2696775399
EE 416 Fundementals of Biomedical Engineering Laboratoiy - Experiment 1
EXP #1: RESISTANCE TRANSDUCERS AND TRANSDUCERS FOR LINEAR POSITION OR FORCE APPLICATIONS
I. INTRODUCTION
Objectives: To review the resistance transducers, to study tłie construction, operation pnnciple and characteristics of an LVDT (Lmear Vanable Differential Transformer), to study the constiuction and characteristics of a variable capacitor, to study the constiuction and characteristics of a strain gauge.
Equipment: Digiac 1750.
Average Time to Complete: 2 hours.
Prereąuisites: Fainihanty with resistance transducers and strain gauges.
II. BACKGROUND INFORMATION A. Resistance Transducers
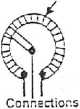
i) Basic construction of rotory and slider types ofvariable resistance:
The unit consists basically of a ‘track’ having a fixed resistance and a vaiiable contact which can be moved along and make continuous contact with the track. If the track resistance is proportional to the length along the track (i.e. lmear track), the output voltage will be proportional to the movement of the vaiiable contact and the unit is suitable for use as a positiontransducer. These units are referred as lmear types. There are also logarithmic types.
The track may comprise a film of caibon fonned on a substrate or may be a length of resistance wire wound on an insulator former. The unit may be constmcted m a rotary form or may be straight as shown m Figurę 1.
Yariable Carbon
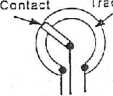
Connections
Wire ccii
Ysriable
Contact
Track
act / TCn *
I ^
] Meta Connections
Rotary Types
Slider type
Figurę 1
ii) Resolution:
The resolution provided by a caibon track resistor is good, the value being mfimtely smali. The resolution for a wire wound resistor is worse, sińce the vaiiable contact will m effect be moving from contact with one tum to contact with the next. The output voltage will therefore increase in steps, these representmg the voltage per tum or a fraction of tlns.

docsity.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
LABORATORY OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERINGRESEARCH AREA AND APPLICATIONSInstitute of Mechanics and Constru
Figurę 12. Laboratory experimental setup for electrical testing of sensing/actuation and processing/
2. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering / Polish Academy of Sciences. Institu
principle Pr i n ci ple Experiment pl©<igjas piat© and (brass 7) wir© m©sh gjued on undersid
(WEITnu* Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Electrical Engineering Institute of Control &
IS EPFaculty of Electrical Engineering * Faculty of Architecture *
Faculty of Electrical Engineering GENERAL INFORMATION The Faculty of Electrical Engineering was esta
1-8 i
BACHELOR PROGRAMMEFIELD OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING AND MACHINĘ BUILDING// FACULTY OF MECHANICAL
Patronage Association of Polish Engineers of Transportation Member ot UEEIV Editors: Jan
830D-IIJ IM TransmiUer The Collins 830D-1B FM Transmitter is a combination of excellent engineering
Wydział Inżynierii Środowiska Faculty of Environmental Engineering V Karty
STOWARZYSZENIE TECHNIKÓW POLSKICH Established in 1940The Association of Polish Engineers in Great
20. Podstawowa charakterystyka bioprocesów BIOPROCESY Inżynieria biomedyczna (Biomedical Engineering
Inżynieria Chemiczna i Procesowa Inżynieria biomedyczna (Biomediail Engineering, BME) wchodzi w skła
więcej podobnych podstron