SCAN0044
38 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System
38 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System
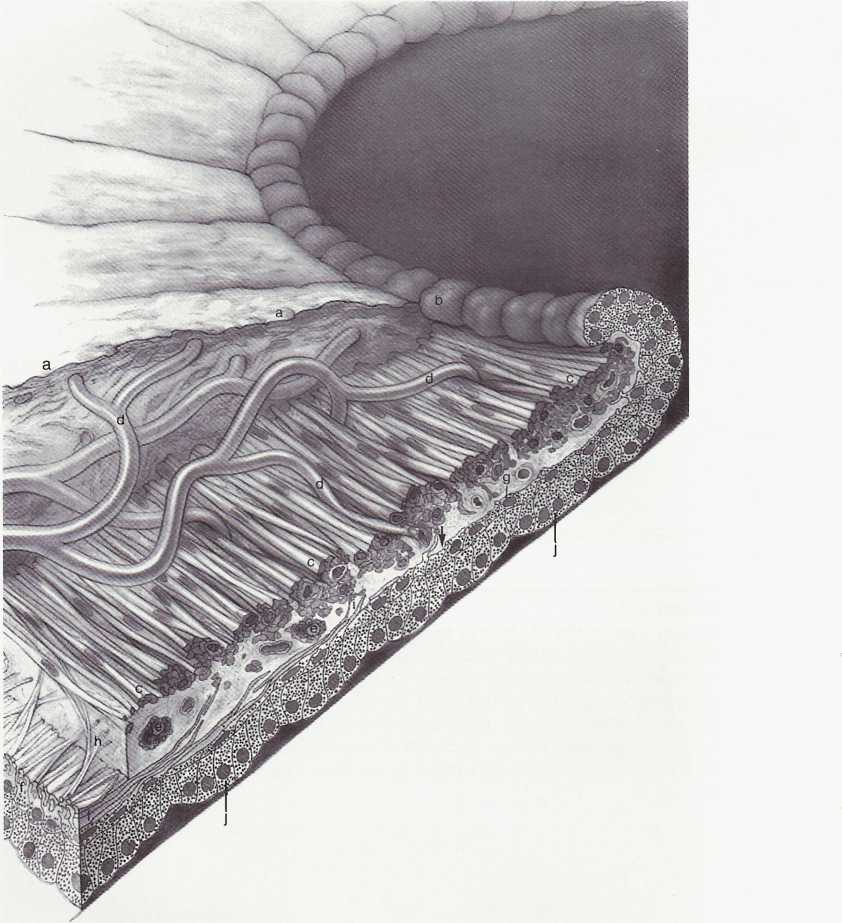
FIGURĘ 3-6
Pupillary portion of the iris. Dense cellular anterior border layer (a) terminates at pigment ruff (b) in pupillary margin. Sphincter muscle is at c. The arcades (d) from the minor circle of iris extend toward pupil and through sphincter muscle. Sphincter muscle and iris epithelium are close to each other at the pupillary margin. Capillaries, nerves, melanocytes, and clump cells (e) are found within and around the muscles. The three to five layers of dilator muscle (f) gradually diminish in number until they terminate behind midportion of sphincter muscle (arrow), leaving Iow, cuboidal epithelial cells (g) to form the anterior epithelium of pupillary margin. Spurlike extensions from dilator muscle form Michel's spur (h) and Fuchs' spur (i), which extend anteriorly to blend with sphincter muscle. Posterior epithelium (j) is formed by tali columnar cells with basally located nuclei. Its apical surface is contiguous with apical surface of anterior epithelium. (From Flogan MJ, Alvarado JA, Weddell JE: Histology of the human eye, Philadelphia, 1971, Saunders.)
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
SCAN0044 crop FIGURĘ 3-6 Pupillary portion of the iris. Dense cellular anterior border layer (a) ter
SCAN0042 10 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 10 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 2-
SCAN0043 36 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 3-2 Periphery of anterior segment of the gl
SCAN0131 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 5-
SCAN0131 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 5-
75024 SCAN0131 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIG
86388 SCAN0154 264 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 14-9 The near pupillary response. Do
33407 SCAN0128 90 Clinical Anatomy of the Visua! System 90 Clinical Anatomy of the Visua! System FIG
SCAN0033 crop Eye Axes Since the eye is not rotationally symmetric (i.e. the centers of curvature of
więcej podobnych podstron