14146
The heat released or consumed duńng particular Chemical reaction can be measured calorimetrically. There are two distinct techniąues iised: a constant volume calorimetry and tlie constant pressnre calorimetry. The former one is nsed to detennine intemal energy change and indii ectly enthalpy change wliile the latter is nsed to detennine enthalpy change directly.
2. Calorimetry
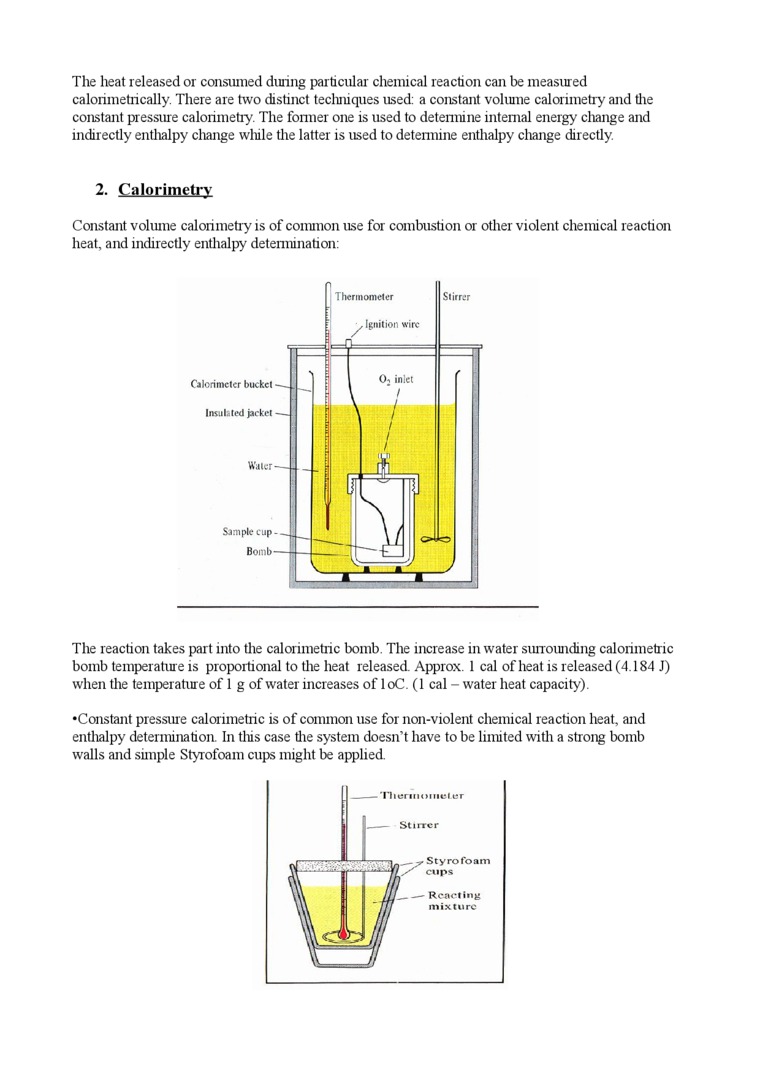
Constant voluine calorimetry is of common nse for combnstion or other violent Chemical reaction heat, and indirectly enthalpy detennination:
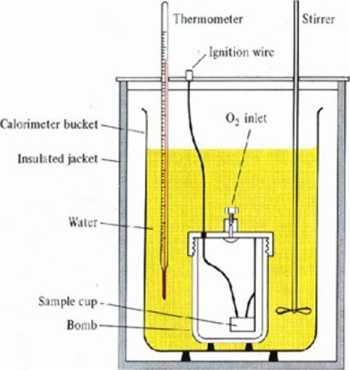
The reaction takes part into the calorimetric bomb. The increase in water sunounding calorimetric bomb temperaturę is proportional to the heat released. Approx. 1 cal of heat is released (4.184 J) when tlie temperaturę of 1 g of water increases of loC. (1 cal - water heat capacity).
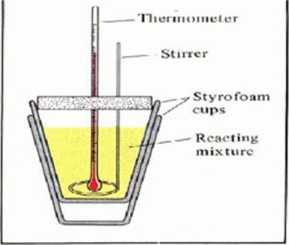
•Constant pressure calorimetric is of common use for non-violent Chemical reaction heat, and entlialpy detennination. In tliis case tlie system doesiTt have to be limited witli a strong bomb walls and simple Styrofoam cups might be applied.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
IV3-4 PHOTOGRAPHIC MEASUREMENTS When there are solid or liquid particles in the flow, velocities can
Fili your bag with coffee beans or loose tea for a gift that can be used and displayed at
synare5 bmp OSCILLATORS. Testing. The output of the oscillators can be measured at the 4093, tuning
CSG143 Complete Spanish Grammar Notę that there are two parts or clauses (clausulas) in the precedin
system 56 THE BEST HOURS FOR DOING THE EXERCISES and their proper seąuence when learnt There are two
2.2.3 Primary and secondary services There are two classes of allocation shown in the following Tabl
IMGx48 268 The Origin of Civilisatiou Armed with the theoretical base we have now built, this concep
ms 018 To the Feflow who is in Doubt There are two kinds of men in the world: one kind, when they wa
htdctmw 025 As usual, we ll study the pix on the page opposite. And this time there are two new word
Review 2B My name: Class: Lessons 11-20 Vocabulary c In the box. There are two extra professlons. sd
My name: Class:Lessons 21-25 Vocabułary 1 Compłete the sentences wlth words from the box. There are
I I Vocabulary 0 1 Match the two parts of the phrases. There are two extra parts. 6 0
L My name: .. Class: Lessons 21-30 Vocabulary 1 Complete the sentences wlth phrases from the box. Th
My na me: Class:Lessons 11-20 Vocabulary 1 Who sald what? Choose from the professlons In the box. Th
więcej podobnych podstron