1
Testing and Scrum
Testing and Scrum
Fall 2007 Scrum Gathering
Fall 2007 Scrum Gathering
Ralph van Roosmalen
Ralph van Roosmalen
Agenda
y
y
Introduction
Introduction
y
y
The Classical Test Approach
The Classical Test Approach
y
y
Organization
Organization
y
y
Test Documentation
Test Documentation
y
y
Test Activities
Test Activities
y
y
Recruitment
Recruitment
y
y
Reporting
Reporting
y
y
Test Automation
Test Automation
y
y
Lessons Learned
Lessons Learned

2
Introduction
Planon > Personal introduction
y
y
Ralph van Roosmalen,
Ralph van Roosmalen,
r.vanroosmalen@planon.nl
r.vanroosmalen@planon.nl
y
y
Computer Science
Computer Science
ba
ba
, studied at the Institute of
, studied at the Institute of
Technology
Technology
y
y
Certified Scrum master
Certified Scrum master
y
y
ISTQB Practitioner
ISTQB Practitioner
y
y
In Software Industry since 1997 as Software Developer,
In Software Industry since 1997 as Software Developer,
Project Manager and currently Test Manager and Scrum
Project Manager and currently Test Manager and Scrum
master at Planon.
master at Planon.

3
Planon > Company
y
y
Standard software for Integrated Workplace
Standard software for Integrated Workplace
Management Solutions
Management Solutions
y
y
Private Dutch Company, Nijmegen,
Private Dutch Company, Nijmegen,
±
±
300 employees,
300 employees,
±
±
50 employees in Software development.
50 employees in Software development.
y
y
Last five years at least 23% growth in revenue, and
Last five years at least 23% growth in revenue, and
turnover of
turnover of
€
€
21 million Euro (2006).
21 million Euro (2006).
y
y
Active in The Netherlands, Germany, Belgium, UK,
Active in The Netherlands, Germany, Belgium, UK,
France, Spain, Austria,
France, Spain, Austria,
Switzerland
Switzerland
, Poland and the
, Poland and the
United States.
United States.
y
y
Goal: to become world leader in
Goal: to become world leader in
Integrated Workplace
Integrated Workplace
Management Solutions in 2010
Management Solutions in 2010
Planon > Software Development
y
y
±
±
50 employees
50 employees
y
y
Six scrum teams
Six scrum teams
y
y
Five working on a product
Five working on a product
y
y
One support team
One support team
y
y
All feature teams
All feature teams
y
y
Team members are interchangeable
Team members are interchangeable
y
y
Using Scrum since 2005
Using Scrum since 2005
y
y
Product Owners are not part of Software Development,
Product Owners are not part of Software Development,
customer
customer
–
–
vendor relation
vendor relation
y
y
Will engage in outsourcing development in 2008 by
Will engage in outsourcing development in 2008 by
using distributed Scrum teams
using distributed Scrum teams

4
Planon > Products
y
y
Planon ProCenter Windows Client
Planon ProCenter Windows Client
y
y
Legacy product,
Legacy product,
±
±
15 years old, Delphi
15 years old, Delphi
y
y
Supported by team SE
Supported by team SE
y
y
Planon Self
Planon Self
-
-
Service
Service
y
y
±
±
5 years old, Delphi
5 years old, Delphi
y
y
Supported by team Net
Supported by team Net
y
y
Planon Talk
Planon Talk
y
y
±
±
5 years old, Delphi
5 years old, Delphi
y
y
Supported by team Net
Supported by team Net
y
y
Planon ProCenter Java Client
Planon ProCenter Java Client
\
\
Web2.0 Client
Web2.0 Client
y
y
3 years old, J2EE environment
3 years old, J2EE environment
y
y
Supported by teams Alpha, Beta and Gamma
Supported by teams Alpha, Beta and Gamma
The Classical Test Approach

5
The Classical Test Approach
y
y
Test team is asked to test a project
Test team is asked to test a project
y
y
Test Manager starts with Project Test Plan
Test Manager starts with Project Test Plan
y
y
Test Manager or Test Leads creates Phase Test plan
Test Manager or Test Leads creates Phase Test plan
y
y
Start reviewing requirements and specifications
Start reviewing requirements and specifications
y
y
Start writing test cases by test engineers
Start writing test cases by test engineers
y
y
Wait for software, until it is almost too late to execute the
Wait for software, until it is almost too late to execute the
test plans.
test plans.
y
y
Start test execution phase
Start test execution phase
y
y
Solve problems found
Solve problems found
y
y
1
1
st
st
retesting
retesting
The Classical Test Approach
y
y
Complaints from the project manager, why is the testing
Complaints from the project manager, why is the testing
phase taking so much time.
phase taking so much time.
y
y
Solve problems found during 1
Solve problems found during 1
st
st
retesting
retesting
y
y
2
2
nd
nd
retesting
retesting
y
y
Regression test and solve problems found during 2
Regression test and solve problems found during 2
nd
nd
retesting
retesting
y
y
Deliver software
Deliver software
y
y
Project evaluation
Project evaluation
y
y
Involvement in the next project too late: it has already
Involvement in the next project too late: it has already
started because the developers were finished with the
started because the developers were finished with the
previous project.
previous project.

6
The Classical Test Approach
y
y
Does not work in Scrum because
Does not work in Scrum because
…
…
y
y
There is no test team
There is no test team
y
y
You deliver potentially shippable software each sprint
You deliver potentially shippable software each sprint
y
y
There is no time to write test plans
There is no time to write test plans
y
y
You can
You can
’
’
t wait until the software is ready
t wait until the software is ready
y
y
There is no time to perform extensive retesting
There is no time to perform extensive retesting
y
y
Requirements and specifications are lean, so
Requirements and specifications are lean, so
y
y
Reviewing of documentation cannot wait until it is finished
Reviewing of documentation cannot wait until it is finished
y
y
Writing test cases based on specifications is difficult
Writing test cases based on specifications is difficult
y
y
There is no test manager within Scrum
There is no test manager within Scrum
The Classical Test Approach
y
y
To make testing work in a Scrum environment, you have
To make testing work in a Scrum environment, you have
to change
to change
…
…
y
y
The organization
The organization
y
y
Testing Documentation
Testing Documentation
y
y
Test Activities
Test Activities
y
y
Recruitment
Recruitment
y
y
Reporting
Reporting
y
y
Regression testing approach
Regression testing approach

7
Organization
Organization
y
y
Testers are integrated into the teams
Testers are integrated into the teams
y
y
So no separate test team
So no separate test team
y
y
Testers are always up
Testers are always up
-
-
to
to
-
-
date
date
y
y
Testers can easily communicate with developers,
Testers can easily communicate with developers,
technical writers and functional designers
technical writers and functional designers
y
y
Test manager is still there, but not in the project
Test manager is still there, but not in the project

8
Organization
y
y
Role of the tester
Role of the tester
y
y
Ask questions
Ask questions
y
y
Bring people together
Bring people together
y
y
Act as the team
Act as the team
’
’
s quality conscience
s quality conscience
y
y
Testing
Testing
y
y
Tester has to earn credit with the rest of the team to fulfil
Tester has to earn credit with the rest of the team to fulfil
this role.
this role.
Testing Documentation

9
Testing Documentation
y
y
Test Policy
Test Policy
y
y
High level document, used for all projects
High level document, used for all projects
y
y
Just 1 A4 in size
Just 1 A4 in size
y
y
Test Strategy
Test Strategy
y
y
Per Test Level, used for all projects
Per Test Level, used for all projects
y
y
Just 1 A4 in size per Test Level
Just 1 A4 in size per Test Level
y
y
Project Test Plan
Project Test Plan
y
y
Describes the deflections compared to the Test Policy
Describes the deflections compared to the Test Policy
and Test Strategy
and Test Strategy
Testing Documentation – Test Policy 1/2
y
y
A Test Policy contains the following sections:
A Test Policy contains the following sections:
y
y
Mission
Mission
y
y
Organization
Organization
y
y
All testers hold the ISTQB Foundation certificate.
All testers hold the ISTQB Foundation certificate.
y
y
On average, each team that builds a software product should
On average, each team that builds a software product should
have one specialized tester on three developers.
have one specialized tester on three developers.
y
y
The team is ultimately responsible for the quality of the delive
The team is ultimately responsible for the quality of the delive
red
red
software.
software.
y
y
Testing Approach
Testing Approach
y
y
The testing approach is aligned with the values of the Agile
The testing approach is aligned with the values of the Agile
manifesto.
manifesto.
y
y
The testing strategy is based on the product risk matrix.
The testing strategy is based on the product risk matrix.
y
y
An automated regression test is available for each standard
An automated regression test is available for each standard
Planon software product. The regression test covers at least the
Planon software product. The regression test covers at least the
product
product
’
’
s high risks areas.
s high risks areas.
10
Testing Documentation – Test Policy 2/2
y
y
Standards
Standards
y
y
Quality Attributes
Quality Attributes
y
y
Functionality
Functionality
y
y
Efficiency
Efficiency
y
y
Test Improvement
Test Improvement
y
y
The testing process is continuously improved by applying the
The testing process is continuously improved by applying the
improvement actions from the team
improvement actions from the team
-
-
and a testing retrospective
and a testing retrospective
that is held after each sprint. This continuously improvement is
that is held after each sprint. This continuously improvement is
embedded in our software process, Scrum.
embedded in our software process, Scrum.
y
y
Evaluation of testing (Performance indicators)
Evaluation of testing (Performance indicators)
y
y
Data is collected on test effort and defects; this data enables
Data is collected on test effort and defects; this data enables
creating metrics to provide input for the test improvement
creating metrics to provide input for the test improvement
process.
process.
Testing Documentation – Test Strategy 1/2
Unit test
The testing of software components. Is planned and designed early in the life cycle, the tests are based on the detailed
design specifications.
Objective
Test the business logic and the application framework.
Responsibility
The team is responsible; the developers are the operators and the testers in some cases the reviewers.
Risk I
Risk II
Risk III
Risk IV
Entry criteria
-
-
-
-
Exit criteria
 Jalopy executed
 Find Bugs executed; no
Correctness bugs and
Bad Practices are left
 100% tests successful
 Unit tests are reviewed
 High coverage
 Jalopy executed
 Find Bugs executed; no
Correctness bugs
and Bad Practices
are left
 100% tests successful
 Unit tests are reviewed
 High coverage
 Jalopy executed
 Find Bugs executed and
no Correctness bugs
are left
 100% tests successful
 Medium coverage
 Jalopy executed
 Find Bugs executed and
no Correctness bugs
are left
 100% tests successful
 Low coverage
Test process
A developer creates Unit
tests, often they are
designed by a
tester. The unit
tests are reviewed
by a tester.
A developer creates
Unit tests, often
they are designed
by a tester. The
unit tests are
reviewed by a
tester.
A developer creates
Unit tests, in
some cases they
are designed by a
tester. Sometimes
they are reviewed
by a tester.
A developer creates
Unit tests.
11
Testing Documentation – Test Strategy 2/2
Milestones deliverables
Unit tests, coverage results and Unit results.
Test case design
techniques
 Boundary value
analysis
 Equivalence
partitioning
 Statement testing
 Cause/Effect
graphing
 Boundary value
analysis
 Equivalence
partitioning
 Statement testing
 Boundary value
analysis
 Statement testing
 Boundary value
analysis
 Statement testing
Type of tools that will
be applied
Find Bugs (Code analysis tool), Emma (Coverage tool), Unit framework
Environments in which
the tests will be
executed
Nightly test environment, subset of unit tests in a continuous build environment.
Typical non-functional
test types
Efficiency.
Metrics
 Number of successful unit tests
 Statement coverage of successful unit tests
 Time behavior of the executed tests
The approach to test
automation
All tests are automated in a unit test framework, their will be no manual testing in this level.
The approach to
retesting and
regression testing
If a problem is fixed in the source, all the automated unit tests will be executed and there will
be one or more new unit tests to prevent reintroduction of the problem.
Testing Documentation – Project Test Plan
y
y
If a project does something different than described in
If a project does something different than described in
the Test Policy or Test Strategies, this can be described
the Test Policy or Test Strategies, this can be described
in the Project Test Plan.
in the Project Test Plan.

12
Testing Documentation – Test Policy And Test
Strategy
y
y
Why write documentation? You say it is reverse
Why write documentation? You say it is reverse
engineering, so why write it down?
engineering, so why write it down?
y
y
Enables to discuss test approach with management and
Enables to discuss test approach with management and
teams
teams
y
y
Used to train new employees
Used to train new employees
y
y
Regularly check to see whether we are still on the right
Regularly check to see whether we are still on the right
track
track
y
y
Used in presentations to (potential) customers
Used in presentations to (potential) customers
y
y
It
It
’
’
s a living document, so we adapt it when necessary.
s a living document, so we adapt it when necessary.
Test Activities

13
Test Activities – Sprint Planning
y
y
Testers are present during the sprint planning
Testers are present during the sprint planning
y
y
Use risk analysis to identify testing tasks
Use risk analysis to identify testing tasks
y
y
Testers estimate test tasks; testing capacity is finite
Testers estimate test tasks; testing capacity is finite
Test Activities – Sprint
y
y
Test the software
Test the software
y
y
Test Scrum; once a week
Test Scrum; once a week
y
y
Testers assists Developers in writing unit tests
Testers assists Developers in writing unit tests
y
y
Testers review unit tests and/or specifications
Testers review unit tests and/or specifications
y
y
Testers personify the team
Testers personify the team
’
’
s quality conscience
s quality conscience
y
y
Daily priority of the team
Daily priority of the team
y
y
Results unit tests
Results unit tests
y
y
Keep track of problems
Keep track of problems

14
Test Activities – Sprint
y
y
Impact
Impact
y
y
Part of the primary
Part of the primary
company process
company process
y
y
Possibility of corrupt data
Possibility of corrupt data
y
y
Number of users
Number of users
y
y
Risk of failure
Risk of failure
y
y
Tools and technology
Tools and technology
y
y
What kind of software:
What kind of software:
maintenance or new
maintenance or new
software
software
y
y
Number of people involved
Number of people involved
Test Activities – Sprint
y
y
Risk I
Risk I
y
y
Extensive
Extensive
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory Testing
y
y
Structured testing, all
Structured testing, all
executed test are automated
executed test are automated
y
y
Testing is done by the most
Testing is done by the most
experienced testers
experienced testers
y
y
Review of Unit tests
Review of Unit tests
y
y
Review of the test cases on
Review of the test cases on
coverage and content
coverage and content
y
y
Code review
Code review
y
y
Review specifications
Review specifications
y
y
Risk IV
Risk IV
y
y
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory Testing
y
y
Some basic unit testing
Some basic unit testing
y
y
Testing can be done by non
Testing can be done by non
-
-
specialized testers
specialized testers

15
Test Activities – Sprint
y
y
ET is very important, also at high risk items
ET is very important, also at high risk items
y
y
Writing test cases based on specifications is difficult
Writing test cases based on specifications is difficult
y
y
ET in combination with formal techniques
ET in combination with formal techniques
y
y
You can
You can
’
’
t wait until the software is ready
t wait until the software is ready
y
y
Testers start with automated test scripts
Testers start with automated test scripts
y
y
Developers have to deliver software piece by piece
Developers have to deliver software piece by piece
Test Activities – End of the Sprint
y
y
Testers participate in the Sprint Retrospective
Testers participate in the Sprint Retrospective
y
y
Testers are present during the Sprint Review meeting
Testers are present during the Sprint Review meeting
y
y
Test Retrospective, retrospective about the test process
Test Retrospective, retrospective about the test process
y
y
Prepare the next sprint, investigate product backlog
Prepare the next sprint, investigate product backlog

16
Recruitment
Recruitment – Process
•
•
Looking for an
Looking for an
“
“
Agile Tester
Agile Tester
”
”
•
•
Interview with Development Manager or Test Manager
Interview with Development Manager or Test Manager
and Recruitment Manager.
and Recruitment Manager.
•
•
Workshop
Workshop
•
•
Four hours
Four hours
–
–
a small effort for a new job
a small effort for a new job
•
•
Every one can say (s)he has knowledge of software
Every one can say (s)he has knowledge of software
testing, but can they prove it?
testing, but can they prove it?
•
•
Final interview
Final interview

17
Recruitment – Workshop
•
•
60 Questions about testing
60 Questions about testing
•
•
What does the applicant know about testing (ISTQB)
What does the applicant know about testing (ISTQB)
•
•
Possibility to discuss testing with the applicant
Possibility to discuss testing with the applicant
•
•
How does (s)he handle stress
How does (s)he handle stress
•
•
Describe at least 20 test cases to test the Font dialog in Word
Describe at least 20 test cases to test the Font dialog in Word
•
•
How creative is the applicant
How creative is the applicant
•
•
Does (s)he use test techniques
Does (s)he use test techniques
•
•
How does (s)he describe the tests
How does (s)he describe the tests
•
•
Case
Case
“
“
communicate with the developer
communicate with the developer
”
”
•
•
How does (s)he handle with the stereotype developer
How does (s)he handle with the stereotype developer
•
•
Can (s)he set the correct priority and severity
Can (s)he set the correct priority and severity
Recruitment
•
•
We believe that soft skills are very important for testers
We believe that soft skills are very important for testers
in a Scrum environment
in a Scrum environment
•
•
Communication
Communication
•
•
Flexibility
Flexibility
•
•
Collaboration
Collaboration
•
•
Test techniques is something you can learn
Test techniques is something you can learn

18
Reporting
Reporting
y
y
Test Reports
Test Reports
y
y
No separate Management report
No separate Management report
y
y
No
No
hidden
hidden
link on a corporate website
link on a corporate website
y
y
But
But
…
…
y
y
Visible for all team members and stakeholders in a
Visible for all team members and stakeholders in a
public place
public place
y
y
Simple and
Simple and
“
“
less is more
less is more
”
”

19
Reporting
y
y
What to report?
What to report?
y
y
Open issues per module
Open issues per module
y
y
Open issues per team
Open issues per team
y
y
Open issues displayed in time
Open issues displayed in time
y
y
% successful unit tests
% successful unit tests
y
y
What to report depends per organization, but
What to report depends per organization, but
…
…
y
y
Report per team, not per individual
Report per team, not per individual
y
y
Use colors: green is good and red is bad (In Western
Use colors: green is good and red is bad (In Western
oriented countries)
oriented countries)
y
y
Keep it really simple
Keep it really simple
Reporting – Monitors in the hall
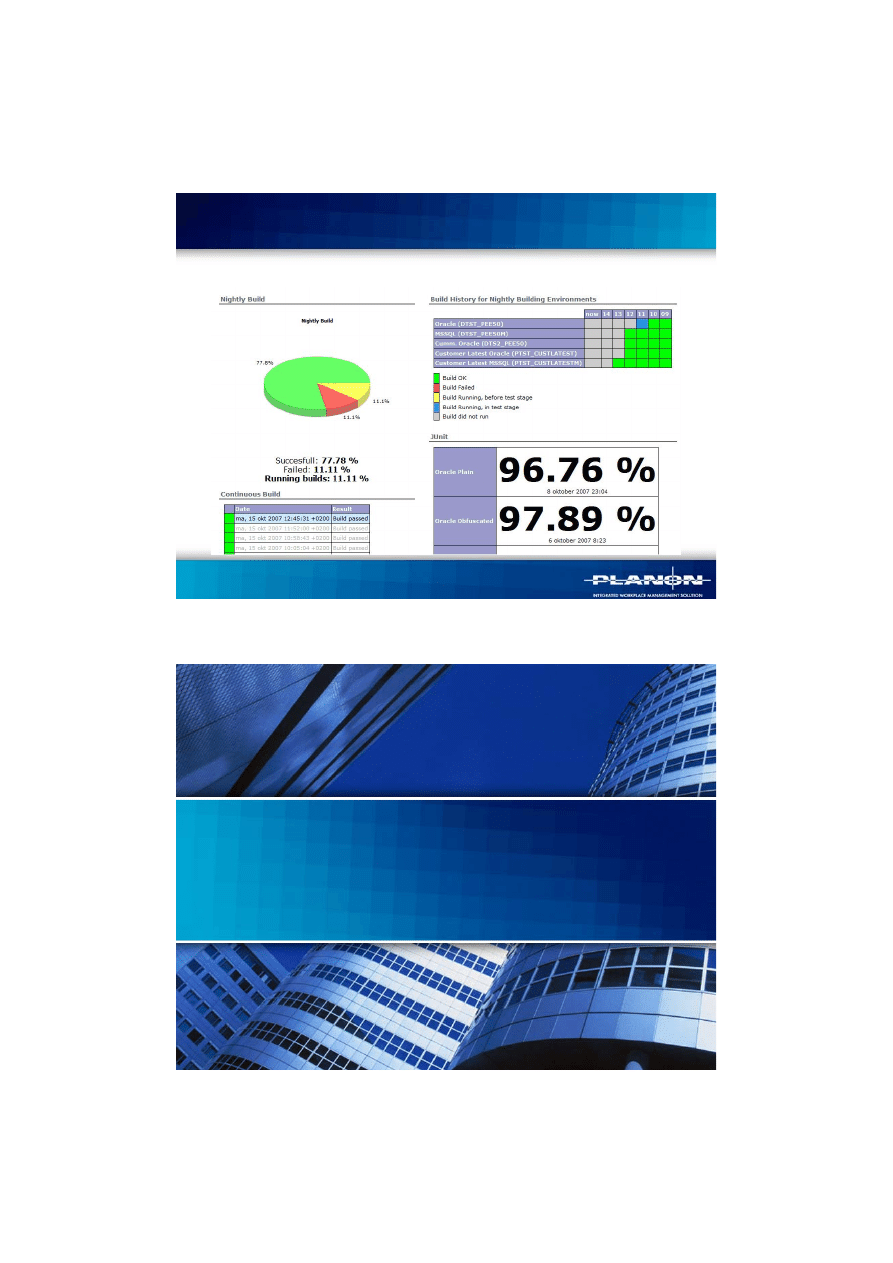
20
Reporting – Example report
Test Automation

21
Test Automation – Why
y
y
There is no time for extensive manual regression testing;
There is no time for extensive manual regression testing;
automation is essential.
automation is essential.
y
y
Necessary because of incremental iterations and to
Necessary because of incremental iterations and to
support refactoring
support refactoring
y
y
As Product Vendor we need to support our products for
As Product Vendor we need to support our products for
years
years
y
y
Instantaneous feedback: all tests are run each night
Instantaneous feedback: all tests are run each night
y
y
Makes the daily work for testers more fun
Makes the daily work for testers more fun
Test Automation – Which tools
y
y
JUnit framework
JUnit framework
y
y
No testing of classes but on a higher level
No testing of classes but on a higher level
y
y
Used by developers to test framework and business
Used by developers to test framework and business
logic
logic
y
y
QF
QF
-
-
Test
Test
y
y
Commercial product for automating tests of Java
Commercial product for automating tests of Java
applications with a graphical user interface
applications with a graphical user interface
y
y
Used to test our Swing client
Used to test our Swing client
y
y
Selenium
Selenium
y
y
A test tool for web applications
A test tool for web applications
y
y
Used to test our Web2.0 client
Used to test our Web2.0 client

22
Test Automation – Approach
y
y
Planon Test Policy:
Planon Test Policy:
“
“
An automated regression test is available for
An automated regression test is available for
each standard Planon software product. The regression test cover
each standard Planon software product. The regression test cover
s
s
at least the product
at least the product
’
’
s high risks areas.
s high risks areas.
”
”
y
y
Developers and tester discuss test automation
Developers and tester discuss test automation
y
y
Developers builds unit tests, testers reviews them or describes
Developers builds unit tests, testers reviews them or describes
the
the
unit tests, depends on the risk and available capacity .
unit tests, depends on the risk and available capacity .
y
y
Tester builds a QF
Tester builds a QF
-
-
Test test script to touch all GUI components and
Test test script to touch all GUI components and
test main use
test main use
-
-
case.
case.
y
y
If there is special coding needed for the Web2.0 client, the tes
If there is special coding needed for the Web2.0 client, the tes
ter
ter
builds a Selenium test script.
builds a Selenium test script.
y
y
Developer and Testers need to communicate to have the right test
Developer and Testers need to communicate to have the right test
automation approach!
automation approach!
Test Automation – Approach
y
y
Tool smith
Tool smith
y
y
Responsible for analyzing the automated test results
Responsible for analyzing the automated test results
y
y
Develops and maintains the automated test
Develops and maintains the automated test
framework
framework
y
y
Reviews the tests scripts
Reviews the tests scripts
y
y
Prevent this role becoming a bottleneck in creating
Prevent this role becoming a bottleneck in creating
automatic test scripts
automatic test scripts

23
Lessons Learned
Lessons Learned – General
y
y
Make no statement about the quality at the end of the
Make no statement about the quality at the end of the
sprint
sprint
y
y
quality should always be good, and if not a product
quality should always be good, and if not a product
backlog item is not finished
backlog item is not finished
y
y
Quality is a team issue not the responsibility of testers
Quality is a team issue not the responsibility of testers
y
y
Testing in Scrum is different, but you can still use the
Testing in Scrum is different, but you can still use the
same old test techniques; use them lean
same old test techniques; use them lean

24
Lessons Learned – General
y
y
How to handle open (customers) issues
How to handle open (customers) issues
y
y
Prioritize issues
Prioritize issues
y
y
Add the issues to the product backlog
Add the issues to the product backlog
y
y
If you do not want to solve an issue, cancel or close it.
If you do not want to solve an issue, cancel or close it.
y
y
If you plan a stabilization phase, you are going to need it.
If you plan a stabilization phase, you are going to need it.
Lessons Learned – Test Manager
y
y
Coach testers
Coach testers
y
y
Review test approach of a product backlog item every
Review test approach of a product backlog item every
sprint of every team
sprint of every team
y
y
Develop a vision on testing together with testers
Develop a vision on testing together with testers
y
y
Develops and maintain the Test Policy, Test Strategy
Develops and maintain the Test Policy, Test Strategy
and Test Project Plan
and Test Project Plan
y
y
Increase the testing knowledge of testers; for example,
Increase the testing knowledge of testers; for example,
hold a monthly professional circle
hold a monthly professional circle

25
Links
y
y
Agile Testing User Group,
Agile Testing User Group,
http://
http://
tech.groups.yahoo.com
tech.groups.yahoo.com
/group/agile
/group/agile
-
-
testing/
testing/
y
y
International Software Testing Qualifications Board,
International Software Testing Qualifications Board,
www.istqb.org
www.istqb.org
y
y
Planon,
Planon,
www.planon
www.planon
-
-
fm.com
fm.com
y
y
QFS,
QFS,
www.qftest.com
www.qftest.com
y
y
Scrum,
Scrum,
www.controlchaos.com
www.controlchaos.com
y
y
Scrum User Group,
Scrum User Group,
http://
http://
groups.yahoo.com/group/scrumdevelopment
groups.yahoo.com/group/scrumdevelopment
/
/
Selenium,
Selenium,
www.openqa.org
www.openqa.org
y
y
TestComplete,
TestComplete,
www.automatedqa.com
www.automatedqa.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Darrieus Wind Turbine Design, Construction And Testing
Electrician's Troubleshooting and Testing Pocket Guide
Implementing and testing a virus throttle
Developing Usability Tools And Techniques For Designing And Testing Web Sites
2005 15 summer wiring matters inspection and testing rcds
Simulation, construction and testing of a two cylinder solar Stirling engine powered by a flat plate
Language Testing, Migration and Citizenship (eds G Extra&P Van Avermaet&M Spotti)
11 3 2 3 Lab Testing Network Latency with Ping and Traceroute
Cruelty of Animal Testing Analysis of Animal Testing and A
Comparative testing and evaluation of hard surface disinfectants
Exercise Standards for Testing and Training
HANDOUT do Constr of tests and konds of testing items
8 3 2 7 Lab Testing Network Connectivity with Ping and Traceroute
Nesser Inspector Van Veeteren 5 The Inspector and Silence RuLit Net
Testing the Relations Between Impulsivity Related Traits, Suicidality, and Nonsuicidal Self Injury
The Rat and the Snake A E Van Vogt
IFL90 ch6 Testing and Troubleshooting intel
Beethoven L van Moonlight sonata Op 27 No 2 1st mvt Adagio flute part and flute & piano part (2 ve
więcej podobnych podstron