl Hormones LEGEND Thick linę indicatcs prinwry action T
47750 netter160 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGYAbsorption of Essential Elements and Vitamins Iron Elem
więcej podobnych podstron