netter155

Gallbladder Structure and Functiun
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
R. and L hepatic duets R. and L. hepatic arteries Common hepalic duet Cystic duet Propcr hepatic artery Common bile duc.l R. gastric artery
Gallbladder-microscopie section (hepatic side)
edge of anterior layer of lesser omentum
of gall-
Cystic duet Cystic duet (pars spiralis) ^ars gjght hepatic duet
Neck
gallbladder
Major papilla (of Vater)
hepatic duet
Common bile duet—microscopie section
4
l%N
Ficure 7.33 Gallbladder Structure and Function
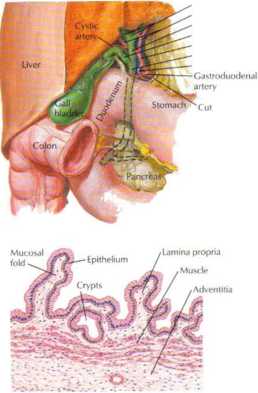
The gallbladder is a smali hollow organ attached to the surface of the hver. It serves to storę and concentrate the bile synthesized by the liver (holds about 20 to 50 ml of bile). Vagal stimulation and chole-cystokinin released from neuroendocrine cells in the duodenum (in response to the presence of fat) cause the gallbladder to contract and transport bile down the cystic duet and the common bile duet, where ii empties into the second (descending) portion of the duodenum. The gallbladder mucosa is specialized for electrolyte and water absorption, which allows the gallbladder to concentrate the bile.
173
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter52 Fxcitation-Conlraclion CouplingMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY HART 3.1 COMPARISION OF MUSCLE STRUCTURE A
Protein structure and function 2. Techniki badawcze w biologii roślin Research techniques in
2 (1621) CONTENTSSUMMARY OF1 Structure and functions of skin and coat Chiara Nołi
26411 netter111 ADH Secrelion and ActiolRENAL PHYSIOLOGY MtCHANISM OF ANT1DIURETIC HORMONE IN REGUŁ
7 Tait, R. D., R. J. Shiel & W. Koste, 1984. Structure and dynamics of zooplankton communities,
i. Introduction CCT diagrams are used for detennination of the phase structure and hardness of steel
Pre-requisite(s): AC1117 or equivalent Co-requisite(s): Nonę Module Content: Capital structure and d
więcej podobnych podstron