
POWDER METALLURGY
Mateusz Soja
Piotr Pabiańczyk
IM sem.3

16.11.2021
2
Introduction
Powder metallurgy is a process for
forming metal parts by heating
compacted metal powders to just
below their melting points.
Powder metallurgy is the study of the
processing of metal powders, including
the fabrication and conversion of metal
powders into useful engineering
components.

Basic P/M Steps
• Raw Material/atomization,
• Mixing,
• Forming/Compaction,
• Sintering,
• Optional Operations,
• Finished Products.
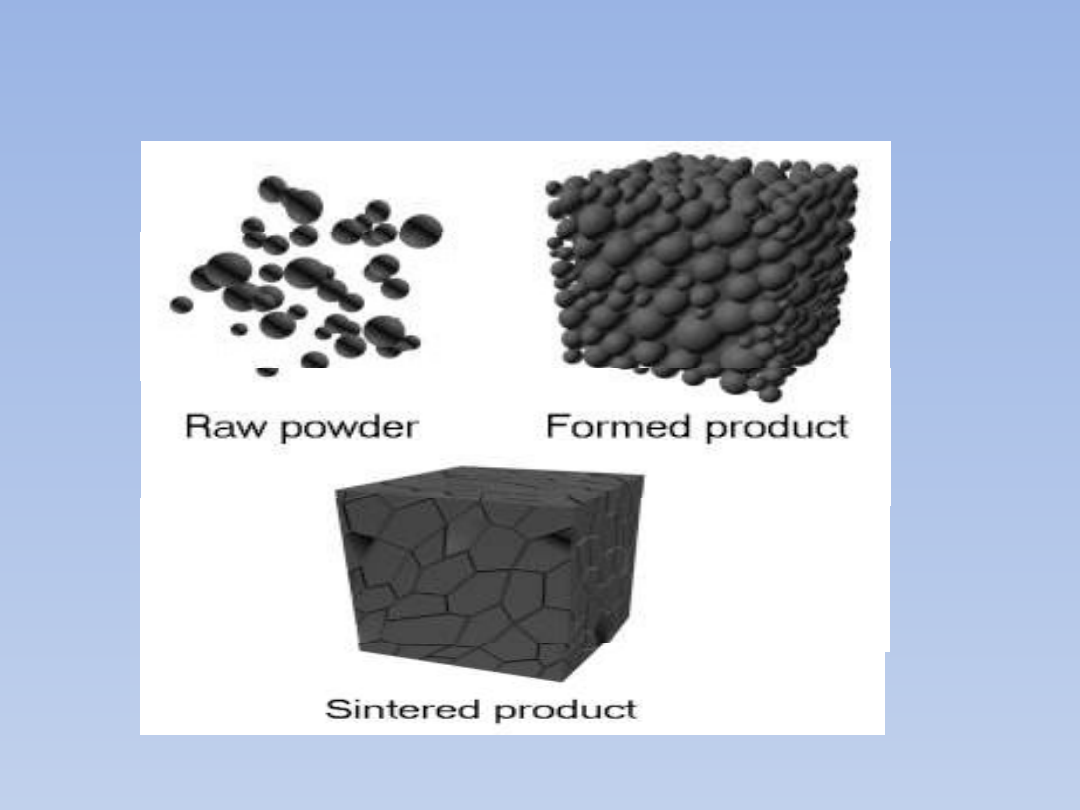
Powder Compaction and
Sintering
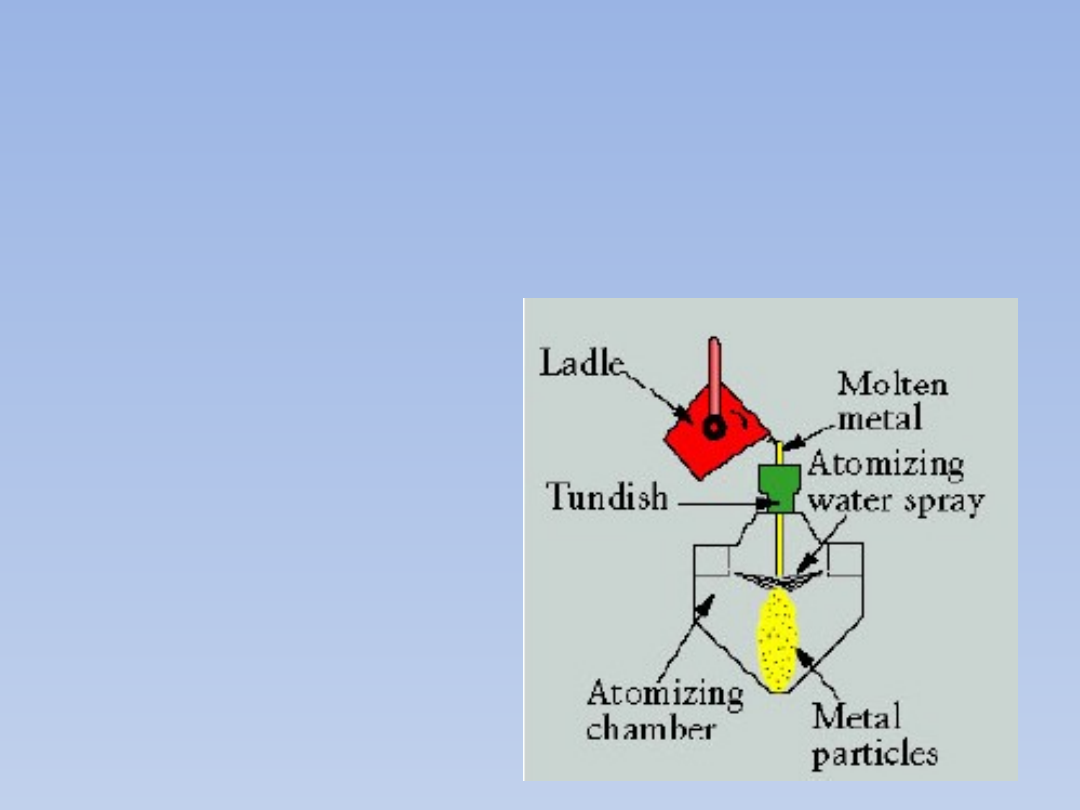
POWDERS
One method of metal-powder
production by melt atomization
Atomization is
accomplished by
forcing a molten
metal stream
through an orifice
at moderate
pressures.

MIXING
Elemental, partially alloyed or pre-alloyed
metal powders are first blended with
lubricants to produce a homogeneous mixture.
Cycyle of mixing:
1. Reduction of oxides,
2. Annealing,
3. Powder Weighings,
4. Adding lubricants,
5. Mixing.

FOMRMING/COMPACTION
Methods of compaction are:
• Pressing,
• Rolling,
• Extrusion,
• Injection molding.
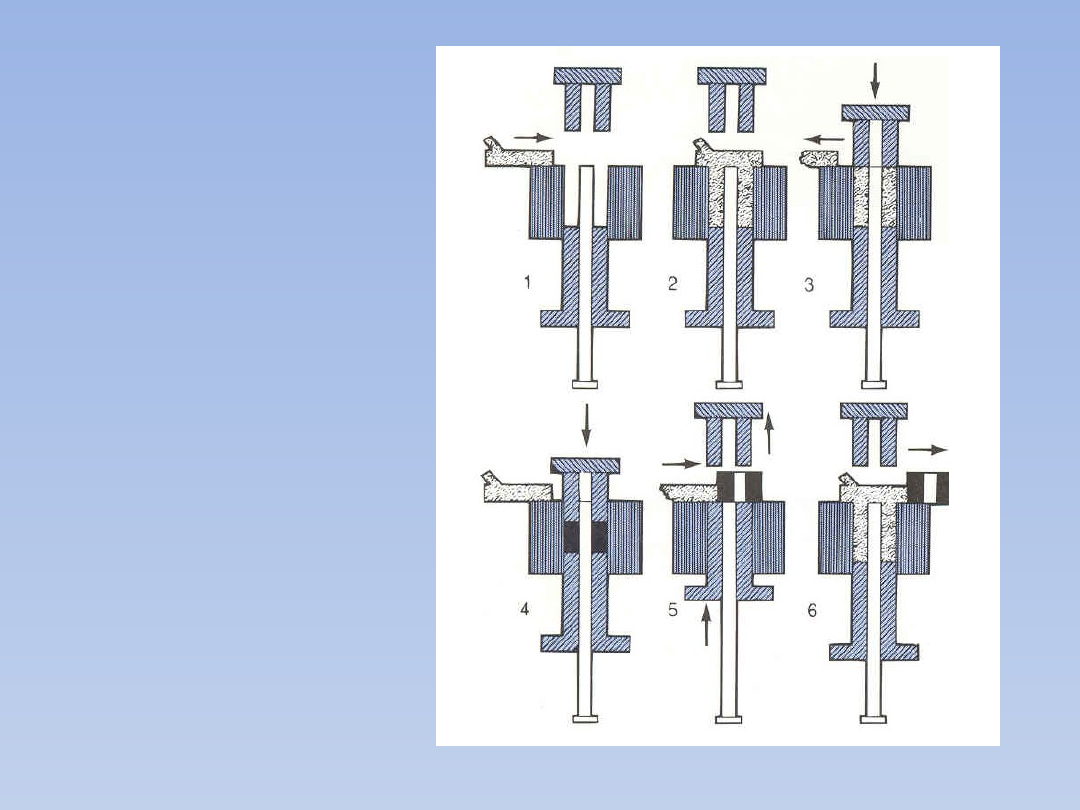
Pressing
Compaction Cycle:
1. Cycle Start
2. Charge die with
powder
3. Compaction
begins
4. Compaction
complete
5. Ejection of
compact
6. Recharging of die

MECHANICAL PRESS

SINTERING
The parts are heated below the
melting point of the base metal, held
at the sintering temperature, then
cooled.
Typical sintering temperatures for
based metals range from 1100 - 1150
celsius degrees
Standard cycle times range from 2-3
hours.

SINTERING FURNACE

Optional Operations
• Heat treatment,
• Impregnation of sintered,
• Machining,
• thermo-chemical treatment,
• Surface treatment of sintered.

Examples of typical parts made by
powder metallurgy processes.

Thx for your attention
Document Outline
- Slide 1
- Introduction
- Basic P/M Steps
- Powder Compaction and Sintering
- POWDERS
- MIXING
- FOMRMING/COMPACTION
- Pressing
- MECHANICAL PRESS
- SINTERING
- SINTERING FURNACE
- Optional Operations
- Slide 13
- Thx for your attention
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
16 197 208 Material Behaviour of Powder Metall Tool Steels in Tensile
Powder Metallurgy
Investigations of White Layer Formation During Machining of Powder Metallurgical Ni Based ME 16 S
Offenzellige Metallschaume
PowderedMetallurgy
Blacksmith The Origins Of Metallurgy Distinguishing Stone From Metal(1)
Metallica Discography Lyrics
Powder
Metallic Text Gimp
4 PIM Powder Injection Molding
METALLICA BLACK TEKSTY
metallica enter sandman level 2z5
Metallographic Methods for Revealing the Multiphase Microstructure of TRIP Assisted Steels TŁUMA
powdermeTALLURGY
Metallica Nothing Else Matters
Metall Alloys
Coating Methods, Powder Technology
Aluminum Metallurgy
więcej podobnych podstron