PROCEDURE
1. Check physician’s order for pressure level at which the
system is to be maintained. Most frequently a positive
pressure is ordered. Occasionally a negative pressure is
ordered.
2. Ensure that “zero cm H
2
O” on the scale monitoring
level is at the anatomical reference point used to estab-
lish zero pressure. Ensures that the pressure set will be
accurate.
a. Supine at midear level.
b. Side lying at nose.
These are the external anatomical reference points that
correspond most closely with the foramen of Monro.
3. Use a string held from the client to zero on the scale to
determine that the two points are level. More clearly
demonstrates that the two points are level. (Figure 26)
4. Ensure that top of the flow chamber (marked with an
arrow) is at the ordered level. If not, loosen the locking
knob, slide the chamber up or down, then tighten the
knob. Enables CSF to drain when it reaches the ordered
pressure level while preventing excessive or too rapid
drainage.
5. Check the patency of the system by movement of CSF
with movement of the client or slightly lower the drain
system and observe for CSF drip and then return the
drain to the ordered position. Make sure that all stop-
cocks are in the “on” position. CSF will not drain when
the tubing is occluded.
6. Be sure clamp between drip chamber and collection bag
is closed. Allows for accurate monitoring of CSF output
and ensures proper functioning of the system.
81
Copyright © 2007 by Thomson Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved.
SKILL 34
SKILL 34
EVD: Maintaining System at Correct Level and
Functioning
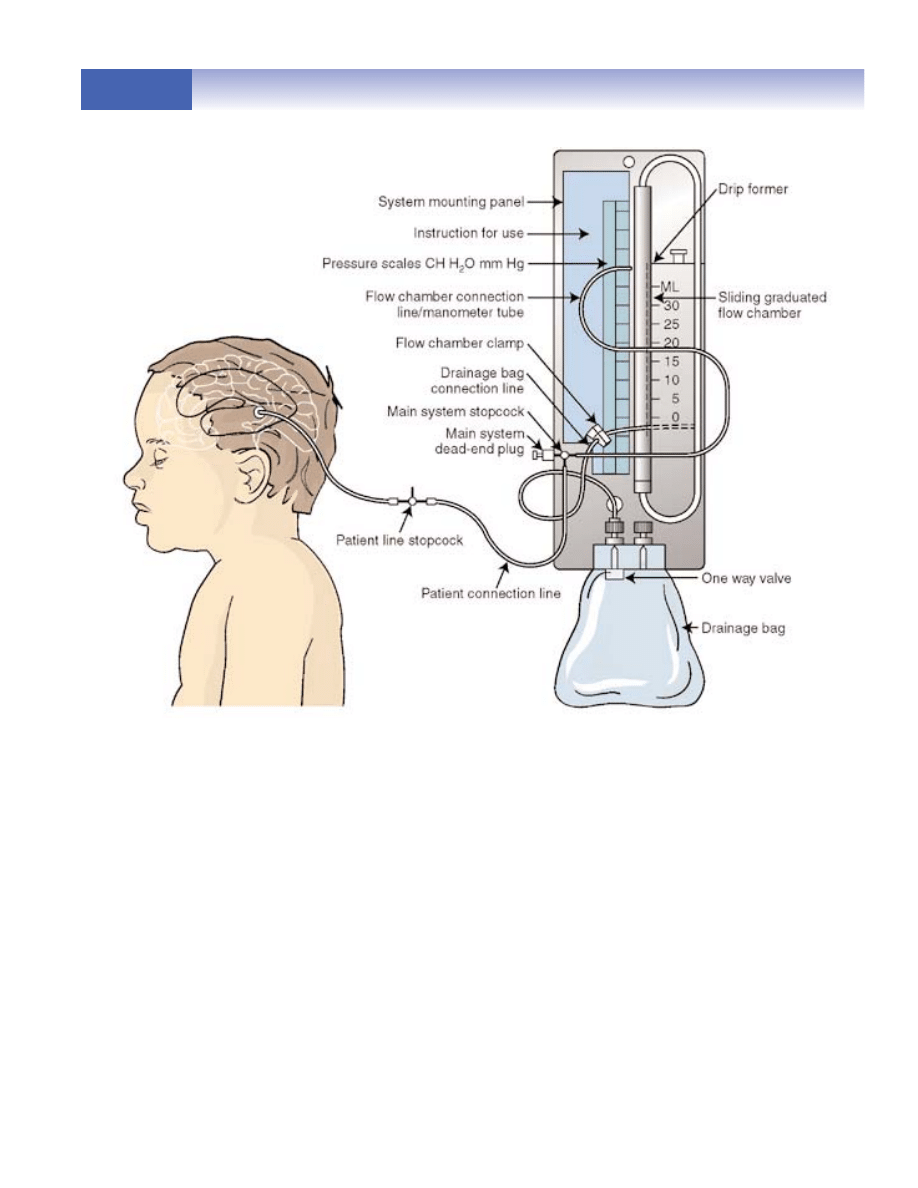
FIGURE 25 Placement of an external ventricular drain (EVD) shown with drainage collec-
tion set-up.
continued
7. Clamp the system off by turning the stopcock to the off
position (Off toward the client). Use the stopcock on the
mounting board. It is most clearly visible when the fol-
lowing situations occur:
a. Client or system will be moved out of alignment with
each other, e.g., when repositioning the client. When
client and system are out of alignment, CSF can drain
too rapidly or too slowly.
b. Crying or increased activity. These increase CSF pres-
sure and increase the flow of CSF into the system.
8. After repositioning the client, realign the system and
open clamp/turn stopcock to the on position.
9. Assess system every hour to ensure proper alignment.
NOTE: Physician will determine how much activity the
client can tolerate (e.g., whether client can get up and
walk) and how long the system can be turned off.
Generally the system is not turned off for more than 30
minutes at a time.
DOCUMENTATION
1. Pressure level of drain and level of drain itself, e.g.,
midear.
2. Patency of the system.
3. Times and duration when drain clamped and how client
tolerated it.
82
Copyright © 2007 by Thomson Delmar Learning, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. All rights reserved.
FIGURE 26 Ensuring “zero cm H
2
O” on the scale, supine; midear level.
SKILL 34
SKILL 34
EVD: Maintaining System at Correct Level and
Functioning
continued
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
2910 Clutch system, checking & correcting fluid level
Body language is something we are aware of at a subliminal level
Body language is something we are aware of at a subliminal level
Skill 35[1] EVD Client Assessment
Skill 38[1] EVD General Nursing Care and Safety
Skill 36[1] EVD Monitoring Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
SYSTEM DIGNOSTYCZNO – METODYCZNY I LEVEL
Transforming Beliefs At Meta Level
David Icke Claims Conspiracy At Highest Level
Skill 37[1] EVD Changing the Drainage Bag
Enzyme Systems that Metabolise Drugs and Other Xenobiotics Current Toxicology
Control Systems Simulation using Matlab and Simulink
(CRAFTS) An Insider Look at Jewelry Making and Beading Chapter 1
American Political System Lack of Cooperation and Polariza
Detection and Function of Opioid Receptors on Cells from the Immune System
72 Handling straight shots at head – height and midriff
8 At work career and promotion
więcej podobnych podstron