46 (412)
3.5.2A.
Specific technique to increase dorsal flexion of the occiput on the atlas.
P sitting.
Starting Position: P: Sitting; left side of head supported against T’s chest.
T: Standing facing P’s left side.
Grip: The tip of T’s right index finger stabilizes the ventral aspect of the right transverse process of P’s atlas. The rest of T’s right index finger and thumb lie along the posterior arch of P’s atlas. P’s head is fixed beetween T’s left hand and chest. T’s left palm cups comfortably over P’s ear, with the arm positioned to avoid uncomfortable pressure on P’s mandible.
Procedurę: Using this grip, T applies traction, and then maintaining this traction, induces ventral glide of P’s occipital condyles on the atlas while moving his/her body to gradually and fully dorsally flex occiput on the atlas.
Stimulation of Antagonists: T retains grip, and asks P to look upwards, thrust chin out, and dorsally flex in the direction just stretched. T resists that movement to stimulate P’s antagonists.
Notes: Ideally, T should induce dorsal flexion involving simultaneous and equal right and left occipital condyle ventral glide on the atlas. However, in practice this is possible with P sitting only if T’s hands are large enough to permit simultaneous stabilization of both transverse pro-cesses of the atlas. In most cases, T will be able to stabilize only one side of the atlas at a time.
So to promote the desired occipital condyle ventral glide, T must treat in two stages, first on P’s right (as shown here), and then on P’s left. The procedurę for P’s left is the mirror image of that shown here; T stands facing P’s right side, stabilizes P's atlas with left hand, and hxes P's head with right hand.
If T is unable to firmly grip P’s head, the supine technique of 3.5.2C, p. 48 may be used.
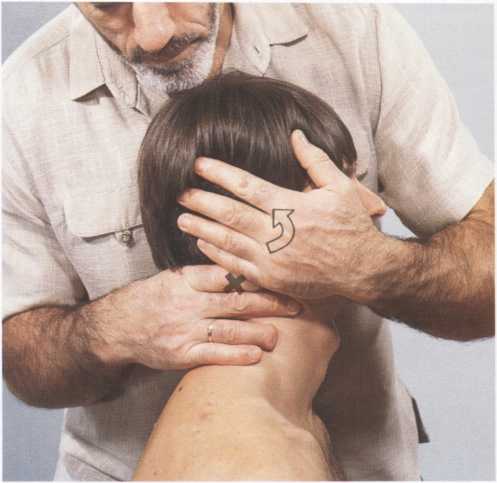
Fig. 30 a. Starting Position.
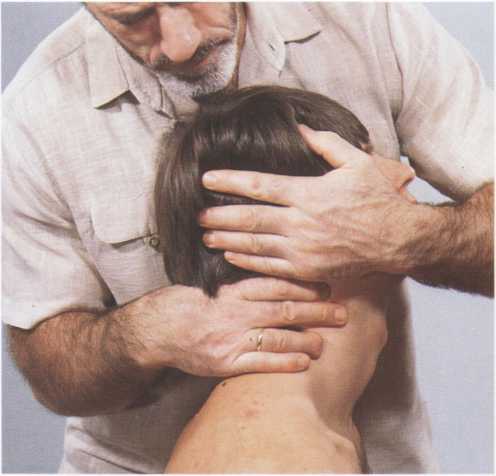
Fig. 30 b. Finał Position.
46
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
49 (372) 3.5.3A. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion of the atlas on the axis. P. sitting.
50 (351) 3.5.3B. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion of the atlas on the axis. P sitting.
51 (336) 3.5.3C. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion of the atlas on the axis. P supine. S
47 (396) 3.5.2B. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion of the occiput on the atlas. P sittin
48 (390) 3.5.2C. Specific technique to increase dorsal flexion of the occiput on the atlas. P supine
60 (278) 3.6.2A. Specific technique to increase dorsal flexion with rotation and lateral flex-ion to
58 (289) 3.6.1A. Non-specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation and later-al flexio
61 (265) 3.6.2B. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation and lateral flex-ion to
62 (263) 3.6.2C. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation and lateral flex-ion to
63 (253) 3.6.2D. Specific technique to increase dorsal flexion with rotation and lateral flex-ion to
64 (250) 3.7.1A. Non-specific technique to increase dorsal flexion with rotation to the right a
65 (245) 3.7.IB. Non-specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation to the right a
66 (237) 3.7.1C. Non-specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation to the right a
67 (234) 3.7.2A1. Specific technique to increase dorsal flexion with rotation to the right and
68 (230) 3.7.2A2. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation to the right and
69 (224) 3.7.2B. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation to the right and l
71 (223) 3.7.2D. Specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion with rotation to the right and l
45 (421) 3.5.1. Non-specific techniąue to increase dorsal flexion. P supine. Starting Position: P: S
56 (315) 3.5.5C. Non-specific technique for the deep ventral muscles to increase dorsal flexion
więcej podobnych podstron