372596248
80
RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)
111-3-16. Development of an lon Beam Sputtering Method to
Prepare Long-Lived Carbon Stripper Foils
I. Sugai, 1 M. Oyaizu, 1 M. Aratani, M. Minami, and M. Yanokura
Carbon stripper foils with long lifetimes are very important for accelerating cascade-type protons and heavy ions. We have developed various methods suited to prepare long-lived carbon stripper foils and improved them to give high reproducibility and creditability. A controlled AC and DC arc discharge (CADAD) method1 1 and an ion-beam sputtering (IBS) method were found to be useful compared with an electron-beam heating and an old DC arc discharge method as discussed previously.3) The foils madę by the CADAD method are widely used at several institutes and universities in this country.
Hitherto, the IBS techniąue has not been popular, because of its Iow sputtering yield of carbon small-scale productivity. Previously3) we investi-gated the lifetimes of carbon stripper foils madę by using various kinds of gas ions for sputtering carbon source materials, and suggested that a foil madę by the IBS method may possibly a super long-lived carbon stripper foil. We have established highly reliable and reproducible conditions for the prepara-tion of long-lived carbon foils by improving the IBS method.
The experimental apparatus for the measure-ment of lifetimes of carbon foils (about 15 /xg/cnr) was almost the same as that described in Ref. 1. Experiments were performed in a high-vacuum chamber (10 4 Pa), using a 3.2 MeV Ne+ ion beam of 2-3 /xA of 3.5 mm in diameter obtained by a Van de Graaff accelerator at the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
The lifetime of foil is conventionally defined as an integrated beam current of ions passing through it before it breaks. We investigated lifetimes of all the foils madę by using various kinds of noble gas ions for sputtering carbon source materials. Com-mercially available (CM) foils showed only a short lifetime of 2.5 mC in average. Figurę 1 shows the lifetimes of carbon foils versus the mass of noble gas ions. As seen from Fig. 1, lifetime of carbon foils depends on the atomie mass of noble gas ions.
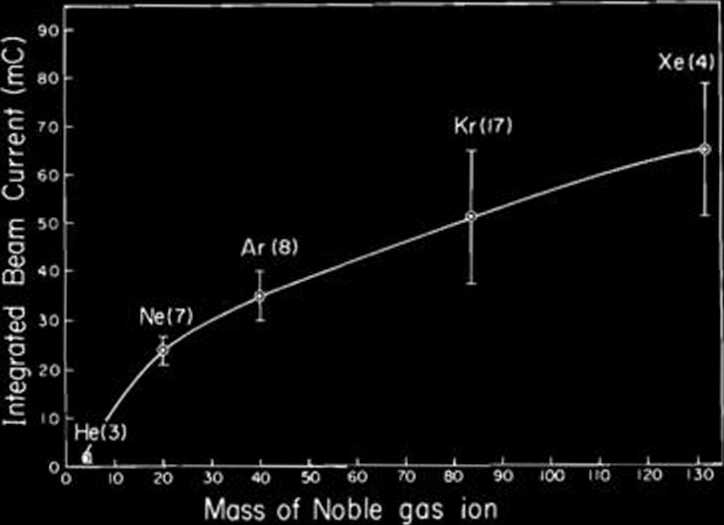
Fig. 1. Dependence of lifetime of carbon stripper foils ver-sus the mass of noble gas ion employed for sputtenng during preparation. Error bars represent mean-squares errors and the numbers in parentheses denote the num-bers of samples investigated.
For a light atomie mass such as 4He, the lifetime is short, 1.2 mC, only haif of the lifetime of the CM-foil (2.5 mC). For 131 Xe, the heaviest atomie mass investigated in the present work, the lifetime is very long, 64 mC in average and 26 times longer than that of the CM-foil. From the dependence of the lifetime of the atomie mass of noble gas employed for sputtering during preparation, we found that foils madę by Kr and Xe shows long lifetimes compared with foils madę by light atomie mass ions such as Ne and Ar. A key point in pro-ducing long-lived foils with Kr or Xe is to make the amount of oxygen in a foil as Iow as possible.
References
1) 1. Sugai and T. Hattori et al.: Nuci Instnon. Methods Phys. Res., A265, 376 (1988).
2) I. Sugai and T. Hattori et al,: fta/.,A236,576 (1985).
3) I. Sugai, M. Aratani, M. Minami, and M. Yanokura: RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep., 23, 85 (1989).
Institute for Nuclear Study, University of Tokyo.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
63 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-2-28. Development of Nuclear Track Microfilters N. Nakanishi
63 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-2-28. Development of Nuclear Track Microfilters N. Nakanishi
92 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5. Instrumentation1. Design of a Microbeamline for a Compact
103 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-9. Test Experiment of the GARIS/IGISOL K. Morita, T. Nomu
110 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-14. Test for Dispersive-Mode Beam Transportto the SMART
116 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-19. Responses of Large Position-Sensitive Detectorsto Hea
11 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-1-2. Three a Disintegration of 12C in the Field of208Pb Nucl
72 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111*3-8. Dry Separation of Radioactive Nuclides from a Gold Targ
94 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-2. Design of a Decay Muon Channel Using an Axially Symmetr
102 RIKEN Accel Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-8. Performance of Isotopic Separation in RIPS T.Nakamura,
105 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-10. Velocity Distribution of IGISOL lon Beams M. Koizumi,
108 RIKEN Accel. Próg. Rep. 24 (1990)111-5-12. Status Report of the RIKEN Swinger-Magnetic Analyzer
więcej podobnych podstron