netter178

Endocrine Pancreas
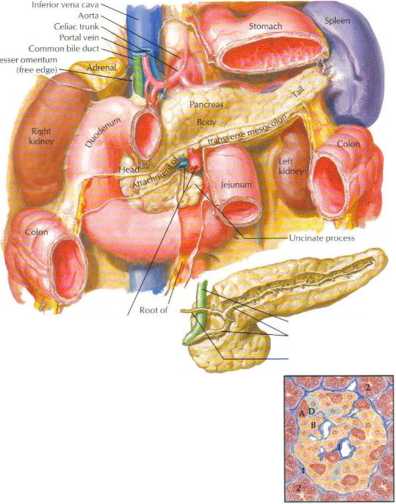
Pancreatic islet A i - ot-),
B : = p ), and D l =8 ) cells. 1. Reticulum, 2. acini
Superior mesenteric vessels mesentery
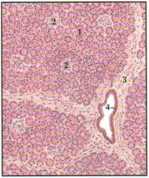
low-power section of pancreas 1. Acini, 2. islet, 3. interłobular septum, 4. interłobular duet
ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY
Common bile duet Principal pancreatic duet (Wirsung's>
Accessory pancreatic. duet (Santorini'$)

Figurę 8.18 Structure of the Endocrine Pancreas
The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. Its digestive enzymes aro socreted into the duodenum via the pan<reatic duet >ystem, and about 99% o i the cells are exocrine in tunction isee Fig-ures 7.26 and 727). The endocrine portion of the pancreas is tepre-sented by clusters of islei cells (of Langerhans) (lower left micro-graph), a heterogeneous population of cells responsible for the elaboration and secretion of glucagon (a-eells), insulin (/3-cells), and somatostatin (8 cells). Glucagon is a fuef-mobilization hormone (sec
Figurę 8.21). Insulin is a fuektorage hormone (see Figurę 8.20). Somatostatin has a number of actions in the Gl tract; within the islets, rt a< ts on both the «- and /$<elis to suppress glucagon and insulin secretion. A tourth celi type, the F celi (not shown), secretes pancreatic polypeptide, whose primar>’ action is to inhibit the secretion of enzymes and HCO, by the exocrine component of the pancreas.
197
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter183 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Gonad and Genital Duet Formation (pulled aside) I .‘rogemtoi•y Testos
netter11 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYCerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Brain Ventricles and CSF Composition Frontal (ant
netter165 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Posterior Pituilary: Oxytocin Oxyto<in pickcd up by capillaries of
netter167 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Growth Hormone Increased linear growth : Decreased adiposity Increase
netter185 ENDOCRINE
więcej podobnych podstron