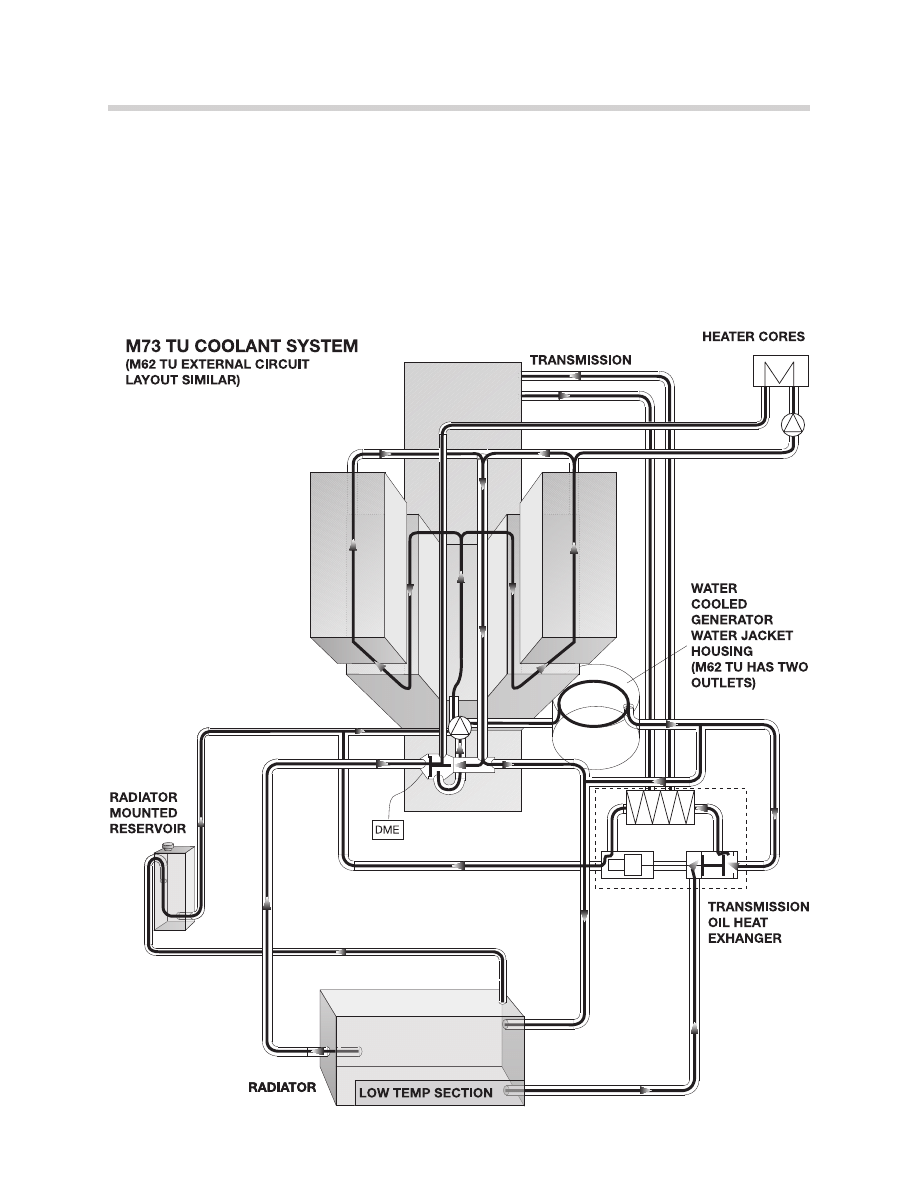
M73 TU & M62 TU COOLING SYSTEMS
OVERVIEW
The cooling systems have been changed for the 1999 model year vehicles. The new com-
ponents consist of a new radiator, coolant expansion tank, transmission fluid heat exchang-
er, DME controlled coolant thermostat and auxiliary fan.
70
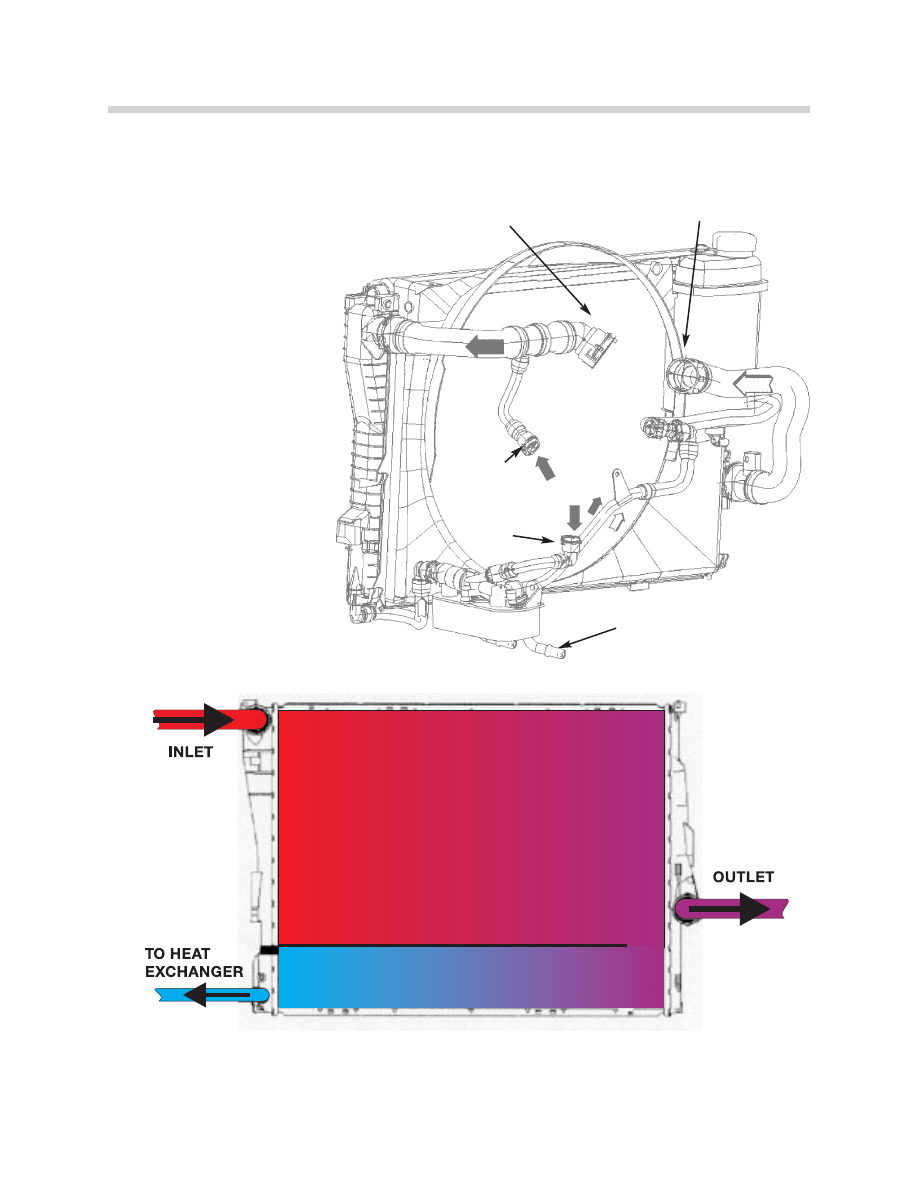
RADIATOR
The new radiator has a
two section cross-flow
design.
The main coolant flow is in
the upper 4/5 section
where the hot engine
coolant temperature is
reduced and cycled
through the system.
The lower 1/5 section is a
low temperature residual
coolant storage area for
the heating and cooling
concept (MTK) first intro-
duced on the E46.
The low temperature
coolant is made available
to the oil and water heat
exchanger on the lower
left side of the radiator.
71
COOLANT DISTRIBUTION
HOUSING CONNECTION
WATER
COOLED
GENERATOR
CONNECTIONS
THERMOSTAT CONNECTION
TRANSMISSION COOLER/HEATER
CONNECTIONS
M62 TU RADIATOR HOSE LAYOUT
72
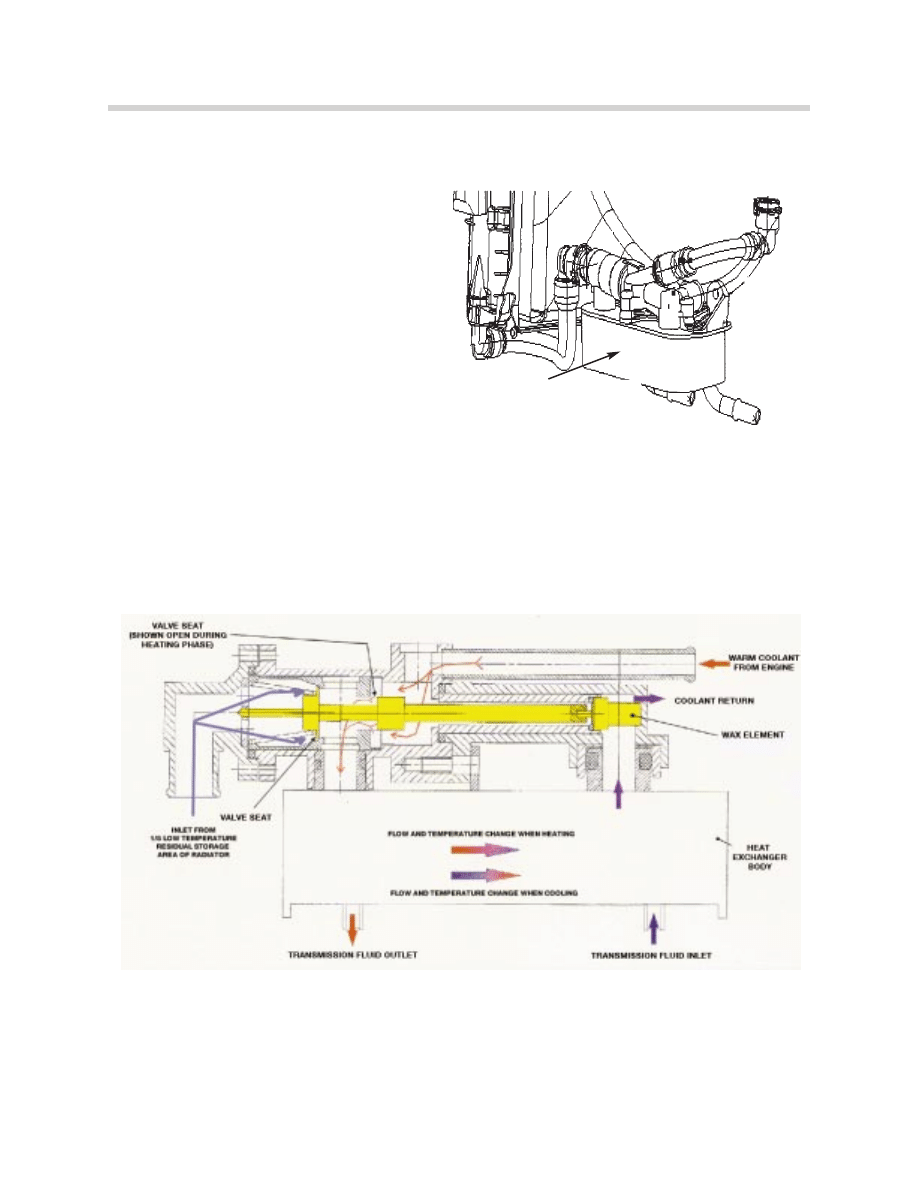
TRANSMISSION FLUID HEAT EXCHANGER
The transmission fluid/engine coolant heat
exchanger concept introduced with the
M52 TU is now also used on all E38 and
E39 vehicles with automatic transmissions.
This system provides a faster warm up of
the automatic transmission fluid by heating
the fluid through the heat exchanger reduc-
ing frictional drag in the transmission faster
after cold start. The addition of this compo-
nent helps to reduce fuel consumption.
On cold engine start-up, the engine's coolant is heated quicker than the automatic trans-
mission fluid.
When the automatic transmission fluid is cold, coolant is guided from the engine (water
cooled generator housing) to the heat exchanger. Coolant flow through the heat exchang-
er is regulated by an integral thermostatically controlled valve. The warm engine coolant
heats the transmission fluid through the exchange of heat (illustration depicts transmission
fluid warm up).
As the transmission fluid rises to operating temperature the engine coolant temperature
also rises which causes the wax core in the integral thermostat to expand and push the
regulation valve against spring pressure. This closes the warm coolant port and opens the
low temperature coolant port from the residual storage area of the radiator. The tempera-
ture change of coolant flow through the heat exchanger continually regulates the tempera-
ture of the transmission fluid.
TRANSMISSION FLUID
HEAT EXCHANGER
Document Outline
- Return to Main Menu
- Emission Compliance Review
- 1999 Drivetrain & Emission Compliance
- M62TU Engine
- DME 7.2
- M62TU & M73TU Cooling System
- 5 Series Sportwagon
- DSC
- DSC
- Xenon Headlights
- LWR Headlight Throw Control
- Visual Entry Aid
- Passive Safety System
- Center Console Switch
- 1999 Navigation System
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
EVAPORATIVE COOLING SYSTEMS
5 Cooling System
05 cooling system
Popular Mechanics Flushing Your Cooling System
Popular Mechanics Repairing Cooling System Leaks
COOLING SYSTEM
Automotive Engine Lubrication & Cooling Systems
G 2 0 DOHC Cooling System Repair doc
general cooling system servicing
cooling system specifications
05 cooling system
ENGINE LUBRICATION & COOLING SYSTEM
5 Cooling System
03 Engine Cooling Heating System
2050 Checking cooling & heating system
więcej podobnych podstron