netter189
Prolacti
ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY
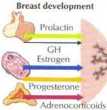
Prolactin-inhihiting factor (PIF), thought to bc dopamine, modulates prolactin secretion. Elcvatod prolactin levcłs increase PIF secretion and cause feedback inhibition of prolactin secretion (shorl-loop feedback inhibition). Estrogen and TRH slimulate prolactin secretion
Pregnancy Laclalion
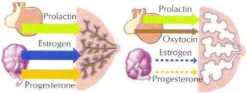
Prolactin, along with GH. estrogen, progeslerone, and adrcnocorticoids, is nccessary for breast development
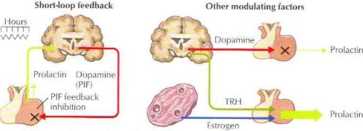
In pregnancy. elevated prolactin, estrogen, and progesterone increase alveolobular development. I ligh estrogen levels inhibit lactation
Sudden decreasc in estrogen and progesterone m presence of prolactin rcsults in milk production. Oxytocin stimulates milk release
Variations in prolactin lcvcl$ by age or condition
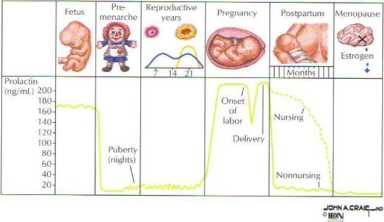
Figurę 8.29 Lactation__
T*w 'Ole of prolactin in breast deyelopment, pregnancy, and laclalion inhibitory control of dopamine (PIF), Abbmńtion: CH, Growlh hor-is summarized in Ihis figurę. Although prolactin is under dual hypo- monę.
Ihalamic control, it is unique because its secretion is under the
208
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter119 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Renal HCO, Reabsorption Factor Principal Site of Action Increased H+
netter176 AldosteroneENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOCY Blood volumc Renal factors Hyperkalemia
netter105 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Bowman s capsule Parietal epithelium Visceral epithelium (podocytes) Mesa
netter124 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Lowrr Esophageal Sphincter mm Mr Normal LES tonę is physiologi
netter132 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Appetite and Hunger Smell I Vcntomcdial hypothalami .offood 1
netter140 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Smali Intestinc Structure: III Mitochondria Tight junctions ■
netter145 DetecationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Certam physiologic. events, as arising (orthocołir r
netter146 LGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Salivary Gland Structure Submandibular gang
netter156 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Overvievv of Cii Trać! Fluid and Electrolyte Transport Ingest
więcej podobnych podstron