372596167
148
H. Tanaka et al.
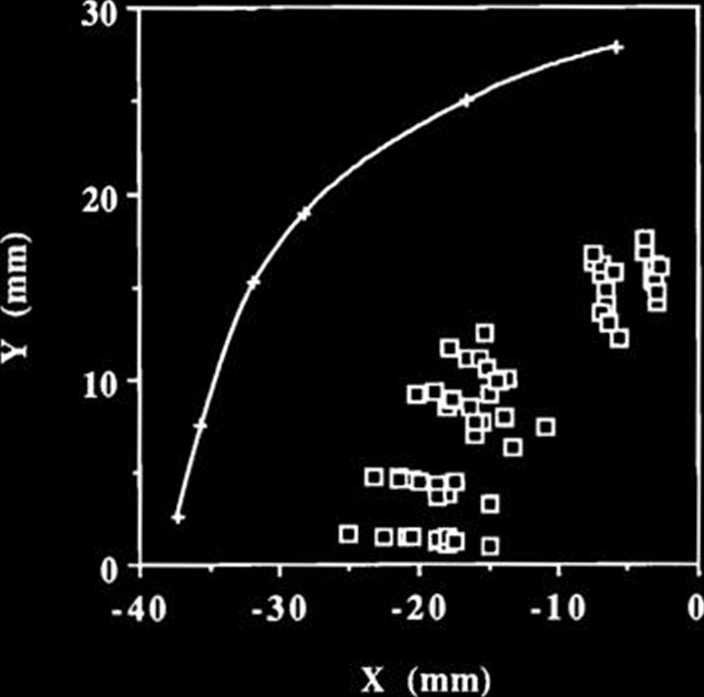
Fig. 2. 8-GeV hybrid lattice dynamie aperture with only random conventional errors. The solid linę represents the ideał dynamie aperture; the open sąuares represent the dynamie aperture with the random conventional errors.
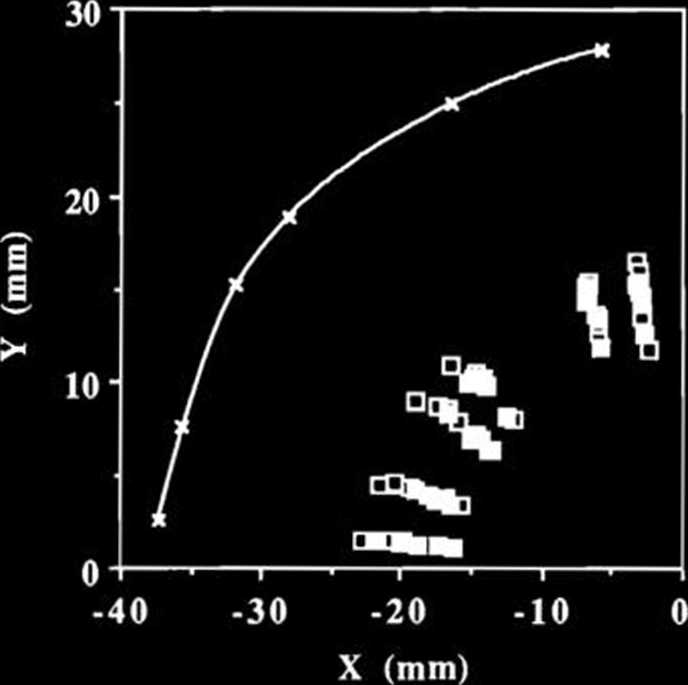
Fig. 4. 8-GeV hybrid lattice dynamie aperture with a -1% constant momentum error, systematic multipole error fields, and random conventional errors. The solid linę represents the ideał dynamie aperture; the open and filled sąuares represent respectively the dynamie aperture with only random conventional errors and three kinds of errors.
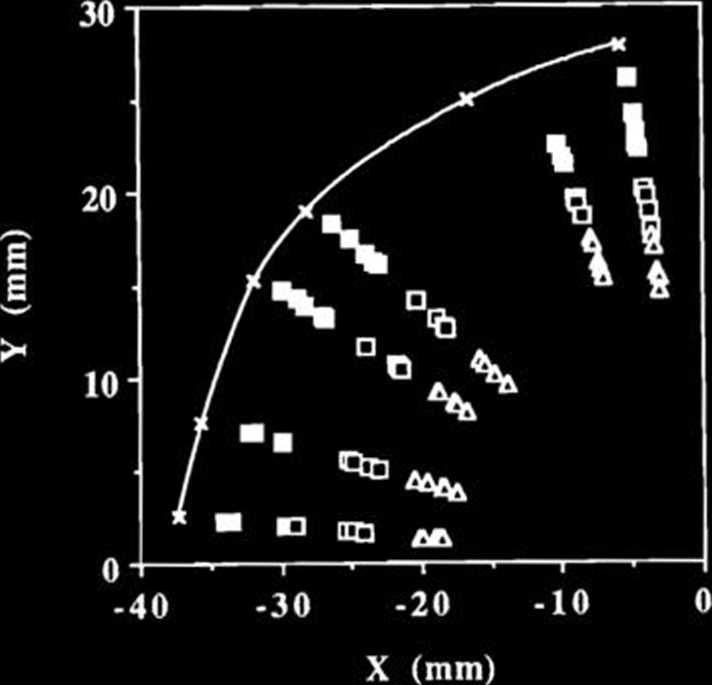
Fig. 3. 8-GeV hybrid lattice dynamie aperture with only systematic multipole error fields. The solid linę represents the ideał dynamie aperture; the filled sąuares represent the dynamie aperture with expected error fields. The open sąuares and triangles represent respectively the dynamie aperture with error fields five and ten times stronger than an expected one.
sequently generate nonlinear effects greatly morę than the systematic multipole error fields. This phenomenon can be explained as follows. The linear field errors break the periodicity of linear functions. This symmetry breaks of the linear functions much enhance the resonance driving terms by the sex-tupole magnets, which are almost cancelled out with perfect symmetries of linear functions under an ideał condition.
References
1) J. Ohnishi and S. Motonaga: llth Int. Conf. on Magnet Technology, Tsukuba, Japan, p. 194 (1989).
2) A. Wrulich: DESY Rep., 84-026 (1984).
3) H. Tanaka, R. Nagaoka, K. Tsumaki, K. Yoshida, and M. Mara: R1KEN Accel. Próg. Rep., 22. 231 (1988).
4) H. Tanaka, R. Nagaoka, K. Yoshida, K. Tsumaki, and M. Hara: ibid., p. 235.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
288 Z. KORUBA ET AL. Fig. 4. (a) Time-dependent profile of the terrain unevenness (bump); (b) time-d
152 J. Ohnishi et al. Fig. 3. Cross-sectional view of a newly designed sex-tupole magnet. X(cm) Fig.
148 A. Kożuch et al. / Leśne Prace Badawcze, 2015, Vol. 76 (2): 144-152 czasu (wyrażone w jednostkac
148 STKESS ANALYSIS Approxiraate ctress analysis of multi-stringed beams with shear de-formatior. of
Wayenumbers (cm- ) Fig. 1. Widmo IR albitu, jadeitu i nefelinu (źródło: Merzbacher et al.,
148 B. Rihn et aUToxicologv 109 (1996) 147-156 undcrstood (Walker et al., 1992; Brody, 1993) while s
et al. (1980) for the stability analysis of Palazzo della Ragione, a 13t h Century building in Milan
148 sous les hautes latitudes augmentaient leur prise alimentaire (McWilliams et al1999; Vćzina et a
M Yacoubi-Khebiza et al. - Un nouveau Microparasellidae du Haut-Atlas 230 Fig. 2. Microcharon ourike
Fig. 3. The 15’ x 15 global geoid undulations produced by EGM96 (Lcmoinc et al., 1998). The undulat
Fig. 1. Geological-structural map of the eastern part of Polish Carpathians (modified, based on Żytk
img024 Motor Control Rałionale Biblioaraphy Berg, K., et al., 1989 Measuring balance in the elderly:
więcej podobnych podstron