9990200011

Data Flow Types basie typesof data transfers
• Control Transfers:
Used to configure a device at attach time and can be used for other device-specific purposes, including control of other pipes on the device.
■ Bulk Data Transfers:
Generated or consumed in relatively large and burstyquantities and have wide dynamie latitude in transmission constraints.
■ Interrupt Data Transfers:
Used for characters or coordinates with human-perceptible echo or feedback response characteristics.
■ Isochronous Data Transfers:
delivery latency. (Also caRed streaming real time transfers).
A pipę supports only one of the types of transfers described above for any given device configuralion
Data Encoding/Decoding
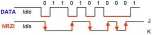
• The USB employs NRZI data encoding when transmitting packets. In NRZI encoding. a *1" is represemed by no change in level and a ’0" is represented by a change in level.
■ The high level represents the J State on the data lines in this and subsequent tigures showing NRZI encoding. A string of zeros causes the NRZI data to loggie each bit time.

Bit Stuffing / Synchronization (SYNC)
|
Bit stuffing is enabled beginning with the i Ihroiighout the entire transmission. The d. Pattern is counted as the first one in a ser transmitler is always enforoed. without ex LSB First ®ylcPaMem , --y (Synchronization) |
3ync Pattern (0x80) and ata 'one' that ends the Sync luence. BI stuffing by the , Packed Data | |
|
\ 0 0 0 0 0 0 t |
..... |
, , ,1^ |
|
DATA | r |
6 x HIGH |
Sluffed Bil |
|
Bit Stuffed |_ |
^_ | |

7
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Defining MySQL Cluster Data Nodes The [ndbd] and [ndbd default] sections are used to configure the b
23vcu03 Insert OLE Control OLE control: Calendar Control 3 Data Outline Control Gr
cproxy 3 FTP Options -X] Set the FTP Port that will be used for REAL Ftp clients to allow data trans
KODY INSTRUKCJI PROCESORA INTEL 8080 DATA TRANSFER GROUP Move Move
Mnemonics Operands Description Operation Flags #Clocks DATA TRANSFER
(e) In RAID Jevels, explain the features of tnose leuels which have very good
m he 3MF onsortium ounders he .3MF file format is set to >ase data transfer, overcome o
cproxy 3 FTP Options -X] Set the FTP Port that will be used for REAL Ftp clients to allow data trans
Cost Pump Cost Data Change Control Valve (A) Trim Impeller (B) VFD (C) Repair Control Valve
v HOSt v Open CL API Calls General Queue: 55A2728E6ED0 ^ Data Transfer v Read Row O ^ Write Row
00065 ndb3dfcfa3fd16c12bb4b6de5950d85 64 Hembree & Zimmer X where Y, is the entire data sample
VI. 4. LESZKO BIAŁY. 263 stąd, że urodził się r. 1192. Data polega niewątpliwie na kombinacyi, i to
VI. 4. LESZKO BIAŁY. 263 stąd, że urodził się r. 1192. Data polega niewątpliwie na kombinacyi, i to
więcej podobnych podstron