66816
INTRODUCTION
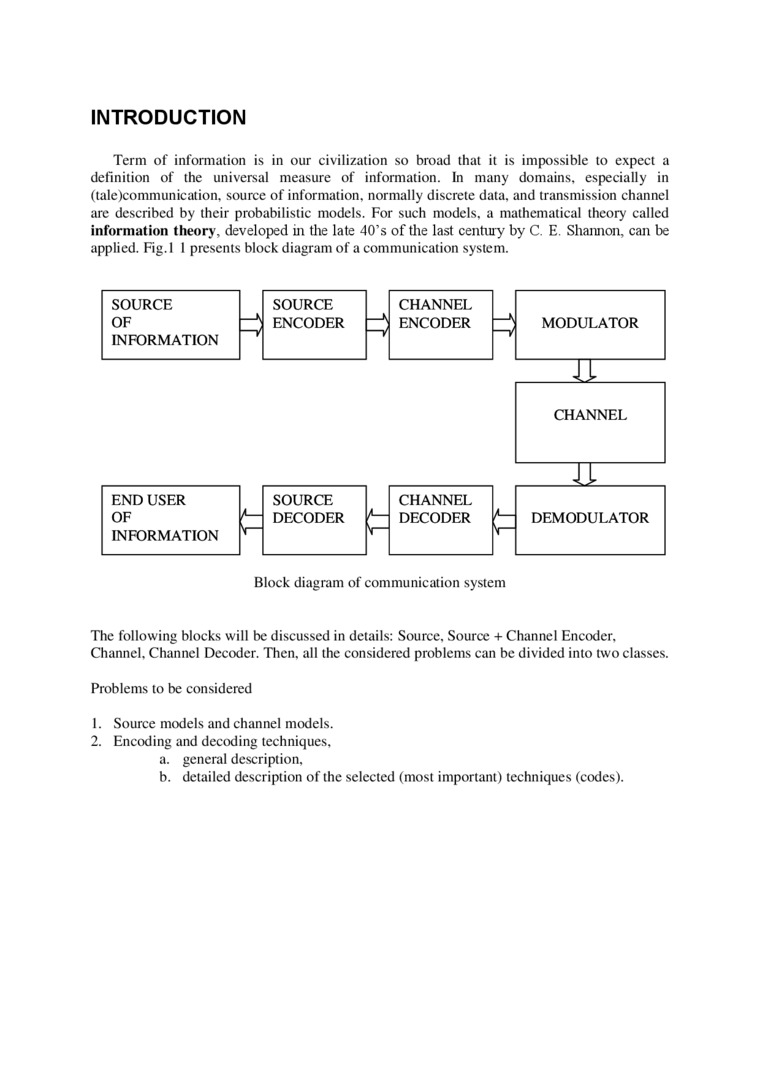
Term of information is in our civilization so broad that it is impossible to expect a definition of the universal measure of information. In many domains, especially in (tale)communication. source of information. normally discrete data. and transmission channel arc dcscribed by thcir probabilistic models. For such niodcls. a niathcmatical theory callcd Information theory, developed in the late 40’s of the last century by C. E. Shannon, can be applicd. Fig.l I prcsents błock diagram of a communication system.
SOURCE
OF
INFORMATION
SOURCE
ENCODER
CHANNEL
ENCODER
MODULATOR
IT
CHANNEL
|
END USER |
SOURCE |
CHANNEL | ||
|
OF |
f— |
DECODER |
DECODER | |
|
INFORMATION |
V— |
Błock diagram of communication system
H
DEMODULATOR
The following blocks will be discussed in dctails: Source. Source + Channel Encoder. Channel. Channel Decoder. Then. all the considcrcd problems can be dividcd into two classcs.
Problems to be considered
1. Source models and channel models.
2. Encoding and decoding techniques.
a. generał dcscription.
b. detailed description of the selected (most important) techniques (codes).
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
The following presentation is going to concentrate mainly on the issue of defining what is meant by
Introduction1 INTRODUCTION1.1 BACKGROUND OF THE STRATEGY, DEVELOPMENT RULES FOR THE DOCUMENT The wor
1. Introduction1.1. Letter of the President of the Board to Shareholders I am delighted to submit th
75732 mbs 060 MY BREATHING SYSTEM are widened. The completeness of inhalation is surę to be frustrat
AŁ-TE* NAT(V Thank you for shopping in our storę. We hope that our starter kit will inspire you to c
Resume The purpose of the work was to clarify the term of the language games. The definitions of thi
idler Idler pulley assembly The countersink of the hinge s holes is meant to be used from the&n
Academic Vocabulary K6 1 Marks: 1 Match the words and the definitions. in a way that is easy to unde
więcej podobnych podstron