Genchem 2014/15
Lecturers
: Prof. Zbigniew Stojek (room 153,
stojek@chem.uw.edu.pl),
Prof. Paweł Kulesza, Prof. Karol Jackowski
Textbooks
: General Chemistry, Whitten et al.
http://
search.barnesandnoble.com/General-Chemistry/Kenn
eth-W-Whitten/e/9780534408602
Chemistry,
(Author), Raymond E. Davis
(Author), Larry Peck (Author),

Tests:
Two tests (partial exams) are planned:
on Nov 14
th
and Jan 13
th
.
0-term exam: Jan 23
rd
1st term exam: Feb 6
th
2nd term exam: Feb 20
th
Two different grading scales will be
used:
1: chemists + physicists,
2: other students
To get help: Write to
<stojek@chem.uw.edu.pl>


What is chemistry ?
- central science
Where does chemistry control the
progress?
Materials, medicine, pharmacology, food
industry, cells, vehicles ….
The Law of Conservation of Matter &
Energy:
The combined amount of matter and
energy in the Universe is fixed

MATTER
- its atomic nature, is constructed of tiny
fundamental particles originated with the early
Greek philosophers, Democritus
- John Dalton, 1802, Elements are made of
extremely small particles called atoms.
-Niels Bohr, Danish physicist, first “rigorous”
theory of the H atom - 1913
Where does the matter come from?
We know that all galaxies move away from the
common center, therefore ….

We know that all galaxies move away from the
common center, therefore ….Big Bang
Quasars are the fastest objects in the space
(270 000 km/s); Hubble telescope
The mass of the Universe:
Imagine:
Our sun is one of 120 billion stars in our galaxy
(Milky Way).
Milky Way is one of 100 billion galaxies of the
Universe.
Longest Distance:
The most distanced objects:
quasars are located 2 billion light years away.
Black matter:
matter that does not emit light
(clouds of dust, burned out stars, black holes,
neutrinos).
It is impossible to estimate the amount of black
matter in the Universe.
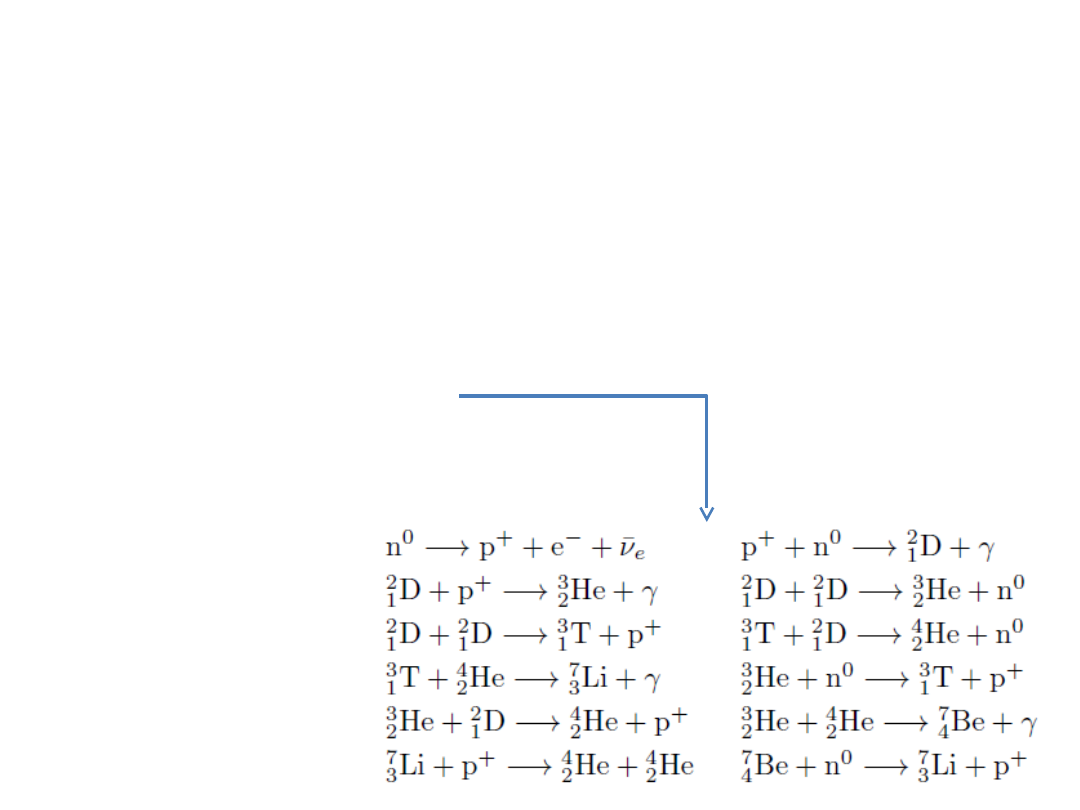
The birth of a star:
contraction of the dust (H atoms) followed by
reaction: 4H He
Old stars: 3He C
complex mechanisms of synthesis of heavier
nuclei
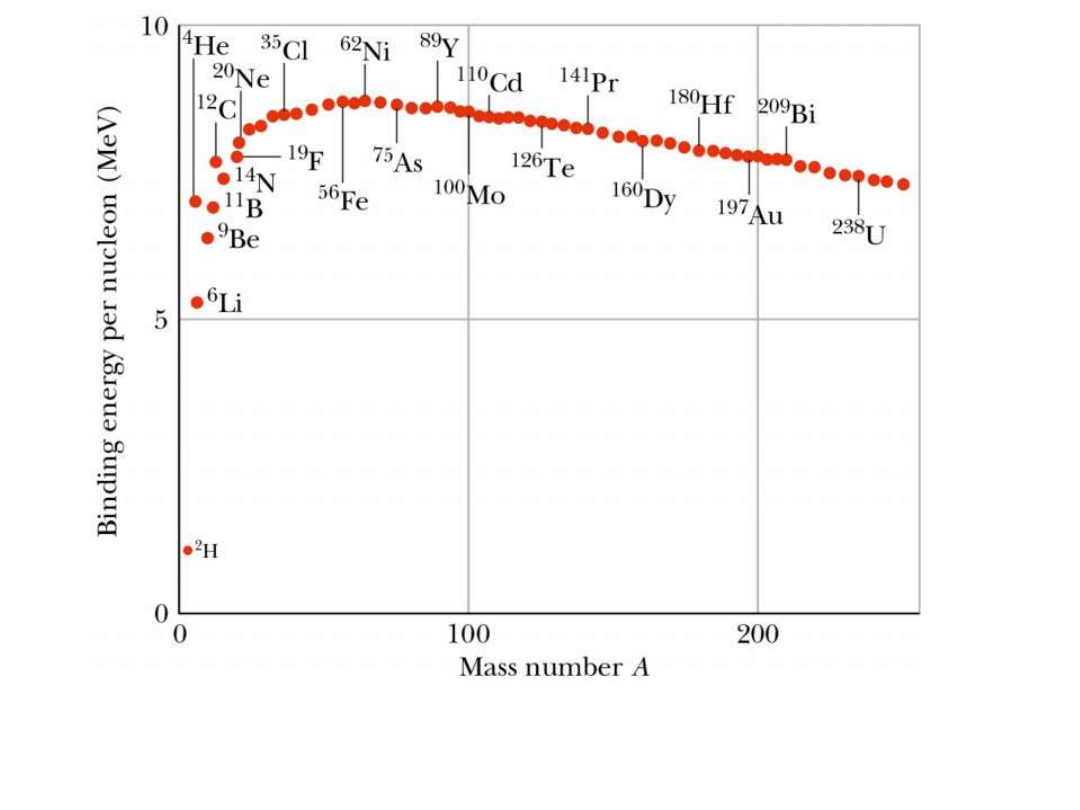
Nucleon binding energy curve (average binding energy
per nucleon in MeV against number of nucleons in nucleus).
Maximum is located at Fe
56
.

An alternative to black matter:
modified Newton's
Law
F = m∙a

Big Bang
(big explosion, big blast, birth of
the Universe)
Circa 12 billion years ago it started.
1 ms later: 10 billion degrees, photons
10 s later: protons, neutrons, electrons
3 min later: temperature dropped to 1 billion
degrees
15 min later: first nuclei
……..
4.6 billion years ago: the Earth is formed
1.5 billion years ago: beginning of life
3 million years ago: human beings appeared

Will the expansion of the Universe
last forever?
We need only 1g of matter per 40 billion
km
3
to stop the expansion and to reverse
the direction (gravitation)
Before the Big Bang there was no time,
space, mass and energy ???.
The Big Bang marks the beginning of all
these things. ???
Matter, antimatter, lack of symmetry

In particle physics, antimatter is material composed of antiparticles,
which have the same mass as particles of ordinary matter but have
opposite charge and other particle properties such as lepton and baryon
number. Encounters between particles and antiparticles lead to
the annihilation of both, giving rise to varying proportions of high-energy
photons (gamma rays), neutrinos, and lower-mass particle–antiparticle
pairs. Setting aside the mass of any product neutrinos, which represent
released energy which generally continues to be unavailable, the end
result of annihilation is a release of energy available to do work,
proportional to the total matter and antimatter mass, in accord with
the mass-energy equivalence equation, E=mc
2
.
Antiparticles bind with each other to form antimatter just as ordinary
particles bind to form normal matter. For example, a positron (the
antiparticle of the electron) and an antiproton can form an antihydrogen
atom. Physical principles indicate that complex antimatter atomic nuclei
are possible, as well as anti-atoms corresponding to the known chemical
elements. To date, however, anti-atoms more complex than antihelium
have neither been artificially produced nor observed in nature. Studies of
cosmic rays have identified both positrons and antiprotons, presumably
produced by high-energy collisions between particles of ordinary matter.
There is considerable speculation as to why the observable universe is
apparently composed almost entirely of ordinary matter, as opposed to a
more symmetric combination of matter and antimatter. This asymmetry
of matter and antimatter in the visible universe is one of the
greatest unsolved problems in physics.
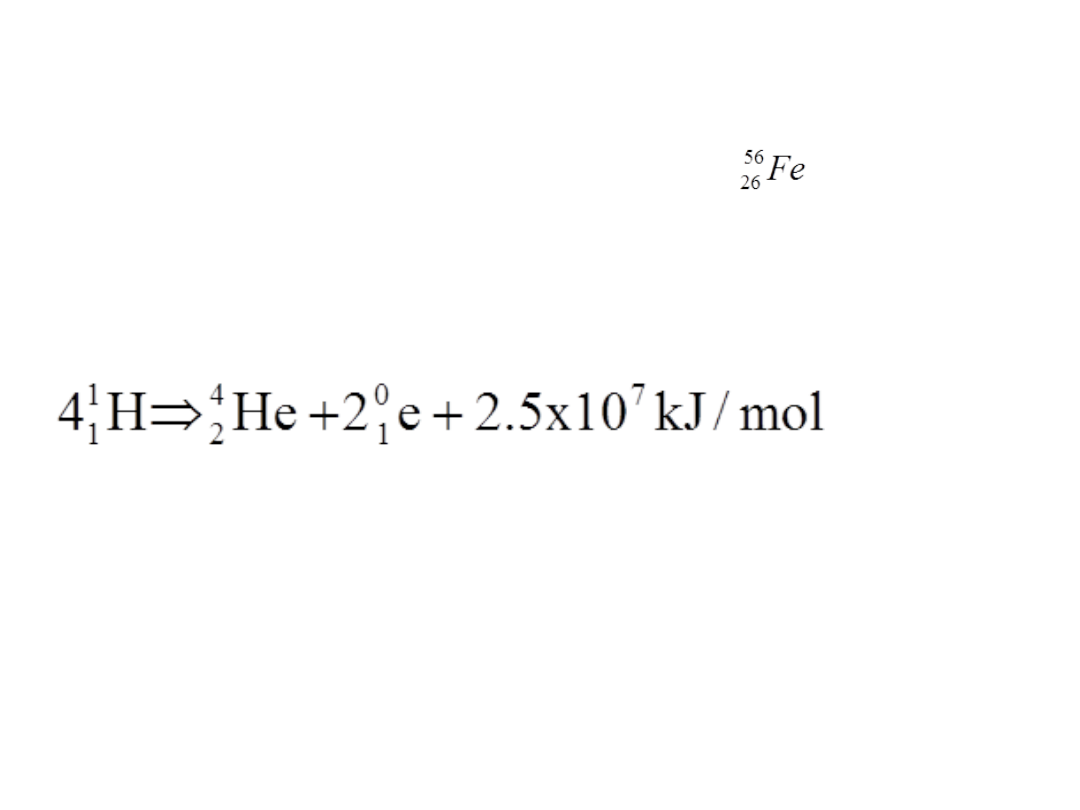
How old is matter?
Cosmos is very young: 1 in the 0-100 scale;
Major nuclear reaction in the stars:
Compare this with acetylene complete combustion:
H
2
C
2
+ 2.5 O
2
2CO
2
+ H
2
O + 1.3x10
3
kJ/mol

Relative Cosmos Atomic Abundance
(Si=1)
*
H
3.18x10
4
Hydrogen
He
2.21x10
3
Helium
Li
49.5x10
-6
Lithium
Be
8.1x10
-1
Beryllium
B
3.5x10
-4
Boron
*C
11.8
Carbon
*N
3.74
Nitrogen
*O
21.5
Oxygen
F
22.4x10
-3
Fluorine
Na
6.0x10
-2
Sodium
Si
1
Silicon
*
Life elements

Molecules in the space
CN
cyanogen
OH
hydroxy group
NH
3
ammonia
H
2
O
water
H
2
CO
formaldehyde
CO
carbon oxide
H
2
HCN
hydrogen cyanide
CH
3
OH
methyl alcohol
HCO
2
H
formic acid
SiO
silicon oxide
CH
3
CHO
acetic aldehyde
H
2
S
hydrogen sulfide
CH
3
-O-CH
3
(di) methyl ether
CH
3
CH
2
OH
ethyl alcohol
SO
2
sulfur dioxide
NO
nitrogen oxide

Enceladus
– diameter 500 km. Its surface is
covered by
an ice layer. There is, probably, a salty-water
ocean below the layer. Does it support life? This
is one of most important questions that bother
astrobiologists.
Titan
- the largest moon of Saturn: The Cassini–
Huygens mission in 2004 led to the discovery of
liquid hydrocarbon lakes on Titan’s surface.
Propen was discovered in 2013.
Interesting compounds on
other planets

Americans
John C. Mather and George F. Smoot
have won
the 2006 Nobel Prize in physics for work that helped
cement the big-bang theory of the universe.
Mather, 60, works at the NASA Goddard Space Flight
Center in Greenbelt, Md., and Smoot, 61, works at
the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in
Berkeley, Calif.
Their work was based on measurements done with
the help of the NASA-launched COBE satellite in
1989. They were able to observe the universe in its
early stages about 380,000 years after it was born.
Ripples in the light they detected also helped to
demonstrate how galaxies came together over time.
"The very detailed observations that the laureates
have carried out from the COBE satellite have played
a major role in the development of modern
cosmology into a precise science," the academy said
in its citation.

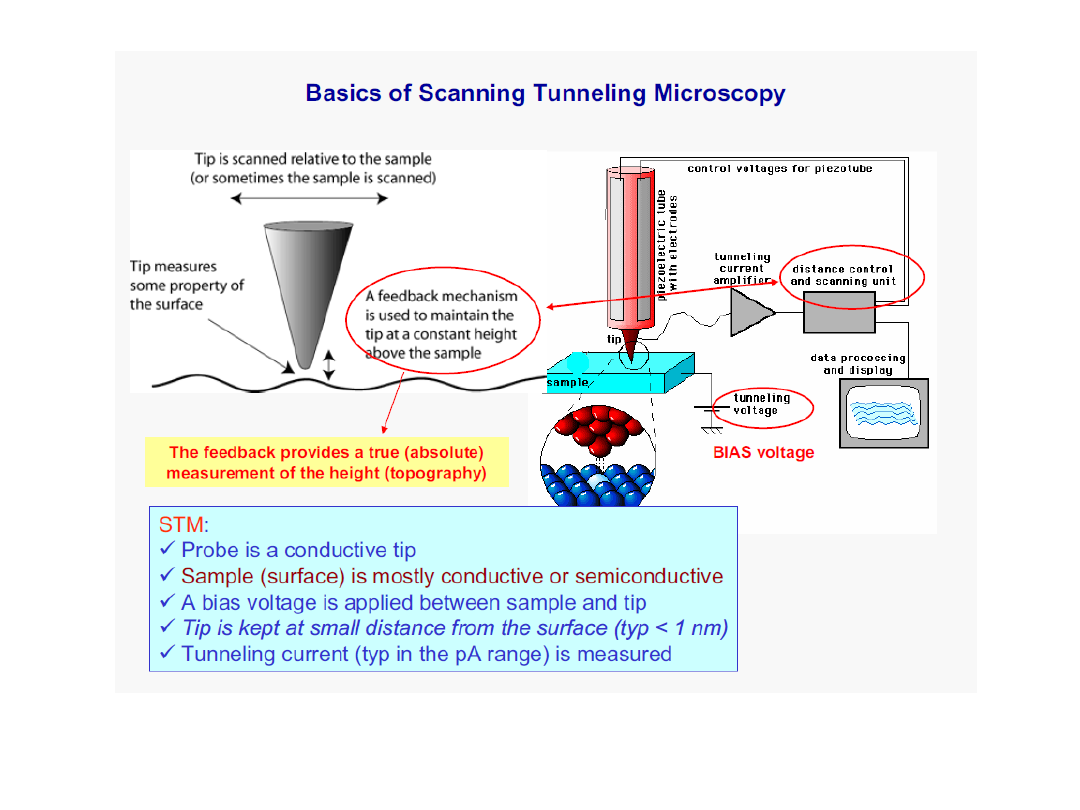
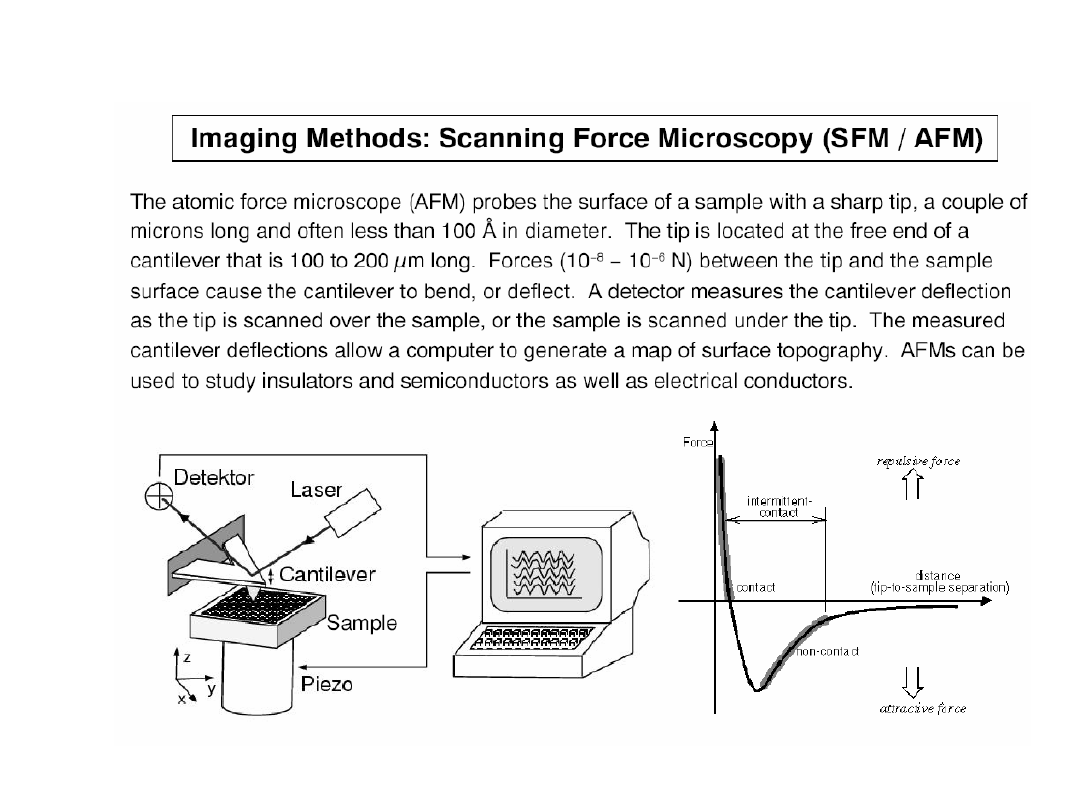
Can a single atom be seen?
Yes, thanks to:
Scanning tunneling microscopy
AND
Scanning force microscopy
(Atomic force microscopy)
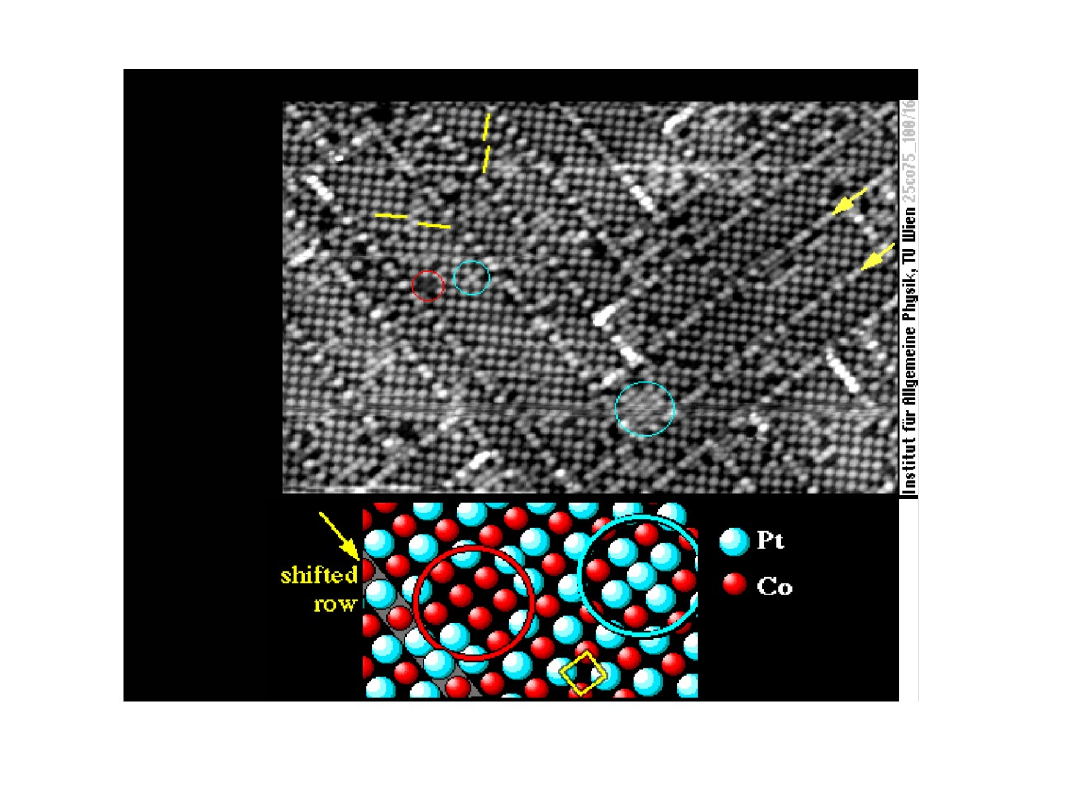
STM micrograph of an alloy surface
Document Outline
- Slide 1
- Slide 2
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Fox The Big Bang Theory [intro] (Wiley, 2002)
Pecel a może Big Bang cz 1
BIG BANG SOFFITTO
Big Bang Monster (piano solo)
Haldeman, Joe The Big Bang Theory Explained (In Light Verse)
Haldeman, Joe The Big Bang Theory Explained (In Light Verse)
BIG BANG PARETE
Haldeman, Joe The Big Bang Theory Explained (In Light Verse)
BIG BANG SOSPENSIONE
Stone Temple Pilots Big Bang Baby
196 Capital structure Intro lecture 1id 18514 ppt
intro 12(Kant A)
O Intro Wstęp
więcej podobnych podstron