55037 skanuj0032 (103)
Neuroanatomy 9. Spinał Cord
9.2 Spinał Cord, Organization of Spinał Cord Segments
Neuroanatomy 9. Spinał Cord
Posterior
column
Posterior
funiculus
Lateral
fasciculus
Anterior
funiculus

pathetic (visceromotor) ne_rm«
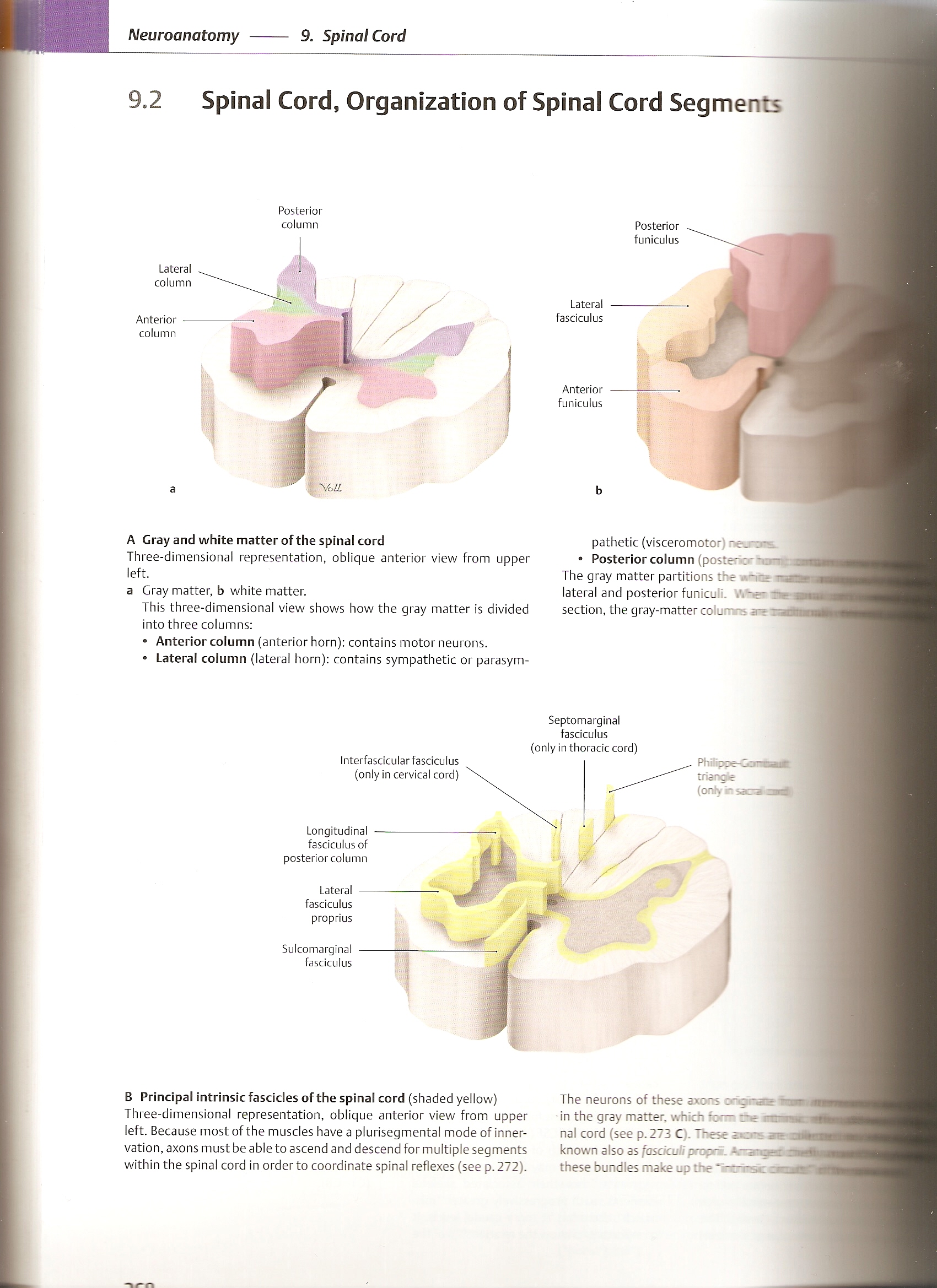
• Posterior column (posterior The gray matter partitions the v.-n~ rnssa j lateral and posterior funiculi. section, the gray-matter columr^ a*?
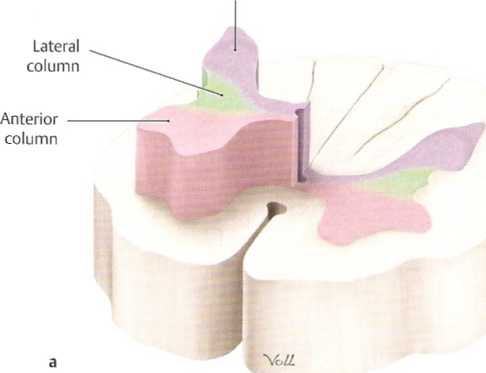
A Gray and white matter of the spinał cord
Three-dimensional representation, oblique anterior view from upper
left.
a Gray matter, b white matter.
This three-dimensional view shows how the gray matter is divided into three columns:
• Anterior column (anterior horn): contains motor neurons.
• Lateral column (lateral horn): contains sympathetic or parasym-
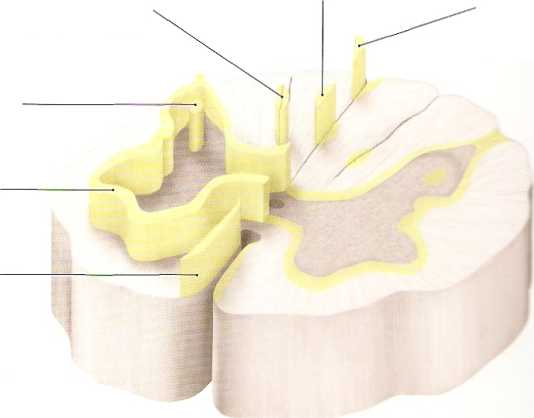
Interfascicular fasciculus (only in cervical cord)
Septomarginal
fasciculus
(only inthoracic cord)
Longitudinal fasciculus of posterior column
Lateral fasciculus proprius
Sulcomarginal fasciculus
Phil i poe-Comwadfc
triange
(onły ir
The neurons of these axons ońarnae in—I in the gray matter, which form rtę rrmra— nal cord (see p. 273 C). These known also as fasciculi propraL these bundles make up the ‘ —i-sc zira/tti
B Principal intrinsicfascides of the spinał cord (shaded yellow) Three-dimensional representation, oblique anterior view from upper left. Because most of the muscles have a plurisegmental modę of inner-vation, axons must be able to ascend and descend for multiple segments within the spinał cord in order to coordinate spinał reflexes (see p. 272).
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
skanuj0032 (103) Neuroanatomy 9. Spinał Cord9.2 Spinał Cord, Organization of Spinał Cord Segments Ne
skanuj0009 (376) Neuroanatomy 9. Spinał Cord.13 Spinał Cord, Topography A Spinał cord and spinał ner
skanuj0009 (376) Neuroanatomy 9. Spinał Cord.13 Spinał Cord, Topography A Spinał cord and spinał ner
skanuj0009 (103) 8. Was wollen die Leute damit sagen? a) b) c) d) Im Vorstellungsgesprach fragt Herr
skanuj0015 (279) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain -landtudinal Mrafcsure ■PHlfillilll
skanuj0016 (266) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain10.4 Coronal Sections: VII and VIII
skanuj0017 (103) Tablica 2: Wartości orientacyjne liniowego współczynnika sprzężenia cieplnego (ciąg
skanuj0030 (103) 46. : . . ; .
więcej podobnych podstron