T
ECH
N
OTE
RHEL 6 Alternate Boot Methods
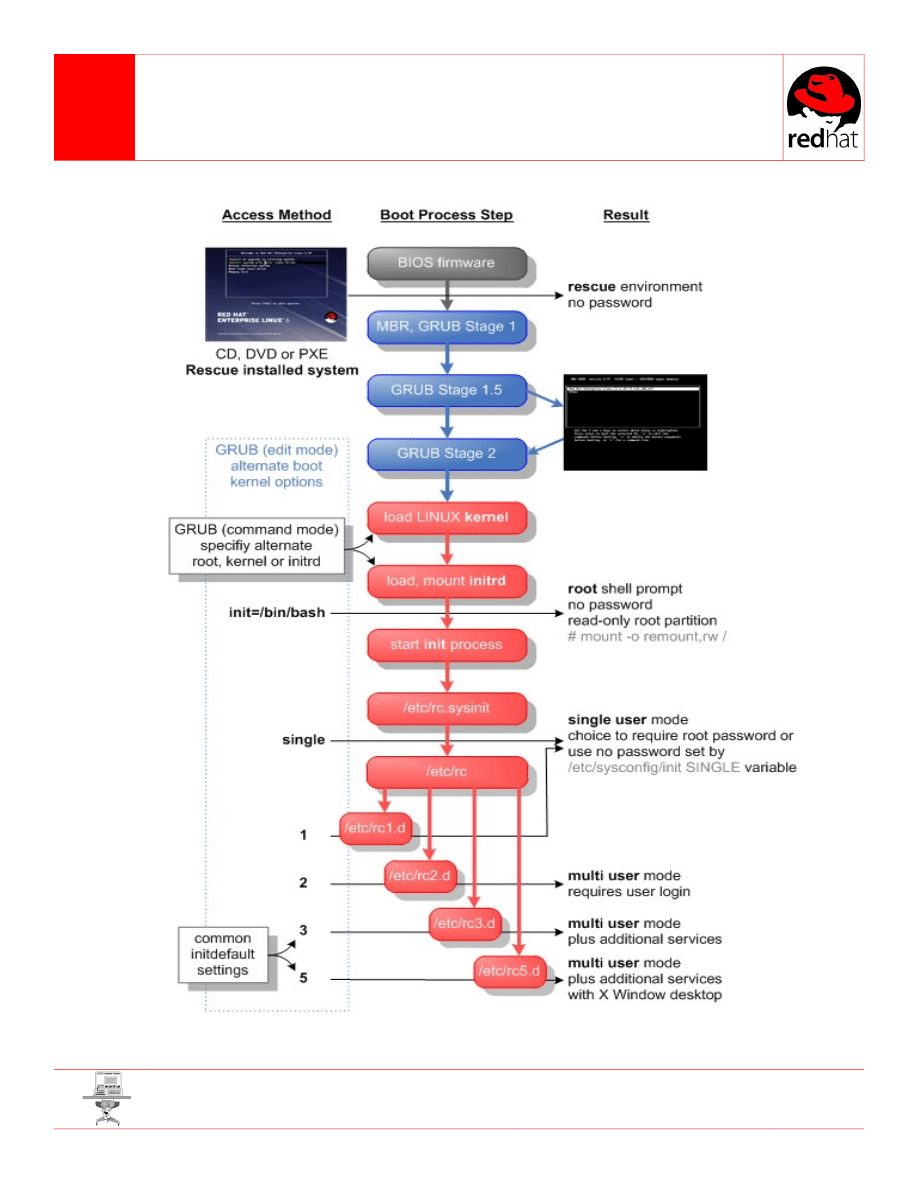
Troubleshooting boot failures or system misconfigurations requires practiced knowledge of
the alternate access methods visually outlined here. Use an earlier run level to avoid an
errant one, drop in quick by displacing init, or perform a system rescue as a final recourse.
RHEL 6 Alternate Boot Methods
July 27, 2013
Page 1

T
ECH
N
OTE
RHEL 6 Alternate Boot Methods
Troubleshooting boot failures or system misconfigurations requires practiced knowledge of
the alternate access methods visually outlined here. Use an earlier run level to avoid an
errant one, drop in quick by displacing init, or perform a system rescue as a final recourse.
rc.sysinit
System Initialization
•
Sets the hostname.
•
Mounts the proc and sysfs filesystems.
•
Activates SELinux if it is set to enforcing or permissive.
•
Initializes hardware using modprobe to load device drivers.
•
Starts the udev device manager.
•
Sets kernel parameters as defined in /etc/sysctl.conf.
•
Starts RAID arrays and device mapper for LVM devices.
•
Checks the root filesystem and remounts it as read/write.
•
Enables disk quotas if they are defined.
•
Forces fsck to run if the system was shut down uncleanly or if a
filesystem has exceeded the time or number of mounts since it was
last checked.
•
Mounts the other filesystems defined in /etc/fstab.
•
Starts swapping.
•
Dumps the current contents of the syslog ring buffer into /var/log/dmesg
so it will be available later.
RHEL 6 Alternate Boot Methods
July 27, 2013
Page 2
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
tech note debugging ha resource groups using rg test
tech note dedicated heartbeat interface
tech note rrdtool workshop
tech note manual screen resolutions
Hiren s Boot CD 16 2 ISO Alternative to Recover Windows Admin Password(1)
Canadian Patent 33,317 Improvements in Methods and Apparatus for Converting Alternating into Direct
Bearden Tech papers Bedini s Method for Forming Negative Resistors in Batteries (www cheniere org)
US Patent 413,353 Method Of Obtaining Direct From Alternating Currents
Fwd dydaktyka, Metody alternatywne
wyklad3 tech bad
Symmetrical components method continued
wyklad 29 i 30 tech bad
REGUŁA DOŁĄCZANIA ALTERNATYWY
Energia alternatywna
boot
info tech geodeta (1)(1)
Jak zamienić prądnicę na alternator w URSUSIE C 330
więcej podobnych podstron