Student's Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
P1
|
P2 |
P3 |
P4 |
P5 |
P6 |
P7 |
P8 |
P9 |
∑ |
Mark |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mobile Communications - examination paper (set A)
1 |
Complete the diagram so that it explains call setup sequence from PSTN/ISDN to MS.
|
Explain acronyms that you use to annotate the diagram: |
||
2 |
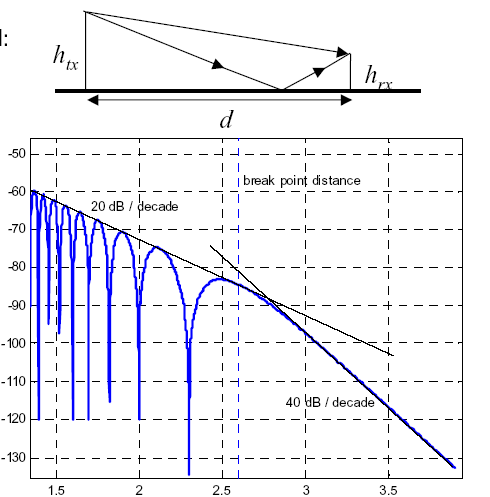
How path attenuation in the two-ray model depends on the distance d? What properties of the ground are typically assumed in this model, and how phase and amplitude of the wave reflected from it change?
|
|||
3 |
Calculate total capacity C of a GSM system assuming: number of frequency pairs L = 48, average cell radius R = 4.37 km, total system area A = 300 000 km2 , 4-cell clusters.
|
|||
4 |
Sketch the GSM normal burst. Name its components, duration, and number of bits.
|
|||
5 |
|
|||
6 |
Explain timing advance technique:
|
|||
7 |
First NMT450 system was launched in: ð 1970 ð 1976 ð 1981 ð 1983 |
COST-231-Walfish-Ikegami model is suitable for ð urban areas ð rural areas ð satellite links ð hilly terrain |
Radius of the n-th Fresnel zone is given by:
|
|
8 |
An antenna with VSWR = 1.25 is connected to the transmitter with a flexible cable of attenuation L1=1 dB and reflection coefficient r1 = 0.05 and a main feeder cable of the length l = 50 m, unit attenuation Lu2 = 0.02dB/m, and reflection coefficient r2 = 0.01. Calculate VSWR of this setup.
|
|||
9 |
Which techniques used in the GSM allow to save energy in Mobile Stations:
|
|||
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
testy, MobCom 2006 F, Imię i nazwisko
testy, MobCom 2006 D, Imię i nazwisko
testy, Test 2006 ZI LodzC, Imię i nazwisko
testy egzaminacyjne z anatomii, legenda do szablonu starego, IMIĘ I NAZWISKO:
Imię i nazwisko
fizyka dynamika - pr klasowa, Imię i nazwisko:
okulistyka wejsciowki gielda, Test+z+anatomii+grupa++++++październikowa, Imię nazwisko…&helli
Sprawozdanie 11, Imię i nazwisko
III Klasa, 4.IIIB.Grupa B(PP), Grupa B Imię i nazwisko ucznia
test-pokarmowy-1, IMIĘ I NAZWISKO:
test, Imię i nazwisko
Ćw nr 45, 45, Imie Nazwisko
7 Chromatografia jonowymienna, 7. chromatografia jonowzmienna, Imię i nazwisko
kartkowka 4, obwód prostokąta i kwadratu, Imię i Nazwisko:
fizyka-energia, Imię i nazwisko:
Wersja B Nerwy i zmysły 2010 Imię i Nazwisko, Spradziany
GPw UE Zestaw pytan 2011 Heffner, Imię i Nazwisko:
więcej podobnych podstron