SCAN0145
178 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System
Epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
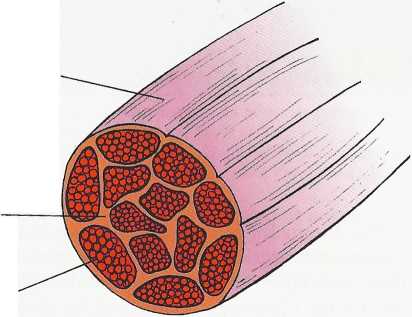
Connective tissue network of striated muscle.
the overall effect of shortening the sarcomere and tł entire muscle.
STRUCTURE OF THE EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES
The extraocular muscles have a denser blood suppl; and their connective tissue sheaths are morę delicat and richer in elastic fibers than is skeletal muscle Fewer muscle fibers are included in a motor unit ii extraocular muscle than are found in skeletal musd elsewhere. Striated muscle of the leg can contain severa hundred muscle fibers per motor unit;6 in the extra ocular muscles, each axon innervates 3 to 10 fibers. Precise fine motor control and ąuick accurate movemen of the extraocular muscles occur because of this denst innervation. Singly innervated fibers have the classic end piąte (en placjue) seen in skeletal muscle; multiph
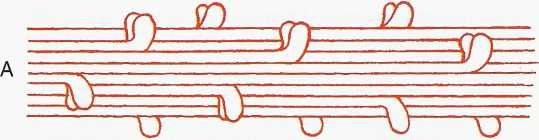
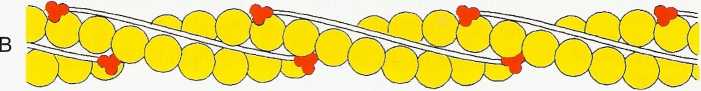
FIGURĘ 10-2
Myosin and actin myofibrils. A, Myosin fibril is composed of two-headed filaments, with heads arranged in a spiral. B, Actin myofibril is composed of double-helix filament to which troponin-tropomyosin complex is attached.
A band I band
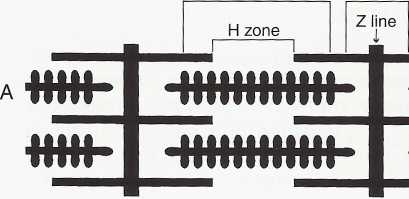
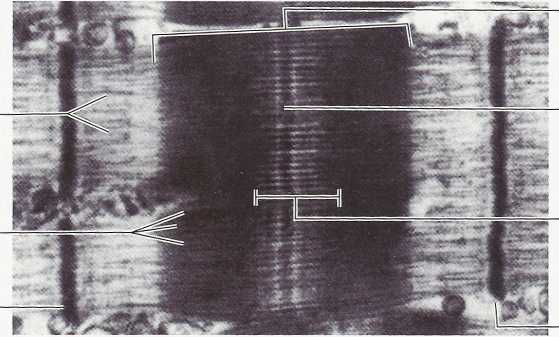
FIGURĘ 10-3
A, Arrangement of thick and thin filaments in sarcomere. B, Photomicrograph of striated muscle, with parts of sarcomere indicated.
(B from Krause W), Cutts JH: Concise text of histology, Baltimore, 1981, Williams & Wilkins.)
B
Actin
filaments
Myosin
filaments
Z linę
A band
M linę
H band
Z linę
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
SCAN0145 178 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System Epimysium Perimysium EndomysiumFIGURĘ 10-1 Connec
SCAN0131 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 5-
SCAN0125 44 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System mented melanocytes, fibroblasts, and collagen band
SCAN0131 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIGURĘ 5-
SCAN0151 214 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System Parotoid lymph nodeFIGURĘ 11-13 Lymphatic drainag
SCAN0152 218 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual SystemFIGURĘ 12-1 Orbit viewed from above showing branch
75024 SCAN0131 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System 96 Clinical Anatomy of the Visual System FIG
więcej podobnych podstron