skanuj0027 (154)

12.11 Radicular Lesions: Motor Deficits
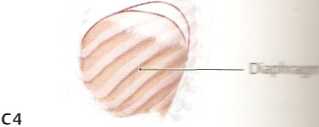
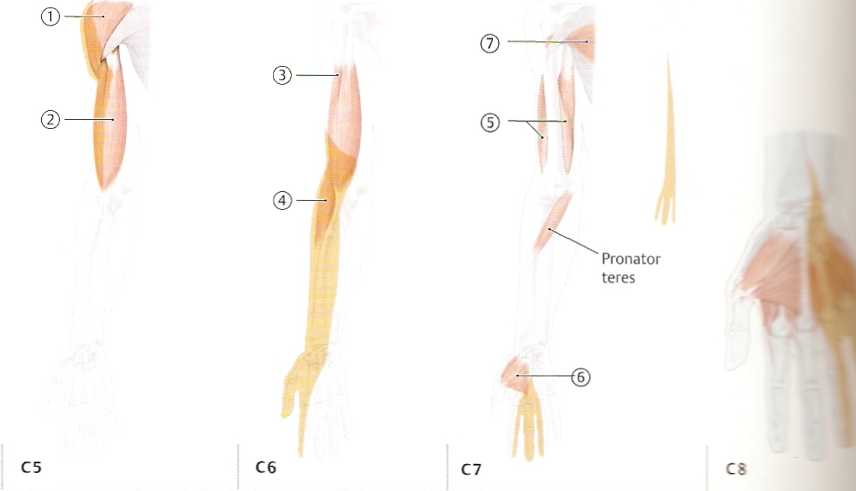
A Indicator musdes of radicular lesions—limb musdes and diaphragm (after Kunze)
Paą, j seoattfl
Location of pain or sensory disturbance
Indicator muscle
Reflexes abolished by a segmental lesion
While a lesion of the sensory dorsal roots leads to sensory disturbances in specific dermatomes (see p. 344 and C, p. 345), a lesion of the motor ventral roots will cause weakness to develop in specific musdes. Just as the affected dermatome indicates the site of the sensory root lesion, the affected muscle indicates the level of the damaged spinał cord segment or its root. The musdes that are predominantly supplied by a particular spinał cord segment are called its indicator musdes (analogous to the dermatomes for the dorsal roots). Because indicator musdes are supplied predominantly but, as a rule, not exdusively by a single segment, a lesion in one segment or spinał nerve root usually causes weakness (paresis) of the affected muscle ratherthan complete paralysis (plegia). Slight weakness may also be noted in musdes that receive some inner-vation from the affected segment but are not principally supplied by it. The indicator musdes in the upper and lower limbs are listed in the ta-bles below. Whereas sensory (dorsal) root lesions may occur in isolation, motor (ventral) root lesions usually occur in association with dorsal root lesions, and therefore the dermatomes are also listed in the tables. Notę: Because these nerves of the trunk are derived directly from the spinał nerve roots without any intervening plexuses, the pattern of seg-mental innen/ation in the trunk is identical to the pattern of peripheral innervation.
|
Location of pain |
Lateral and posterior side |
Dorsoradial upper arm, |
Posterior side of upper arm, |
Ulnarace stwh |
|
or sensory |
of shoulder, anterolateral |
radial forearm |
extensor side of forearm |
to |
|
disturbance |
side of proximal forearm |
—* thumb |
—♦ second/third (fourth) finger | |
|
Indicator muscle |
© Deltoid |
© Biceps brachii |
© Triceps brachii, hand and |
------ , J |
|
(and other |
© (Biceps brachii) |
© (Brachioradialis) |
digital flexors and extensors |
fleios i |
|
affected musdes) |
© Thenar musdes |
(TriGeasta^^H | ||
|
© Pectoralis major (atrophy of |
~ąor-£OHM | |||
|
Reflexes abolished |
stemocostal part) | |||
|
by a segmental |
Biceps reflex |
Biceps reflex |
Triceps refłex |
Trfcss - =fer |
|
lesion |
(Brachioradialis ref!ex) |
(Brachioradialis refłex) |
(Trómner reflex) |
(TtoMni^H |
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
skanuj0027 (154) 12.11 Radicular Lesions: Motor Deficits A Indicator musdes of radicular lesions—lim
85123 skanuj0282 (5) O O W 0, 2/6, 4/6 • o W 1/6, 3/6, 5/6 o Al W 5/12 , 11/12 Al W 1/12,
p30 (11) rd support rod nut (located back of inner choin gucrrd) and remove support rod. 26. &
424 (12) 397 Conservation Instrumental analysis More-accurate analysis of metal composition, corrosi
skanuj0019 (234) A A-A Rys. 2.11. Układ żeber stali zbrojeniowej 18G2 (A—II) Rys. 2.12. Układ żeber
skanuj0019 (234) A A-A Rys. 2.11. Układ żeber stali zbrojeniowej 18G2 (A—II) Rys. 2.12. Układ żeber
skanuj0013 (154) 2009-12-04 Potencjał czynnościowy mięśnia sercowego Potencjał spoczynkowy wynosi -9
skanuj0004 (13) Model 11.Model 12. Materiały: 10gambma
skanuj0008 (340) 8. 9. 10.11.12. 13. 14. Mary is a very_student, never failing to do her homework. D
79243 skanuj0004 (13) Model 11.Model 12. Materiały: 10gambma
skanuj0004 (33) •mg/1 11.Jaka jest dopuszczalna zawartość SO2 w winach owocowych 12.Co wyraża i jaki
88479 skanuj0008 (340) 8. 9. 10.11.12. 13. 14. Mary is a very_student, never failing to do her homew
79243 skanuj0004 (13) Model 11.Model 12. Materiały: 10gambma
skanuj0008 (494) I 12 w:;
więcej podobnych podstron